TOP 5 TAKKAR NEWS OF THE DAY (22nd FEBRUARY 2023)
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. UNITED NATIONS HIGH SEAS TREATY
TAGS: PRELIMS-GS-II- INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a new round of negotiations on the United Nations High Seas Treaty began in New York.
THE EXPLANATION:
About United Nations High Seas Treaty:
- It is known as the ‘Paris Agreement for the Ocean’, and the treaty to deal with Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction has been under discussion for several years.
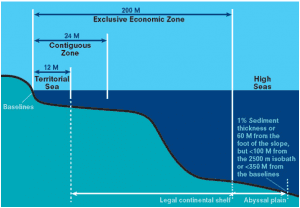
- The proposed treaty concerns the ocean existing beyond the Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ) that lie from the coast of a country to about 200 nautical miles into the sea (Countries have special rights for exploration till 200 nautical miles).
- The treaty was to be negotiated under the United Nations Convention on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS) of 1982.
About the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- UNCLOS became effective on 16th November 1982.
- It superseded the four Geneva Conventions of April 1958, which respectively concerned the territorial sea and the contiguous zone, the continental shelf, the high seas, fishing and conservation of living resources on the high seas.
- As per UNCLOS, the sea is divided into 4 parts:
- Territorial waters
- Contiguous Zone
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
- Continental Shelf
2. WHAT IS NEW START TREATY?
TAGS: PRELIMS-GS-II- INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Russian President announced that Moscow was suspending its participation in the New START treaty with the United States.
THE EXPLANATION: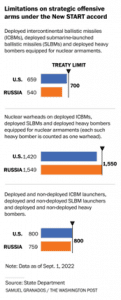
About New START Treaty:
- It is known as The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START).
- It is the last remaining nuclear arms deal between Russia and the United States of America, and it was extended for five years in 2021.
- Objective: The New START caps the number of nuclear warheads well below Cold War limits.
What is the timeline of this treaty?
- New START continues the bipartisan process of verifiably reducing U.S. and Russian strategic nuclear arsenals begun by former Presidents Ronald Reagan and George H.W. Bush.
- The treaty was signed by US President Barack Obama and Russian counterpart Dmitry Medvedev in Prague in 2010.
- New START replaced the 1991 START I treaty, which expired in December 2009, and superseded the 2002 Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty (SORT), which terminated when New START entered into force.
- Both Russia and the United States announced that they met New START limitations by Feb. 5, 2018.
- Importance: New START is the first verifiable U.S.-Russian nuclear arms control treaty to take effect since START I in 1994.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3. WHAT IS ASTROSAT?
TAGS: PRELIMS-SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has recently made an Announcement of Opportunity (AO) to allow scientists and researchers to analyze data from the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission, AstroSat.
THE EXPLANATION:
About AstroSat: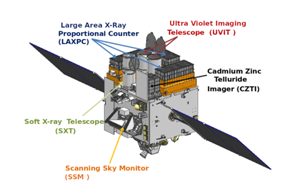
- It is India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory.
- It is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The spacecraft control center at Mission Operations Complex (MOX) of ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bengaluru, manages the satellite during its entire mission life.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is around 5 years.
Scientific Objectives:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
4. WHAT IS ULTRASAT?
TAGS: PRELIMS-SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: NASA will launch Israel’s first space telescope mission, the Ultraviolet Transient Astronomy Satellite (ULTRASAT) in early 2026.
THE EXPLANATION:
About ULTRASAT: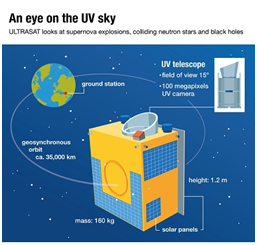
- ULTRASAT is an ultraviolet observatory with a large field of view, that will investigate the secrets of short-duration events in the universe, such as supernova explosions and mergers of neutron stars.
- It is planned to launch into a geostationary orbit around Earth
- NASA will provide the launch opportunity, Flight Payload Adapter, and other launch-related responsibilities for ULTRASAT.
What is a geostationary orbit?
- Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at the same rate as Earth.
- This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position.
- To perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km. This is much farther from Earth’s surface compared to many satellites.
- This particular orbit is used for meteorological and communications satellites.
- The geostationary orbit is a special case of the geosynchronous orbit, which is any orbit with a period equal to Earth’s rotation period.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. WHAT IS MULETHI?
TAGS: PRELIMS
THE CONTEXT: Himachal Pradesh has recently begun the commercial cultivation of licorice (Mulethi) to become the first state in India to have organized cultivation of Mulethi.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Mulethi:
- Mulethi, commonly known as licorice, is a sweet-tasting perennial shrub.
- Scientific name: Glycyrrhiza glabra
- The roots have a sweet taste due to the presence of glycyrrhizin, which is 50 times sweeter than sucrose.
- It has been traditionally known and used as medicine in Ayurveda (known in Ayurveda as ‘Yashtimadhu’) for rejuvenation.
Uses:
- Herbal medicines use Mulethi for its natural sweetness.
- It is also used in traditional medicines against chest and lung diseases.
- It is used to flavor candies, tobacco, and alcohol, artificial and natural sweeteners.
Health Benefits:
- It has anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial
- It is known to boost immunity due to the increase in the production of macrophage and lymphocytes.
- Mulethi herb can treat asthma, cough, cold, sore throat, and other respiratory ailments.
- It helps in weight loss as it contains flavonoids that help to reduce excessive fats accumulated in the body.
- It helps improve the digestive system, lessens the acidic level in the intestines, and also helps to detox our body.
Distribution:
- The plant thrives in a dry and sunny climate and is cultivated in subtropical and warm temperate regions.
- Countries producing licorice include Iran, Afghanistan, China, Pakistan, Iraq, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Turkey.
- It is also cultivated in Punjab and Sub Himalayan tracts in India.