INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
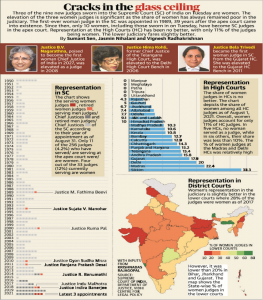
1. NINE NEW SUPREME COURT JUDGES TAKE OATH
THE CONTEXT: Chief Justice of India N V Ramana administered the oath of office to the new judges in a swearing-in ceremony held in the auditorium of the Supreme Court’s additional building complex.
ANALYSIS:
- It is for the first time in the history of the apex court that nine judges took oath of office at one going.
- With the swearing-in of the nine new judges, the strength of the Supreme Court has now risen to 33, including the CJI, out of the sanctioned strength of 34.
- The government’s nod to appoint nine judges comes a week after the Supreme Court collegium, ending a nearly two-year-long impasse, sent its recommendations.
- Justice Oka will be the most senior among the nine judges.
- Others in the list include, in order of seniority, Gujarat High Court Chief Justice Vikram Nath, Sikkim High Court Chief Justice J K Maheshwari, Telangana High Court Chief Justice Hima Kohli, Karnataka High Court judge Justice B V Nagarathna, Justice C T Ravikumar of Kerala High Court, Justice M M Sundaresh of Madras High Court, Justice Bela Trivedi of Gujarat High Court, and senior advocate P S Narasimha.
- Justices Nath, Nagarathna and senior advocate Narasimha will join the line of succession for the office of the CJI. While Justice Nath and Narasimha are likely to have tenure of just over six months, the expected first woman CJI is likely to have a relatively short tenure of just over a month.
- With the additions, the apex court will have four women judges for the first time — Justices Nagarathna, Kohli and Trivedi, besides Justice Indira Banerjee, the only woman judge in SC at present.
Reference: Indian express
2. NATIONAL PARTIES COLLECTED OVER ₹3,370 CRORE FROM FROM UNKNOWN SOURCES
THE CONTEXT: According to poll rights group Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR), National parties collected 3,377.41 crore rupees from unknown sources in the 2019-20 financial year, which was 70.98% of the total income of these parties.
ANALYSIS:
- In a new report, the ADR said that the BJP declared ₹2,642.63 crore as income from unknown sources, the highest among the national parties, which also include the Congress, the NCP, the CPI, the CPI(M), the TMC and the BSP.
- The Congress declared ₹526 crore as income from unknown sources which is 15.57% of the total income of the national parties from unknown sources.
- National parties collected ₹3,377.41 crore from unknown sources in the financial year 2019-20, which is 70.98% of the total income of the parties. Out of the ₹3,377.41 crore as income from unknown sources, share of income from Electoral Bonds was ₹2,993.826 crore or 88.643%.
- Between 2004-05 and 2019-20, the national parties collected ₹14,651.53 crore from unknown sources.
- Unknown sources are income declared in income tax returns, but without giving source of income for donations below ₹20,000. Such unknown sources include ‘donations through Electoral Bonds’, ‘sale of coupons’, ‘relief fund’, ‘miscellaneous income’, ‘voluntary contributions’, ‘contribution from meetings/morchas’.
- The details of donors of such as voluntary contributions are not available in the public domain.
- The ADR recommended that scrutiny of financial documents submitted by political parties should be conducted annually by a body approved by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India and the Election Commission of India to increase transparency and accountability of political parties with respect to their funding.
Reference: The Hindu
3. FAMILIES OF MILITANT RECRUITS OFFERED AN OLIVE BRANCH
THE CONTEXT: Top Army and police officers held a conversation-cum-counselling session with around 80 families of militant recruits in south Kashmir in a bid to initiate their safe return to the mainstream.
ANALYSIS
- These families whom we met were asked to convince their children [newly-recruited terrorists] to return to the mainstream. We made an earnest appeal to them.
- The Army promised to offer all assistance if the youths intend to lay down their arms.
- The Army said the interaction was intended to instill confidence and convey the intent of the security forces, among the families of active terrorists.
- According to the police figures, militant recruitment has shown no let-up since the Centre ended J&K’s special constitutional position on August 5, 2019.
- A total of 167 youths were recruited by militants in 2020 and 88 have been recruited this year so far.
Reference: The Hindu
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
4. MECHANIZED SCAVENGING SYSTEM
THE CONTEXT: CSIR-CMERI is developing a Mechanized Scavenging System, which was initiated after intensive studies of the diverse nature of Indian Sewerage Systems and the manner of its chokages.
ANALYSIS:
- The technology is Modular in design so as to ensure customised deployment strategies as per situational requirements.
- The System also focuses upon Sustainable Usage of resource i.e. Water as the System sucks in Slurry Water from the choked Sewerage Systems and after adequate filtration of the same redirects the same for Clearing of Chokages using Self-Propelling Nozzle.
