THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
1. PROJECT NILGIRI TAHR
THE CONTEXT: The Tamil Nadu Budget for FY 2022-23 allocated an amount of Rs.10 crore for protecting the state animal, Nilgiri Tahr.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The first-of-its-kind project aims to protect the endemic to the Nilgiris and the southern portion of the Western Ghats in Tamil Nadu and Kerala and raise awareness about it.
- The Nilgiri tahr population restricted to the fragmented patches of grasslands in the Mukurthi National Park.
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 under Schedule 1 protects this ungulate species, which is also listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. The Nilgiri tahr (nilgiritragushylocrius) lives in montane grasslands with rocky cliffs between 300 and 2,600 metres above mean sea level. Mukurthi, Glenmorgan of the Nilgiris, Anamalai, Grass Hills, Coimbatore’s Siruvani hills, Dindigul’s Palani hills, Megamalai of Theni, Agasthyamalai ranges, and Eravikulam in Kerala are all good places to see the elusive species.
Value Addition:
About Mukurthi National Park:
- The park was previously known as Nilgiri Tahr National Park.
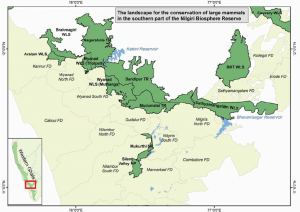
- It was declared as a National Park in the year of 1990. Total area of the park is about 78.46 Km2. The park is characterized by montane grasslands and shrublands interspersed with sholas in a high-altitude area of high rainfall, near-freezing temperatures and high winds.
- The park is a part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, India’s first International Biosphere Reserve. As part of the Western Ghats, it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1 July 2012. The Park is sandwiched between the Mudumalai National Park and the Silent Valley National Park.
2. THE GREAT BARRIER REEF SUFFERS WIDESPREAD CORAL BLEACHING
THE CONTEXT: According to the Australian government agency the Great Barrier Reef is suffering widespread and severe coral bleaching due to high ocean temperatures two years after a mass bleaching event.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The report by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Authority, which manages the world’s largest coral reef ecosystem, comes before a United Nations delegation is due to assess whether the reef’s World Heritage listing should be downgraded due to the ravages of climate change.
- The reef has suffered significantly from coral bleaching caused by unusually warm ocean temperatures in 2016, 2017 and 2020. The previous bleaching damaged two-thirds of the coral.
- In July 2021, Australia garnered enough international support to defer an attempt by UNESCO, the United Nations’ cultural organization, to downgrade the reef’s World Heritage status to “in danger“because of damage caused by climate change.
Value Addition:
What is coral spawning?
- Coral spawning is an annual event where corals simultaneously reproduce. During this synchronised breeding, coral polyps release millions of tiny egg and sperm bundles into the water. Each bundle must find another bundle from the same species to fertilise.
- Coral spawning is an annual event where corals simultaneously reproduce.
- During this synchronised breeding, coral polyps release millions of tiny egg and sperm bundles into the water.
- Each bundle must find another bundle from the same species to fertilise. By spawning on mass, corals increase the likelihood of finding and fertilising a matching bundle.
When does coral spawn?
- This depends on a number of factors including their location, the water temperature and tides.
- On the Great Barrier Reef, inshore reefs typically spawn in October, while outer reefs spawn during November or December.
- Spawning follows a full moon and water temperatures must have risen enough to stimulate the maturation of the egg and sperm bundles. The timing of spawning is also impacted by the length of the day, the tide and salinity levels in the water.
- Spawning only happens at night and lasts from a few days up to a week. Different species of coral spawn on different days to prevent crossbreeding.
About Great Barrier Reef:
- The Great Barrier Reef is the world’s largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands.
- The reef is located in the Coral Sea (North-East Coast), off the coast of Queensland, Australia.
- The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space and is the world’s biggest single structure made by living organisms.
- The reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps. It was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981.
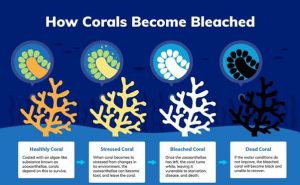
Coral Bleaching:
- The stunning colours in corals come from marine algae called zooxanthellae, which live inside their tissues.
