ECONOMIC SURVEY 2021-22: CHAPTER 7- AGRICULTURE AND FOOD MANAGEMENT
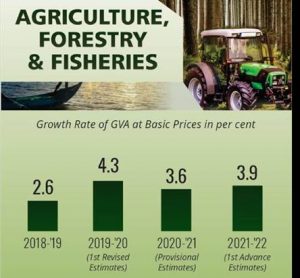
THE INTRODUCTION: The Agriculture sector which accounts for 18.8 percent of the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the country in 2021-22 has experienced buoyant growth in the past 2 years. It grew at 3.9 percent in 2021-22 and 3.6 percent in 2020-21 showing resilience in the face of COVID-19 shock. The Survey attributes this to “good monsoon, various Government measures to enhance credit availability, improve investments, create the market facility, promote infrastructure development and increased provision of quality inputs to the sector”. It also observes that livestock and fisheries have experienced buoyant growth and had helped the sector perform well.
GROSS VALUE-ADDED AND GROSS CAPITAL FORMATION
- The share of the agriculture and allied sector in total GVA of the economy has settled at around 18 percent in the long term states the Survey. In the year 2021-22 it is 18.8 percent and in the year 2020-21, it was 20.2 percent. Another trend observed is, higher growth in allied sectors (Livestock, Forestry and Logging, Fishing and Aquaculture) compared to the crop sector. Recognizing these allied sectors as engines of high growth the Committee on Doubling Farmers’ Income (DFI 2018) had also recommended focused policy with a concomitant support system to boost agricultural incomes.
- There is a direct correlation between capital investments in agriculture and its growth rate. The Gross Capital Formation in the agricultural sector relative to the GVA in the sector is showing a fluctuating trend in sync with the variation in private sector investments, whereas the public sector investments have remained stable at 2-3 percent over the years. The Survey suggests “higher access to institutional credit to farmers and greater participation of the private corporate sector” may improve private sector investment in agriculture. Towards this end, the Survey recommends offering an appropriate policy framework to crowd-in corporate investments along with an increase in public investments along the entire agricultural value chain.
AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION
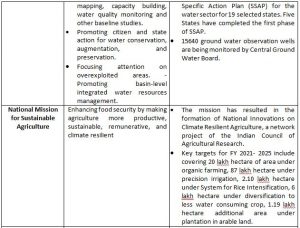
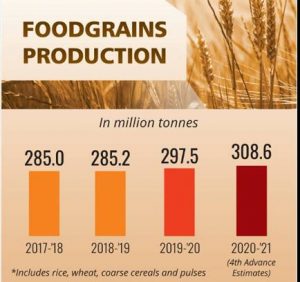
- The Survey states that as per the First Advance Estimates for 2021-22 (Kharif only), total food grain production is estimated at a record level of 150.50 million tonnes, an increase of 0.94 million tonnes over Kharif production in the year 2020-21. Survey also points out that the production of rice, wheat, and coarse cereals had increased at Compound Annual Growth Rates (CAGR) of 2.7, 2.9, and 4.8 percent respectively over the period between 2015-16 and 2020-21. For pulses, oilseeds, and cotton during the same period, it has been 7.9, 6.1, and 2.8 percent respectively.
- India is the second-largest producer of sugar in the world. India has become a “sugar surplus nation” says the Survey. It points out that since 2010-11, the production has outstripped the consumption except in the year 2016-17. This has been made possible by ensuring and protecting the sugarcane farmers against price risk through Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP), enhancing the liquidity of mills by incentivizing them to divert excess sugarcane/sugar to ethanol production and provide financial assistance for transportation to sugar mills to facilitate the export of sugar says Survey.