- CSIR-CMERI technology provides in-situ option for Mechanized Scavenging as well as purification of Water. The design of the Technology is such that the Water Filtration Mechanism may be changed/modified as per the customised needs/requirements with the ability to change/redesign the Filter Media.
- The Vehicle-mounted Filtration Units will be able to augment and use Water from Surface Drain and Flooded Areas and purify it into Water suitable for Agricultural, Household and Drinking Water usages.
- The Drinking Water Scarcity prevalent in Flood-Affected regions can be solved to a certain by providing instantaneous and in-situ Water Purification solutions at ease. This provides a consolidated Technology Solution in a Flood-Affected region as it will be able to clear Drainage Chokages in flood-affected regions, which will help in providing an outlet for flood stagnated Water, as well as provide Water Purification solutions in Flood Disaster Zones.
Reference: PIB
INDIAN ECONOMY
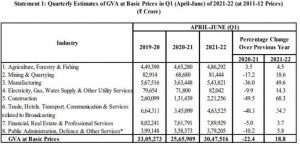
5. ECONOMY GROWS 20.1% IN Q1 FY22
THE CONTEXT: As per the provisional estimates of GDP released by the MoSPI, India GDP Q1 Data: India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for the April-June quarter (Q1) of the ongoing financial year 2021-22 (FY22) grew by 20.1 per cent.
ANALYSIS:
- The GVA at basic prices during Q1 of FY22 was 8 per cent, against (-)22.4 per cent in the corresponding quarter year ago
- The sharp rise in Q1 GDP data can be mainly attributed to a low base last year. The Indian economy had contracted by a record (-)24.4 per cent in the corresponding quarter last year owing to the impact of the nationwide lockdown that was imposed to curb the transmission of the Covid-19, which brought all non-essential activities to a halt.
- A recent Reuterspoll of 41 economists showed gross domestic product rose 20.0 per cent in the three-month period ended June.
- Separately, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in its monetary policy committee meeting earlier this month had projected the Q1 GDP to grow at 21.4 per cent.
- In value terms, the GDP stood at Rs 32,38,020 crore in Q1 FY22, higher than Rs 26,95,421 crore in corresponding period of FY21 but lower than Rs 35,66,708 crore in Q1 FY20.
- In the first quarter, the manufacturing sector, rose by 49.6 per cent against a contraction of (-)36 per cent a year ago, while the construction sector grew at 68.3 per cent in Q1 FY22 vs. (-)49.5 per cent a year ago.
- The sector of trade, hotels, transport, communication & services related to broadcasting gained 34.3 per cent against a contraction of (-) 48.1 per cent.
- Apart from this, the agriculture, forestry and fishing sector which had grown at 3.5 per cent in the corresponding quarter last year grew 4.5 per cent in Q1 FY22.
- Electricity, gas, water supply and other utility services segment grew by 14.3 per cent in the first quarter of this fiscal, against a 9.9 per cent contraction a year ago.
- The financial, real estate and professional services grew by 3.7 per cent in Q1 FY22 compared to a contraction of (-)5.0 per cent, while public administration, defence and other services grew at 5.8 per cent, compared to (-)10.2 per cent a year earlier.
6. INDEX OF EIGHT CORE INDUSTRIES FOR JULY 2021
THE CONTEXT: The Office of Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) is released Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) for the Month of July, 2021.
ANALYSIS:
- ICI measures combined and individual performance of production in selected eight core industries viz. Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity.
- The Eight Core Industries comprise 40.27 percent of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The combined Index of Eight Core Industries stood at 134.0 in July 2021, which increased by 9.4 per cent (provisional) as compared to the Index of July 2020. The production of Coal, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity industries increased in July 2021 over the corresponding period of last year.
SOURCE: IE
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
7. INDIA OFFICIALLY TALKS TO TALIBAN
THE CONTEXT: In the first official contact with Taliban, Indian envoy to Qatar Deepak Mittal met Taliban leader Sher Mohammad Abbas Stanekzai at the Indian Embassy.
ANALYSIS:
- It said that the discussions focused on safety, security and early return of Indian nationals stranded in Afghanistan. The travel of Afghan nationals, especially minorities who wish to visit India, also came up.
- Ambassador Mittal raised India’s concern that Afghanistan’s soil should not be used for anti-Indian activities and terrorism in any manner.
- The Taliban Representative assured the Ambassador that these issues would be positively addressed.
- This came at a time when in view of the evolving situation in Afghanistan, Prime Minister Narendra Modi had recently directed that a high-level group comprising External affairs minister S Jaishankar, NSA Ajit Doval and senior officials focus on the immediate priorities of India.
- This group has been meeting regularly over the past few days. It is seized of issues pertaining to the safe return of stranded Indians, the travel of Afghan nationals (especially minorities) to India, and ensuring that Afghanistan territory is not used for terrorism directed against India.
