TOP 5 TAKKAR NEWS OF THE DAY (5th JANUARY 2023)
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. JALLIKATTU-CULTURAL PRACTICE OR CRUELTY?
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-II-GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: Amid the Supreme Court quash the Tamil Nadu Regulation of Jallikattu Act, 2009 in 2014, the State said the ban on Jallikattu was perceived as an onslaught against the cultural identity of the people of Tamil Nadu.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Jallikattu?
- It is a bull-taming sport and a disputed traditional event in which a bull such is released into a crowd of people.
- Multiple human participants attempt to grab the large hump on the bull’s back with both arms and hang on to it while the bull attempts to escape.
- Participants hold the hump for as long as possible, attempting to bring the bull to a stop. In some cases, participants must ride long enough to remove flags on the bull’s horns.
- It is typically practised in the state of Tamil Nadu as a part of Pongal (harvest) celebrations in January.
Issue with the sport
- An investigation by the Animal Welfare Board of India concluded that “Jallikattu is inherently cruel to animals”.
- Human deaths: The event has caused several human deaths and injuries and there are several instances of fatalities to the bulls.
- Manhandling of animals: Animal welfare concerns are related to the handling of the bulls before they are released and also during the competitor’s attempts to subdue the bull.
- Cruelty to animal: Practices, before the bull is released, include prodding the bull with sharp sticks or scythes, extreme bending of the tail which can fracture the vertebrae, and biting of the bull’s tail.
- Animal intoxication: There are also reports of the bulls being forced to drink alcohol to disorient them, or chilli peppers being rubbed in their eyes to aggravate the bull.
Arguments in favour
- Native breed conservation: According to its protagonists, it is not a leisure sport available but a way to promote and preserve the native livestock.
- Cultural significance: Jallikattu has been known to be practiced during the Tamil classical period (400-100 BCE) and finds mention in Sangam texts.
- Man-animal relationship: Some believe that the sport also symbolizes a cordial man-animal relationship.
2. 50 ASI-PROTECTED MONUMENTS DISAPPEAR
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS-I
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Culture recently told Parliament that 50 of India’s 3,693 centrally protected monuments were missing.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Fifty of India’s 3,693 centrally protected monuments have gone missing, according to the Ministry of Culture has told Parliament.
What are centrally protected monuments?
- The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act (AMASR Act) regulates the preservation of monuments and archaeological sites of national importance. The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), which is under the aegis of the Union Ministry of Culture, functions under this Act.
- The Act protects monuments and sites that are more than 100 years old, including temples, cemeteries, inscriptions, tombs, forts, palaces, step-wells, rock-cut caves, and even objects like cannons and mile pillars that may be of historical significance.
- According to the provisions of AMASR Act, ASI officials are supposed to regularly inspect the monuments to assess their condition. Apart from various conservation and preservation operations, ASI officials can also file police complaints, issue show cause notices for the removal of encroachments, and communicate to the local administration the need for demolition of encroachments.
How can a monument go “missing”?
- The ASI was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, when he realised the need for a permanent body to oversee archaeological excavations and conservation. But while the body remained largely dysfunctional in the 19th century owing to fund crunch, in the decades preceding Independence, it became very active. A bulk of the protected monuments were taken under the ASI’s wings during the 1920s and 30s, up till the 50s, according to the sources.
- But in the decades after independence, the focus of successive governments was on health, education and infrastructure, rather than protecting heritage. Even within the scope of heritage, the aim was to uncover more monuments and sites, instead of conservation. So in due course, many monuments and sites were lost to activities like urbanisation, construction of dams and reservoirs, and even encroachments.
- As per the ASI submission in Parliament, 14 monuments have been lost to rapid urbanisation, 12 are submerged by reservoirs/dams, while 24 are untraceable, which brings the number of missing monuments to 50.
- The agency told the Parliamentary committee that security guards were posted at only 248 of the 3,693 monuments. “The committee notes with dismay that out of the total requirement of 7,000 personnel for the protection of monuments, the government could provide only 2,578 security personnel at 248 locations due to budgetary constraints”.
