THE INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
TAMIL NADU TOPS FOOD SAFETY INDEX
THE CONTEXT: Tamil Nadu topped the State Food Safety Index, followed by Gujarat and Maharashtra. Among the smaller States, Goa stood first, followed by Manipur and Sikkim. Among the Union Territories, Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi and Chandigarh secured first, second and third ranks.
THE EXPLANATION:
- This was the fourth State Food Safety Index award, which was started in 2018-19 with the aim of creating a competitive and positive change in India’s food safety ecosystem. States that showed significant improvement were also felicitated.
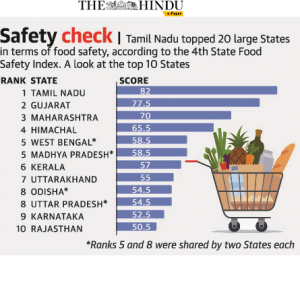
State Food Safety Index (SFSI)
FSSAI has developed State Food Safety Index to measure the performance of states on various parameters of Food Safety.
This index is based on the performance of State/ UT on five significant parameters set by the Health Ministry, namely
- Human Resources and Institutional Data
- Compliance
- Food Testing – Infrastructure and Surveillance
- Training & Capacity Building and
- Consumer Empowerment
The Index is a dynamic quantitative and qualitative benchmarking model that provides an objective framework for evaluating food safety across all States/UTs.
THE NATIONAL AIR SPORTS POLICY
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Civil Aviation launched National Air Sport Policy 2022 (NASP 2022). NASP 2022 lays out the vision of making India as one of the top sports nations by 2030, by providing a safe, affordable, accessible, enjoyable and sustainable air sports ecosystem in India.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Air sports, as the names suggests, encompasses various sports activities involving the medium of air. These include sports like air-racing, aerobatics, aero modeling, hang gliding, paragliding, para motoring and skydiving etc. India has the potential to be among the leading nations in the world of air sports. It has a large geographical expanse, diverse topography, and fair-weather conditions.
- It has a large population, especially the youth. It has a growing culture for adventure sports and aviation. The NASP 2022, is a step in this direction. It has been drafted based on the inputs received from policy makers, air sports practitioners and public at large and will ensure establishment of good quality of infrastructure, equipment, instructors and services.
The policy will cover the following air sports in India: –
- Aerobatics
- Aero modeling and model rocketry
- Amateur-built and experimental aircraft
- Ballooning
- Drones
- Gliding and powered gliding
- Hang gliding and powered hang gliding
- Parachuting (including skydiving, BASE jumping and wing suits etc.)
- Paragliding and para motoring (including powered parachute trikes etc.)
- Powered aircraft (including ultra light, micro light and light sports aircraft etc.)
- Rotorcraft (including autogyro)
Under the new policy, there will be four-tier governance structure for air sports in India namely
- Air Sports Federation of India (ASFI) as the apex governing body
- National associations for individual air sports or a set of air sports, as appropriate
- Regional (e.g. West/ South/ North East etc.) or State and Union Territory level units of the national air sports associations, as appropriate; and
- District-level air sports associations, as appropriate
Key Objectives of NASP 2022:-
- Promote an air sports culture in the country
- Enable adoption of international good practices in safety including but not limited to, air sports infrastructure, equipment, operations, maintenance and training
- Develop a simple, stakeholder-friendly and effective governance structure
- Enhance participation and success of Indian sportspersons in global air sports events; and
- Promote design, development and manufacturing of air sports equipment in India in line with the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
JOINT COUNT OF ELEPHANT AND BIG CATS
THE CONTEXT: The Central government will for the first time this year present a unified count of the tiger, leopard and elephant populations of the country, according to officials in the Union Environment Ministry.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The tiger survey is usually held once in four years and elephants are counted once in five years. According to the most recent 2018-19 survey, there were 2,967 tigers in India. According to the last count in 2017, there were 29,964 elephants in India.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA):
- Tiger survey in India is conducted by the NTCA, every four years.
- NTCA is a statutory body, constituted under Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It was established in 2005 following the recommendation of the Tiger Task Force.
- Objectives:
- To provide statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance of its directives become legal.
- To Foster accountability of Centre-State in management of Tiger Reserves.
- To address livelihood interests of local people in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
Functions:
- To approve the tiger conservation plan prepared by the state government.