- The group has also been monitoring the ground situation in Afghanistan and international reactions, including the Resolution passed by the UN Security Council.
SOURCE: IE
8. UNSC RESOLUTION ON TALIBAN
THE CONTEXT: The United Nations Security Council under India’s presidency passed the Resolution that reminded Taliban to stand by its commitment to prevent international terrorism.
ANALYSIS:
- Resolution 2593 of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) addresses India’s major concerns on Afghanistan at this time.
- The observation came hours after the UNSC under India’s presidency passed the Resolution that reminded Taliban to stand by its commitment to prevent international terrorism but left the P-5 countries divided over the issue.
- The Resolution failed to get consensus support from all the permanent members of the UNSC. Russia and China abstained during the voting over the draft saying it divided the approach to the Afghan crisis.
- Russian representative at the UNSC pointed out that the author of the draft resolution, that is the U.S., has divided terrorists in Afghanistan into “ours and theirs” indicating at a changing stance of the U.S. towards the Taliban and its allied Haqqani Network which has in the past attacked both American and Indian targets in Afghanistan.
- Foreign Secretary Harsh Vardhan Shringla, representing India at the UNSC highlighted the role of Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed and said that these outfits should be “called out and condemned” without referring to the Haqqani Network that is likely to come up at the Taliban Sanctions Committee for a discussion among the members for possible delisting.
- The Indian diplomatic team at the U.N. tried to build consensus and reached out to “high-level official contacts” on all sides. The draft resolution called upon the Taliban to stand by its commitment to stop any terrorist activity from originating from the territory of Afghanistan.
- Sources said that a high-level group consisting of External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar, National Security Adviser Ajit Doval and senior officials are focused on ensuring evacuation of stranded Indians from Afghanistan and also airlifting of religious minority groups from Kabul.
SOURCE: TH
9. MEDICAL SUPPLIES TO BANGLADESH
THE CONTEXT: Indian Navy’s Offshore Patrol Vessel INS Savitri departed Visakhapatnam and is enroute to Chittagong, Bangladesh to support the ongoing efforts of the Bangladesh military and government agencies in combating the ongoing wave of the Covid pandemic in their country.
ANALYSIS:
- The ship will arrive on 02 September carrying two 960 LPM Medical Oxygen Plants (MOP), one each for Bangladesh Navy and Dhaka Medical College.
- INS Savitri, is an indigenously built Offshore Patrol Vessel of the Indian Navy under the Eastern Naval Command based at Visakhapatnam. As part of the Government of India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region), the Indian Navy has been proactively engaging with countries in the region and has been at the forefront of numerous humanitarian missions spanning the entire extent of the Indian Ocean including South/ South East Asia and East Africa.
- Earlier, Indian Naval Ship Shakti had transported 100 T of LMO to Colombo, Sri Lanka, whilst INS Airavat is currently on a deployment to South East Asia for trans-shipment of medical aid to Indonesia, Vietnam and Thailand.
- India and Bangladesh have a close, long-standing relationship covering a wide spectrum of activities and interactions, which has strengthened over the years.
- The people of India and Bangladesh also share close cultural bonds and a shared vision of democratic society and a rules-based order.
SOURCE: PIB
10. CONCERN RISES OVER AFGHANISTAN’S SAARC MEMBERSHIP
THE CONTEXT: With uncertainty hanging over the international representation of Afghanistan under the Taliban, a question has risen over its membership in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), which is scheduled to meet next in Islamabad.
ANALYSIS:
- Veteran diplomats here observed that the fate of Afghanistan’s membership, and even the future of SAARC to some extent, depends on the Taliban creating an inclusive government.
- Afghanistan was admitted into the SAARC as the eighth member in 2007.
ABOUT SAARC
- It was established with signing of SAARC Charter in Dhaka in 1985.
- Its secretariat is in Kathmandu, Nepal.
- It objective is to promote the welfare of the people of South Asia and to improve their quality of life, and to accelerate economic growth, territorial integrity, mutual trust and benefit etc.
- Eight members: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- Highest decision-making authority: Summit level Meetings of the Heads of State or Government of Member States.
- South Asia Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA), the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) of SAARC, came into force in 2006.
- India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Nepal are five common countries in SAARC as well as BIMSTEC groupings.
Reference: The Hindu
Q1. Consider the following statements:
- SAARC was established in 1985.
- Its headquarter is located in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Afghanistan is not a member of SAARC.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 31, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Q.1 Answer: d)
Explanation:
- UNEP hosts the secretariats of several multilateral environmental agreements and research bodies, including CBD, the Minamata Convention on Mercury, CMS and CITES.
Q.2 Answer: a)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Malabar rebellion, also known as the Moplah rebellion, was an armed revolt staged by the Mappila Muslims of Kerala in 1921.
- Statement 2 is correct: Mappilas were Muslim peasant community in Malabar region.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Moplah tenants agitated against the Hindu landlords (locally referred to as janmi) and the British government.