CROP DIVERSIFICATION
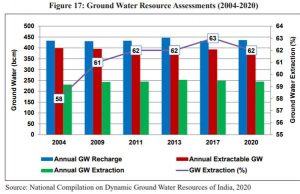
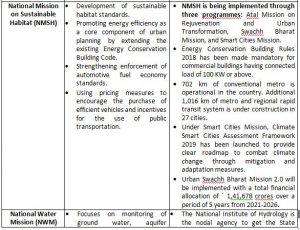
- The existing cropping pattern is skewed towards the cultivation of sugarcane, paddy, and wheat which has led to the depletion of fresh groundwater resources at alarming rates, it also points out that extremely high water stress levels are recorded in the country’s north-western region.
- To promote water use efficiency and sustainable agriculture and ensure higher incomes to farmers, the Government is implementing the Crop Diversification Programme in the original green revolution States viz., Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh as a sub-scheme under Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana since 2013-14 to shift area under paddy cultivation towards less water-intensive crops such as oilseeds, pulses, and Nutri-cereals, etc. The program also focuses on shifting areas under tobacco cultivation to alternative crops in States viz. Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, West Bengal among other tobacco-producing states. The government is also using price policy to signal farmers to diversify their crops.
WATER AND IRRIGATION
- 60 percent of the net irrigated area in the country is serviced through groundwater. The rate of extraction of groundwater is very high (more than 100%) in the states of Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, and Rajasthan. Noting that increased coverage under micro-irrigation can be the most effective mode of water conservation, the Survey suggests these States need to focus on both medium and long-term groundwater recharge and conservation plans.
- To mobilize resources to expand coverage of micro-irrigation, a Micro-Irrigation Fund (MIF) with a corpus of Rs. 5000 crores were created under NABARD during 2018-19. As of 01.12.2021, projects with loans under MIF amounting to Rs. 3970.17 crore has been approved for 12.81 lakh hectares of micro-irrigation area. Further, the Survey highlights that under Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, as of 14.12.2021 total area of 59.37 lakh hectares has been covered under micro-irrigation in the country from 2015-to 16.
NATURAL FARMING
- To sustain agricultural production through eco-friendly processes in tune with nature, ensure chemical-free produce and preserve soil productivity government is also encouraging farmers to adopt natural farming techniques. Towards this end, the government is implementing a dedicated scheme of the Bharatiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhati Programme (BPKP).
AGRICULTURAL CREDIT AND MARKETING
- The agricultural credit flow for the year 2021-22 has been fixed at Rs. 16,50,000 crores and till 30thSeptember 2021, against this target a sum of Rs.7,36,589.05 crores has been disbursed. Moreover, under the Atma Nirbhar Bharat program, the government also announced an Rs. 2 lakh crore concessional credit boost to 2.5 crore farmers through Kisan Credit Cards (KCC). Towards this end, banks have issued KCCs to 2.70 crore eligible farmers as of 17.01.2022. Further Government has extended the KCC facility to the fisheries and animal husbandry sector in 2018-19.
- To link the farmers with markets and to help them in trading and realizing competitive and remunerative prices for their produce the government has been working continuously to improve market linkages and marketing infrastructure. Towards this end, the APMCs have been recognized as eligible entities under Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF). Additionally, under the National Agricultural Market (e-NAM) scheme as of 1stDecember 2021, 1000 mandis of 18 States and 3 UTs have been integrated with the e-NAM platform.
- The Government has also launched a central sector scheme of ‘Formation and Promotion of 10,000 Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs)’ to form and promote 10,000 FPOs by 2027-28. As of January 2022, a total of 1963 FPOs have been registered under the scheme. The government has also established a full-fledged Ministry of Co-operation in July 2021 to provide a greater focus on the cooperative sector.
NATIONAL MISSION ON EDIBLE OILS
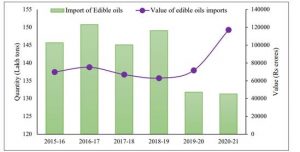
- India is the world’s second-largest consumer and number one importer of vegetable oil. The oilseed production in India has been steadily growing since 2016-17. It was showing a fluctuating trend before that. It had grown at almost 43 percent from 2015-16 to 2020-21.