VALUE ADDITION:
Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958
- The AMASR Act provides for preservation of ancient and historical monuments and archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
- It provides for the regulation of archaeological excavations and for protection of sculptures, carvings and other like objects.
- The Archaeological Survey of India functions under the provisions of this act.
- The Act prohibits construction in ‘prohibited area’, an area of 100 meters around protected monument.
- It does not permit construction in such prohibited areas even if it is for public purposes, except under certain conditions.
- The central government can extend the prohibited area beyond 100 meters.
- The iconic monuments in India, Taj Mahal, Ajanta Caves, The Great Stupa at Sanchi and the Sun Temple of Konark, among others are designated as “ancient monuments of national importance” and protected under the AMASR Act. The Archaeological Survey of India is the custodian of these monuments.
- National Monument Authority will make a recommendation, for construction of public works to the central government, only if it is satisfied that there is no reasonable possibility of moving the construction outside the prohibited area.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
3. INDIA-FRANCE STRATEGIC DIALOGUE
TAGS-GS-II-INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: The 36th India-France dialogue will record a forward movement with French President Emmanuel Macron committed to support India for developing advanced military industrial complex.
THE EXPLANATION:
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE DIALOGUE
Aircraft Engines and Submarines
- One area where India is seeking French assistance is in the manufacturing of aircraft engines. India is looking for a transfer of technology to enable it to make engines for its indigenous twin-engine fighter, as well as the design and development of next-generation military and civilian engines for future fighter and transport platforms. The Tata group has already teamed up with Airbus to manufacture C295 tactical transport aircraft in Gujarat, and this partnership is set to be expanded to include the production of other civilian and military aircraft through a joint venture with France.
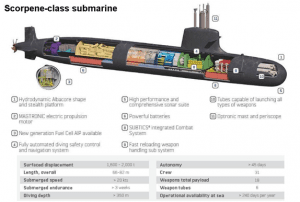
- In addition to aircraft engines, India is also interested in continued French assistance with the production of submarines. The Kalvari (French Scorpene) class submarine line is set to deliver its final submarine this year, and India is hoping that France will help to continue the manufacturing line at Mumbai Dockyards. The plan is to retrofit diesel attack submarines with indigenous air independent propulsion (AIP) systems for long endurance. It is expected that progress will be made on both aircraft engines and long-range submarines during this year’s strategic dialogue with France.
Indo-Pacific Security and Space Cooperation
- Another key topic of discussion during the strategic dialogue will be the Indo-Pacific region, where France is ready to help India with ocean bed mapping and the development of underwater drones and sensors.
- With the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) of China becoming increasingly aggressive in the Indo-Pacific, and rapidly expanding its warship and nuclear submarine force, India and its allies must be prepared for any eventualities in the Indian Ocean, which is fast becoming a new frontier. In order to ensure maritime domain awareness and security from the east coast of Africa to the far Pacific, India and France have formed a trilateral group with the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- In addition to security in the Indo-Pacific, India and France are also working together in the field of space technology, sharing knowledge in an effort to counter China’s rapid strides in this area.
Terrorism and Regional Stability
- During the strategic dialogue, Bonne will also be briefed by Doval on the posture of the PLA along the 3488 km Line of Actual Control (LAC) between China and India, and the two leaders will discuss ways to bring both Russia and Ukraine to the negotiating table to end the conflict that began in February 2022.
- Another topic of discussion will be the issue of radicalization in the region, particularly in the Af-Pak region, in the wake of the rise of the Taliban, as well as terrorism emanating from Pakistan and targeting India, as seen in the recent terrorist attacks in Rajouri by the Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Tayebba (LeT) group.
ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
4. SILENT VALLEY BIRD SPECIES GOES UP TO 175
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a bird survey conducted at the Silent Valley National Park in the December 2022 identified 141 species, of which 17 were new.