- This algae provides the corals with an easy food supply thanks to photosynthesis, which gives the corals energy, allowing them to grow and reproduce.
- When corals get stressed, from things such as heat or pollution, they react by expelling these algae, leaving a ghostly, transparent skeleton behind.
- This is known as ‘coral bleaching’. Some corals can feed themselves, but without the zooxanthellae most corals starve.
- Causes for Coral Bleaching include Change in Ocean Temperature, Runoff and Pollution, Overexposure to sunlight and Extreme low tides.
3. AFRICAN TECHNIQUE USED TO TRANSLOCATE DEER FROM KEOLADEO
THE CONTEXT: An uncommon experiment with Africa’s Boma technique undertaken at Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan’s Bharatpur district for capturing and translocating spotted deer is set to improve the prey base in Mukundara Hills Tiger Reserve.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Boma Technique?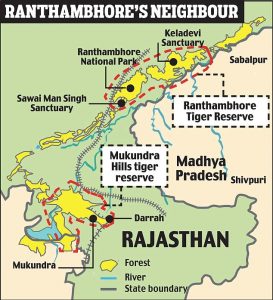
- The Boma capturing technique, which is popular in Africa, involves luring of animals into an enclosure by chasing them through a funnel-like fencing. The funnel tapers into an animal selection-cum-loading chute, supported with grass mats and green net to make it opaque for animals, which are herded into a large vehicle for their transport to another location.
- This old technique was earlier utilised to capture wild elephants for training and service. Following its adoption in Madhya Pradesh in recent years, Boma has been put to practice for the first time in Rajasthan for sending the ungulates to the prey-deficient Mukundara reserve as the kills for tigers and leopards.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority’s (NTCA) technical committee has approved a proposal to shift two tigers from Ranthambhore National Park to Mukundara, which lost two tigers and two cubs in 2020 and is now left with an eight-year-old tigress. The reserve, spread across 759 sq. km area, was created with the portions of Darrah, Chambal and Jawahar Sagar wildlife sanctuaries in south-eastern Rajasthan.
Boma technique: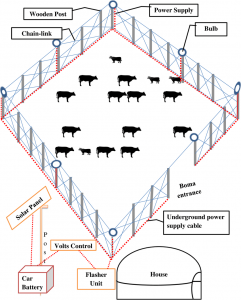
THE SECURITY AFFAIRS
4. IAF TO EMPLOY ‘DIRECT TACTICAL PLANNING’ FOR S-400
THE CONTEXT: According to IAF official has told a parliamentary standing committee that countering the potent weapon of the adversary will be based on India’s “direct tactical planning”.
THE EXPLANATION:
- India is in the process of acquiring a batch of S-400 Triumf missile systems from Russia.
- The S-400 is considered the most advanced air-defence system worldwide. The missile is capable of protecting its air defence bubble against missiles, rockets, cruise missiles and aircraft.
- The system is already available with China, which has deployed it along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in eastern Ladakh amid the 18-month military standoff.

About S-400 Triumf
- S-400 Triumf is a mobile, surface-to-air missile (SAM) system. It was developed by Russia’s Almaz Central Design Bureau for Marine Engineering in the 1990s, as an upgrade to the S-300 family.
- The first battalion of the newest surface-to-air missile systems assumed duty on August 6, 2007. China was the first foreign buyer of the missile, in 2014.
- Since then, countries like Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Belarus and India have all acquired or expressed interest in the system. S-400 missile systems are organized across the 30K6E administration system. It is having a range of 400kms.
Connect the dots:
- US Congressional report had warned that “India’s multi-billion-dollar deal to purchase the Russian-made S-400 air defence system may trigger US sanctions on India under the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act” (CAATSA).
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. NARASINGHAPETTAI NAGASWARAM BAGS GI TAG
THE CONTEXT: The ‘Narasinghapettai nagaswaram’, an ancient musical instrument hand-crafted by artisans from Narasinghapettai, a nondescript village in Tiruvidaimarudur taluk in Thanjavur, has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
THE EXPLANATION:
This highly complex musical instrument, dating back to the 13th century, involves intricate craftsmanship and only a few artisans in Narasinghapettai have inherited the skill of chiselling the wooden instruments.