- To ensure that the tiger reserves and areas linking one protected area/tiger reserve with another are not diverted for ecologically unsustainable uses.
- To facilitate and support the tiger reserve management in the state for biodiversity conservation.
Chairman: Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
Latest Tiger Survey:
- As per the latest Tiger Census conducted in 2018-19, tiger population in India has increased to 2967.
- India accounts for about 70% of the world’s tiger population.
Elephant Census:
- India does have an elephant census but this is largely a headcount of elephants in various elephant habitats conducted by state forest departments.
- The last census was carried out in 2017 and concluded that India has 29,964 elephants.
- According to current population estimates, there are about 50,000-60,000 Asian elephants in the world, with more than 60 per cent of them in India.
- Asian elephants are listed as “Endangered” on the IUCN Red List of threatened species.
- In 2020, 87 elephants and 359 people died in human-elephant conflicts.
Methods used for conducting census:
- Tigers are counted by deploying camera traps, identifying individuals based on stripes, as well as statistical analysis.
- The “head counting” method which is used for conducting elephant counting, has become obsolete and it frequently leads to double counting.
New method proposed:
- In August 2021, the Union government had made public the new population estimation protocol to be adopted in the all-India elephant and tiger population survey in 2022.
- Under the new method, Elephant numbers would be estimated by States based on DNA analysis of their dung droppings and statistical techniques.
The methodology will involve three phases:
- ground surveys, analyses of remotely sensed data and camera traps.
- Elephant populations using this method will be assessed for first time.
- The procedure is routinely used for estimating tiger and leopard populations in India.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
RBI HIKES REPO RATE BY 50 BASIS POINTS
THE CONTEXT: The Monetary Policy Committee of Reserve Bank of India, which met from 6-8 June 2022, has unanimously decided to hike the Repo Rate by 50 basis points to 4.90 %. Consequently, Standing Deposit Facility Rate stands adjusted to 4.65% and Marginal Standing Facility rate and Bank Rate to 5.15%.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The MPC has observed that the global economy continues to grapple with multi-decadal high inflation and slowing growth, persisting geopolitical tensions and sanctions, elevated prices of crude oil and other commodities and lingering COVID-19 related supply chain bottlenecks.
- Economic indicators for April –May (2022) indicate a broadening of the recovery in economic activity in India. Urban demand is recovering and rural demand is gradually improving. Merchandise exports posted robust double-digit growth for the fifteenth month in a row during May while non-oil non-gold imports continued to expand at a healthy pace, pointing to recovery of domestic demand.
Real GDP growth for 2022-23 is estimated at 7.2%
- According to NSO provisional estimates released on May 31, India’s GDP growth in 2021-22 is estimated at 8.7%, higher than pre-pandemic level.
Measures to benefit Cooperative Banks
- Taking into account the increase in housing prices since the limits were last revised and considering the customer needs, it has been decided to increase the existing limits on individual housing loans by cooperative banks. Accordingly, the limits for Tier I /Tier II UCBs shall stand revised from ₹30 lakh/ ₹70 lakh to ₹60 lakh/ ₹140 lakh, respectively. As regards RCBs, the limits shall increase from ₹20 lakh to ₹50 lakh for RCBs with assessed net worth less than ₹100 crore; and from ₹30 lakh to ₹75 lakh for other RCBs.
- Urban cooperative banks can now extend doorstep banking services to customers Will enable these banks to better meet the needs of their customers, especially senior citizens and differently abled persons-
- Rural cooperative banks can now extend finance to commercial real estate (loans to residential housing projects) within existing aggregate housing finance limit of 5% of total assets
Enhancement of limit on e-mandate transactions
- To further augment customer convenience and facilitate recurring payments like subscriptions, insurance premia and education fees of larger value, limit per transcation for e-mandate based recurring payments increased from ₹5,000 to ₹ 15,000.
Enhancing scope of UPI payment system.
- Now, credit cards too can be linked with UPI platform, beginning with RuPay cards. This will provide additional convenience to users and enhance scope of digital payments. UPI has become the most inclusive mode of payment in India. Currently, over 26 crore unique users and 5 crore merchants are onboarded on the UPI platform.
Glossary:
What is Monetary policy?
Monetary policy refers to the use of instruments under the control of the central bank to regulate the availability, cost and use of money and credit.
