DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (OCTOBER 03, 2022)
INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. THE REVIVAL OF SUKAPAIKA RIVER
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the NGT has directed the state government of Odisha to revive Sukapaika River within 6 months.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has instructed the Odisha government to revive Sukapaika River, a distributary of Mahanadi River.
- It has directed the state government to create a dedicated fund for this river’s revival.
- The tribunal also directed the Odisha government to make budgetary allocation of Rs.49.67 crore to rejuvenate the river within one month and complete the whole river revival project by March 13, 2023.
- NGT alleged that the Sukapaika river in Cuttack district became dead because of the closure of its mouth in the 1950s.
- Sukapaika river originates from Ayatur Village in Cuttack district and flows some 40 km before re-joining the Mahanadi River in Tarapur in the same district.
- When it was flowing freely, Sukapaika river acted as a source of drinking water, irrigation and other livelihood opportunities to over 425 villages under 26 gram panchayats.
- Residents of these villages cultivated potato, tomato, cauliflower etc., and were involved in fisheries. These economic activities have ceased to be lucrative after the closure of the river’s mouth.
- In 1952, the Odisha government blocked the starting point of the river with an embankment to prevent flooding in the delta of Sukapaika.
- In 1957, two major projects – Hirakud Dam and Naraj barrage – were built on Mahanadi River to curb flooding. However, the embankment at the starting point of Sukapiaka river was not removed, leaving the distributary completely dependent on rainwater.
- Since the river has lost its water holding capacity, it remains dry for almost the whole year. This has negatively affected half-a-million people in the villages in the region. The riverbed has been eroded and is invaded by hyacinth. Several encroachments have started taking place along the course of the dead river over the years and the entire riverbed was converted into a dumping ground for solid and liquid wastes.
ABOUT THE RIVER:
Sukapaika is one of the several distributaries of the mighty Mahanadi river in Odisha. It branches away from the Mahanadi at Ayatpur village in Cuttack district and flows for about 40 kilometres (km) before rejoining its parent river at Tarapur in the same district. In the process, it drains a large landmass comprising over 425 villages under 26 gram panchayats in three blocks.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. INDIA LOCKS DEAL WITH ARMENIA TO EXPORT MISSILES, ROCKETS AND AMMUNITION
THE CONTEXT: In a significant move to boost India’s defence export, the country has signed an export order for missiles, rockets, and ammunition to Armenia because the Asian nation is engaged in a border conflict with Azerbaijan.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to sources, the value of the contracts has not been revealed yet, however, it is estimated that military equipment worth over ₹2,000 crore will be exported to the country in the coming months.
- Earlier this month, the government-to-government route was used to ink a number of contracts for the supply
 of arms and ammunition to Armenia.
of arms and ammunition to Armenia. - “This order includes six additional first-ever export of the indigenous Pinaka multi-barrel rocket This weapon, which is already in service with the Indian Army, has been designed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and manufactured by private sector companies in the country”.
- In addition to this, the anti-tank rockets, and ammunitions will also be supplied from India to Amenia under the bundled deal.
- Over the past few years, India has been making significant efforts to increase military weapons exports, with policy reforms, and active support of the central government to secure overseas orders.
- Meanwhile, the government has recently said that India’s exports have grown by 334 per cent within five years, and the country is now exporting to over 75 countries its defence products. The country has also witnessed the commissioning of its first indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant in Kochi.
- According to sources , the trend that had prevailed for the last 75 years. Since the beginning, India has continued to be one of the largest importers of defence products in the world. He expressed the need to reverse this trend and make India a top exporter of defence products across the world.
About Pinaka multi-barrel rocket launcher
- The Pinaka is a multi-barrel rocket launcher developed by DRDO. It is currently used by the Indian Army,
 especially at the international borders with Pakistan and China.
especially at the international borders with Pakistan and China. - This indigenously developed rocket launcher is capable of locating the enemy launchers and tracking the incoming artillery shells, mortar rounds and rockets. One Pinaka has 6 launchers, 6 loader trucks, 6 replenishment vehicles, two command post-transporting vehicles and a vehicle to transport the meteorological radar to provide wind-related data.
ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
3. FSI REPORT ON TIGER SAFARI PROJECT IN CORBETT TIGER RESERVE
THE CONTEXT: Thousands of trees were illegally cut down in the Corbett Tiger Reserve by the Uttarakhand government for the implementation of a safari project.
THE EXPLANATION:
- A survey by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) revealed that 6,093 trees were illegally cut down in the Corbett Tiger Reserve for the Pakhro tiger safari project.
- Only 163 trees were permitted to be cleared for this safari project.
- The FSI launched the survey after a complaint was filed by an environmental activist to the National Tiger Conservation Authority alleging that thousands of trees were being felled in and around the project areas.
- The Uttarakhand Forest Department has not accepted the findings made by the recently released FSI report and is seeking clarification on the timeline and the source of the satellite images and method for calculating the number of felled trees.
- Apart from the FSI, the National Tiger Conservation Authority and the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change also found irregularities in the project’s implementation. They were set up investigating committees to probe these irregularities.
- Earlier, the Central Empowered Committee has asked the state government to submit its views on the findings of the different committees investigating the illegal clearing of forest areas and construction activities in the Corbett Tiger Reserve and the Kalagarh forest.
- It has also urged the state government to specify the reason behind the forest land being diverted for a tiger safari in Pakhro range, though it is not a site-specific activity.
About Corbett Tiger Reserve
- Corbett National Park and the neighbouring Sonanadi together make up the Corbett Tiger Reserve. It is famed for hosting the world’s highest density of tiger population.