- The demand for edible oil in India would remain high due to population growth, urbanization, and the consequent change in dietary habits and traditional meal patterns.
- Given the persistently high import of edible oil, to increase oil production the Government had been implementing a centrally sponsored scheme of National Food Security Mission: Oilseeds (NFSM – Oilseeds) since 2018-19 across all districts in the country.
- The scheme the government has set up 36 oilseed hubs between 2018-19 and 2019-20 to increase the availability of high yielding quality seed. For Kharif 2021, the union government had allocated 9.25 lakhs of oilseed mini kits of high yielding varieties to states for distribution.
- Further, in August 2021, the Government had launched the National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to augment the availability of edible oils by “harnessing area expansion and through price incentives”. The scheme aims to cover an additional area of 6.5 lakh hectares for oil palm by 2025-26 and thereby reach a target of 10 lakh hectares ultimately.
- Currently 3.70 lakh hectares area under oil palm cultivation. Also, the scheme aims to increase the Crude Palm Oil (CPO) production to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 and up to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
FOOD MANAGEMENT
- India runs one of the largest food management programs in the world. The Survey highlights that during the year 2021-22, the government had allocated 1052.77 lakh tonnes of food grains to States/UTs under the National Food Security Act, 2013, and other welfare schemes compared to 948.48 lakh tonnes in 2020-21.
- The government has further extended the coverage of food security through the additional provision of 5Kg food grains per person per month through the Pradhan Mantri Gareeb Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY). Under the scheme during 2021-22, the government had allocated 437.37 LMT of food grains and in 2020-21, 322 LMT of food grains free of cost to around 80 crore NFSA beneficiaries to ameliorate the hardships faced by the poor due to economic disruption caused by COVID-19 pandemic.
- The government had also approved the centrally sponsored pilot scheme ‘Fortification of Rice and its Distribution under PDS’ on 14.02.2019 for three years.
- The scheme is being implemented in 15 districts (1 district per State) and the government had distributed 3.38 LMT of fortified rice till December 2021 under the pilot scheme.
- During Kharif Marketing Season (KMS) 2020-21, 601.85 lakh metric tonnes (LMT) of rice have been procured against an estimated target of 642.58 LMT. In the KMS 2021-22, a total of 566.58 LMT of paddy (equivalent to 379.98 LMT rice) was procured as of 16.01.2022. During RMS 2021-22, 433.44 LMT of wheat was procured against 389.92 LMT procured during RMS 2020-21. Also, during the Kharif & Rabi Marketing Season 2020-21, approximately 11.87 LMT of coarse grains has been procured which is the highest in the last five years.
AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH AND EDUCATION
- Every rupee spent on agricultural research and development, yields much better returns. Increasing R&D spending on agriculture is, therefore, not only a vital necessity for ensuring food security but also important from the socio-economic point of view.
- Agricultural research and education are crucial for “development of environmentally sustainable global food system, ensuring food and nutrition security and increasing farm income by cost minimization and yield maximization” says the Survey. It points out that the National Agricultural Research System of India has produced significant results. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) during 2020 and 2021 notified/released a total of 731 new varieties/hybrids of field crops. The Department of Agriculture Research and Education (DARE) has developed 35 special trait varieties including bio-fortified and stress-tolerant varieties of field and horticulture crops during 2021-22.


CONCLUSION: The performance of the agriculture and the allied sector has been resilient to the COVID 19 shock. The sector grew at 3.6 percent in 2020-21 and improved to 3.9 percent in 2021- 22. However, as shown by the latest SAS report, the fragmentation of landholdings has led to alternate sources such as livestock, fishery, and wage labor becoming significantly important for an agricultural household. The increasing importance of allied sectors including animal husbandry, dairying, and fisheries in the growth and income of the farmers indicates that focus needs to shift more towards harnessing the potential of allied activities. There is also a need to improve the productivity of small and marginal farmers through the development and implementation of smallholding farm technologies.