The unique feature of the ‘Narasinghapettainagaswaram’ is its production process as they are handmade unlike other machine-made nagaswarams. Also, ‘Aacha’ wood, which is naturally water-resistant, is procured specifically from the Cauvery river basin for making the instrument. But fresh wood cannot be used and the instrument is crafted with old wood which is at least 100 years old. The reeds themselves are made from the leaves of a locally grown plant called ‘naanal’, a bamboo variety.
The nagaswarams produced in Narasinghapettai are marketed and sold in different states and in countries including Singapore, Malaysia and Sri Lanka. According to the officials, there are 46 products have been granted GI in Tamil Nadu so far.
Value addition:
Some Interesting facts about GI Tag:
- GI tag is the abbreviation of Geographical Indications tags in India. It came into force with effect from 15th September 2003.
- A geographical indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- The products which are given the Geographical Indication tag in India are regarded as the invaluable treasures of incredible India.
- This tag is valid for a period of 10 years following which it can be renewed.
- Union Minister of Commerce and Industry had launched the logo and tagline for the Geographical Indications (GI) of India.
- The first product to get a GI tag in India was the Darjeeling tea in 2004.
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 (GI Act) is a sui generis Act for the protection of GI in India.
- India, as a member of the WTO, enacted the Act to comply with the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights.
- Geographical Indications protection is granted through the TRIPS Agreement.
- This tag is issued by the Geographical Indication Registry under the Department of Industry Promotion and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Geographical indications are typically used for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts, and industrial products.
- The Gucchi mushroom, one of the most expensive mushrooms in the world, from the state of Jammu and Kashmir was recently given the GI tag in India.
Benefits of GI Tags
- A geographical indication right enables those who have the right to use the indication to prevent its use by a third party whose product does not conform to the applicable standards.
- Geographical indication tags are given to the products for
- Legally protecting the goods.
- Preventing unauthorised or illegal use of geographical indication tags by others.
- Helping customers in getting the original items that contain all the specific traits.
- Promoting the economic prosperity of manufacturers/ producers of items under GI tags. Items with GI tags get enhanced demand in national as well as international markets.
6. WORLD HAPPINESS REPORT 2022
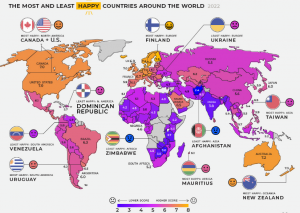
THE CONTEXT: Finland has been named the world’s happiest country for a fifth year running, in an annual UN-sponsored index. The report ranked Denmark in the second place, with Switzerland, Iceland, and the Netherlands rounding up the top five happiest places in the world.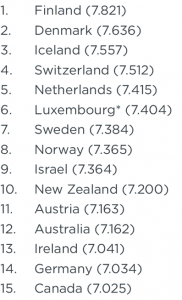
THE EXPLANATION:
- Published ever since 2012 by United Nations Sustainable Development Solutions Network, the World Happiness Report is based on people’s own assessment of their happiness, as well as economic and social data. For the World Happiness Report 2022, people across 149 countries were asked to rate their happiness.
- The World Happiness Report ranks 146 countries based on a variety of factors, such as per capita GDP, social support, healthy life expectancy, freedom of choice, generosity and perceptions of corruption.
- India ranks 136 on the 2022 World Happiness Report. It is among the 11 least happy countries. (2021 positioned India at rank 139 out of 149).
- According to the Happiness Report 2022 list, Afghanistan is the saddest country in the world (146th). Afghanistan is followed by Lebanon and Zimbabwe. China ranks 72nd on the list, while Russia, which is attacking Ukraine, ranks 80th. Ukraine ranks 98th in the Russian attack.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY 21ST MARCH 2022
Q. For translocation of Asiatic lions, which of the following forest ecosystem is more suitable?
a) Tropical evergreen forest
b) Moist deciduous forest
c) Dry deciduous forest
d) Montane forest
ANSWER FOR 16TH MARCH 2022
ANSWER: A
EXPLANATION:
- The primary objective of the alliance is to work for efficient consumption of solar energy the reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Countries that do not fall within the Tropics can join the alliance and enjoy all benefits as other members, with the exception of voting rights
The ISA is headquartered in Gurugram, Not in France.
Spread the Word