- It houses 230 tigers, with 14 tigers per 100 sq km. The Corbett National Park was established as Hailey National Park in 1936 and was later renamed in honour of the famous naturalist Jim Corbett, who played a major role in the establishment of this national park. It was the first national park to come under Project Tiger.
4. FAST-MELTING ARCTIC ICE IS TURNING THE OCEAN ACIDIC, THREATENING LIFE
THE CONTEXT: A team of researchers has flagged the changing chemistry of the western region of the Arctic Ocean after discovering acidity levels increasing three to four times faster than ocean waters elsewhere.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The team also identified a strong correlation between the accelerated rate of melting ice and the rate of ocean acidification. The study, published in ‘Science’, the journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, is the first analysis of Arctic acidification that includes data from 1994 to 2020.
- Scientists have predicted that by 2050, Arctic sea ice in this region will no longer survive the increasingly warm summers. As a result, the ocean’s chemistry will grow more acidic, creating life-threatening problems for the diverse population of sea creatures, plants and other living things that depend on a healthy ocean. Crabs, for example, live in a crusty shell built from the calcium carbonate prevalent in ocean water. Polar bears rely on healthy fish populations for food, fish and sea birds rely on plankton and plants, and seafood is a key element of many humans’ diets.
- Seawater is normally alkaline, with a pH value of around 8.1.
- First, the water under the sea ice, which had a deficit of carbon dioxide, now is exposed to the atmospheric carbon dioxide and can take it up freely.
- The seawater mixed with meltwater is light and can’t mix easily into deeper waters, which means the carbon dioxide is concentrated at the surface.
- The meltwater dilutes the carbonate ion concentration in the seawater, weakening its ability to neutralise the carbon dioxide into bicarbonate and rapidly decreasing ocean pH.
INTERNAL SECURITY
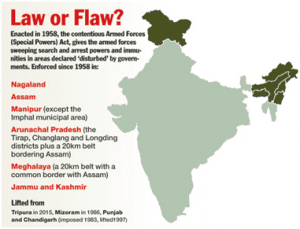
5. AFSPA EXTENDED IN NAGALAND, ARUNACHAL PRADESH
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland for another six months.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Tirap, Changlang and Longding districts in Arunachal Pradesh and the areas along the Assam border, are declared as “disturbed areas” under Section 3 of the AFSPA 1958 for a period of six months from October 1,2022.
- In Tripura the Act was revoked by the MHA in 2015 and in Meghalaya from 1st April 2018.
About Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act 1958
- The genesis of the law can be traced to the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Ordinance 1942which was enacted by the British to subjugate the rebels in the country during the Quit India movement, particularly in Assam and Bengal .
- The law continues to be enforced in its new format as the Armed Forces
Provisions:
- Under Section 3, the Central Government or the Governor of the State or administrator of the Union Territory
 can declare the whole or part of the State or Union Territory as a disturbed area.
can declare the whole or part of the State or Union Territory as a disturbed area. - An area can be disturbed due to differences or disputes between members of different religious, racial, language or regional groups or castes or communities.
- Section 4 gives the Army powers to search premises and make arrests without warrants, to use force even to the extent of causing death, destroy arms/ammunition dumps, fortifications/shelters/hideouts and to stop, search and seize any vehicle.
- Section 6 stipulates that arrested persons and the seized property are to be made over to the police with the least possible delay.
- Section 7 offers protection of persons acting in good faith in their official capacity. The prosecution is permitted only after the sanction of the Central Government.
Rationale behind its imposition
- Effective functioning of forces in counter-insurgency / terrorist operations.
- Protection of members of Armed forces.
- Maintaining Law & Order.
- Security & sovereignty of the nation.
Criticisms
- Atrocities and human rights violations by security agencies.
- Against democratic regime & threat to Fundamental Rights
- Ineffectiveness in countering insurgency.
- Fake encounters (Santosh Hegde Committee) & create an atmosphere of impunity among security agencies.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
6. THE EDUCATION MINISTRY LAUNCHES PM YOUNG AUTHORS MENTORING SCHEME YUVA 2.0
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Education launched YUVA 2.0 – Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors, a programme to train young and budding authors to promote reading, writing and book culture in the country, and project India and Indian writings globally.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The second edition of the Young, Upcoming and Versatile Authors (YUVA) scheme was launched by the Union Ministry of Education as part of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav or India @75 project.
- The scheme is a mentoring programme for young and budding authors below the age of 30.
- Its objective is to promote the culture of reading and writing across India and showcase Indian writing at the international level.
- It aims to bring the perspective of the Indian youth on the theme “Democracy (institutions, events, people, constitutional values past, present and future)”.
- It will benefit budding authors capable of writing on a wide-range of subjects focused on the promotion of Indian culture, heritage and knowledge across the globe.
- The launch of the latest edition of YUVA scheme comes after the first edition witnessed a huge participation from young authors in 22 different regional languages as well as in English.
- The theme for the inaugural edition was ‘National Movement of India’, with the focus on “Unsung Heroes”, “Role of Unknown Places in Freedom Movement” and other subjects.
About PM-YUVA scheme
- Pradhan Mantri – Mentorship’s Scheme for Young writers (PM-YUVA) was launched on May 29, 2021. It is being implemented by the National Book Trust (NBT), India. Under this initiative, 75 young authors will be chosen based on the manuscripts submitted. The selections will be made by a committee set up by the NBT.
- The chosen authors will get mentors who will guide and help develop the selected proposals into fully-complete books. The authors will be provided a scholarship of Rs.50,000 each month for a period of 6 months. 10 per cent of the royalty will be received by the authors on the publication and sale of the books.
- The published books will be translated into different Indian languages to promote Ek Bharat Shrestha Bharat and boost cross-cultural and linguistic ties within India.