Goals of Monetary Policy
- Price Stability along with growth
- The agreement on Monetary Policy Framework between the Government and the Reserve Bank of India in 2015 defines the price stability objective explicitly in terms of the target for i.e.,
(a) below 6 percent by January 2016
(b) 4 percent (+/-) 2 percent for the financial year 2016-17 and all subsequent years.
Monetary Policy Committee:
The Monetary Policy Committee is a statutory and institutionalized framework under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, for maintaining price stability, while keeping in mind the objective of growth. It is recommended by the Urjit Patel Committee in 2014.

Repo rate & Reverse repo rate?
- Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank gives loans to commercial banks against government securities. Reverse repo rate is the interest that RBI pays to banks for the funds that the banks deposit with it.
Headline inflation:
- It is a measure of the total inflation within an economy, including commodities such as food and energy prices (e.g., oil and gas), which tend to be much more volatile and prone to inflationary spikes.
CPI- Inflation:
Consumer Price Index or CPI is the measure of changes in the price level of a basket of consumer goods and services bought by households.
- The CPI captures changes in price level at the consumer level.
- Changes in prices at the producer level are tracked by the Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- CPI can capture the change in the prices of services which the WPI cannot.
Open Market Operations:
- Open Market Operations refers to buying and selling of bonds issued by the Government in the open market.
- One of the Quantitative Tools: OMO is one of the quantitative tools that RBI uses to smoothen the liquidity conditions through the year and minimise its impact on the interest rate and inflation rate levels.
- Quantitative tools control the extent of the money supply by changing the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), or bank rate or open market operations.
THE EXCLUSIVE PRELIMS FACTS
ORGANISATION OF THE ISLAMIC COOPERATION
- The Organisation of the Islamic Cooperation is the world’s second-largest multilateral body after the UN.
- It was established by the First Islamic Summit Conference held in Morocco in September 1969.
- It was known as the Organisation of Islamic Conference until 2011
Objective:
- To safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony among various people of the world.
Members:
- As of now, 57 members, all of them are Islamic countries or Muslim majority members.
- The Central African Republic, Russia, Thailand, Bosnia & Herzegovina, and the unrecognised Turkish Cypriot “state”, have Observer status.
India & OIC
- India has the world’s second-largest Muslim community, and had been invited to the founding conference at Rabat in 1969, but was humiliatingly ejected at Pakistan’s behest.
- In 2006, as India turned the economic corner and improved ties with the US, Saudi Arabia invited Delhi to join as an observer.
- However, India refrained from joining citing that it did not want to join an organisation founded on religion. Secondly, there was the risk that improving bilateral relations with individual member states would come under pressure in a grouping, especially on issues such as Kashmir.
- The OIC is mainly controlled by Saudi Arabia, but Pakistan, as the only Islamic country with nuclear weapons, has had a large say since its inception.
Changing terms:
- After building close ties with powerful members such as UAE and Saudi Arabia, India has been confident of riding over any statement by the grouping.
- India has consistently underlined that J&K is an “integral part of India and is a matter strictly internal to India”, and that the OIC has no locus standi on the issue.
- In 2019, India made its maiden appearance at the OIC Foreign Ministers’ meeting, as a “guest of honour”.
- The OIC includes two of India’s close neighbours, Bangladesh and Maldives. Both countries privately admit they do not want to complicate their bilateral ties with India on Kashmir.
Significance of OIC for India:
- OIC’s growing economic and energy interdependence with India has become important in recent times.
- Individually, India has good relations with almost all member nations. Ties with the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
THE DATA POINT
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION FOR 8THJUNE2022
Q1. India is a member of which of the following groupings?
- NSG
- Wassenaar Arrangement
- Australia Group
- MTCR
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 2, 3 and 4 only
d) All of them
ANSWER FOR THE7THJUNE 2022
Answer: C
Explanation:
Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- It is the second-largest intergovernmental organization after the United Nations with a membership of 57 states.
- It was established in September 1969.
- Headquarters- Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.(therefore, statement C is incorrect)
- It is the collective voice of the Muslim world.
- India is not member of OIC.
- Indian Foreign minister was invited as a guest of honour at 46th Session of the Council of Foreign Minister in 2019 (the 50th anniversary of OIC).