THE EXPLANATION:
- This year’s survey marked the 30th anniversary of the first bird survey in Silent Valley. Brown wood owl, Banded Bay cuckoo, Malabar woodshrike, White-throated kingfisher, Indian nightjar, Jungle nightjar, and Large cuckooshrike were among the 17 species newly identified in the Silent Valley.
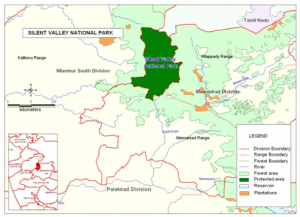
Silent Valley National Park:
- It is a beautiful representation of the last remaining rainforest of Kerala. The forests of the Silent Valley National Park harbour some of the most pristine, unique and highly productive forests in the world.
- Silent Valley is located in the Southwestern corner of Nilgiris.
- A perennial river named Kunthipuzha is passing through the western side of the park, from north to south direction finally merging into Bharathapuzha.
- Fauna: Silent Valley Park is known for many highly endangered species such as lion-tailed macaque, tiger, gaur, leopard, wild boar, panther, Indian Civet and Sambhar.
- The indigenous tribal groups that live within park boundaries include Irulas, Kurumbas, Mudugas and Kattunaikkars.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INTERVENTION
5. TELANGANA JOINS FREE RICE SCHEME
TAGS: GS-II-GOVERNMENTS SCHEMES & INTERVENTIONS
THE CONTEXT: The Telangana government has recently made the decision to join the free rice scheme of the Central government under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
THE EXPLANATION:
- This initiative aims to provide assistance to families in need by distributing free rice to those who are eligible under the NFSA. The Telangana government’s decision to join this scheme demonstrates a commitment to addressing issues of food security and poverty in the state.
- The Central scheme envisages the supply of five kilograms of rice per person per month to 54.44 lakh NFSA cardholders in the state. However, the Telangana government will extend this benefit to an additional 35.52 lakh cardholders, at its own cost.
- Previously, both types of cardholders were receiving free rice under the Prime Minister’s Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, which is a part of the Public Distribution System (PDS). The Central government used to supply this rice at a subsidized price of ₹3 per kilogram. However, the Telangana government added its own subsidy of ₹2 per kilogram and distributed the PDS rice for only ₹1 per kilogram.
Uncertainty Surrounding Amount of Rice Supplied
- It is currently unclear whether the state government will continue to supply six kilograms of rice per person per month, as it did under the PMGKA, or if it will restrict this amount to the five kilograms specified under the NFSA.
- The Telangana government has made the decision to join the free rice scheme of the Central government under the National Food Security Act in order to provide assistance to families in need. Although there is some uncertainty surrounding the amount of rice that will be supplied, the state government is committed to distributing free rice to all cardholders starting on January 5, 2022.
About PMGKAY
- In March 2020, during the initial phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, the central government had announced the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) welfare scheme. Initially, the scheme was planned for a period of 3 months but since then, it has been extended several times.
- This scheme looked to provide every individual covered under the National Food Security Act, 2013 (NFSA) with an additional 5 kg of grains (rice or wheat) free of cost, along with the 5 kg of subsidized food grain that is already being provided through the country’s Public Distribution System (PDS). It covers people belonging to Below Poverty Line – Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and Priority Households (PHH) categories.
- It also covers other vulnerable people like widows, terminally ill, elderly, landless agricultural labourers, primitive tribe households, informal sector workers etc. More than 81.35 crore people are benefiting from this scheme. Wheat has been allocated for 6 states and union territories and rice has been provided for the rest. This supplements the monthly entitlements under the NFSA.
Connect the Dots:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA)
- What is the difference between Central sector schemes and Centrally sponsored schemes





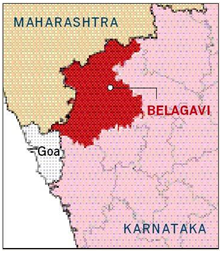 lines. In 1957, unhappy with the demarcation of boundaries, Maharashtra demanded realignment of its border with Karnataka.
lines. In 1957, unhappy with the demarcation of boundaries, Maharashtra demanded realignment of its border with Karnataka.