TOP 5 TAKKAR NEWS OF THE DAY (14th JANUARY 2023)
ART AND CULTURE
1. MAGH BIHU- MAKAR SANKRANTI
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS-I-ART & CULTURE
THE CONTEXT:Recently, the President of India greeted fellow citizens on the eve of Lohri (which falls on 13th January 2023) Makar Sankranti, Magh Bihu and Pongal (which fall on 14th January 2023).
THE EXPLANATION:
Bihu
- Bihu is one of Assam’s most prominent cultural events, celebrating the changing seasons.
- The festival of Bihu has three forms: Bohag Bihu, Kati Bihu and Magh Bihu. Each of these falls in the agriculture calendar.
- This day is considered auspicious in the Hindu lunar year as well and is known as the Makar Sankranti, i.e., the day when the sun begins its northward journey or Uttarayan and transitions into the Hindu zodiac sign of Makara.
Makar Sankranti
- It is celebrated in different ways across India under different names, each region having its unique customs and traditions.
- In Tamil Nadu, it is celebrated as Thai Pongal, where the festival is celebrated for four days, with the first day being Bhogi Pongal, the second day being Surya Pongal, the third day being Mattu Pongal and the fourth day being Kaanum Pongal.
- In Andhra Pradesh, Bengal, Kerala, Bihar, Goa, Karnataka, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, and Uttar Pradesh, it is celebrated as Makar Sankranti.
- In Gujarat and Rajasthan, it is celebrated as Uttarayana, and people take a dip in holy rivers and perform rituals to mark the beginning of the sun’s northward journey.
- In Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Punjab, it is celebrated as Lohri, where people light bonfires and perform folk dances around them.
HEALTH, ENVIRONMENT AND CLIMATE CHANGE
2. UNITED NATIONS INSTITUTE FOR WATER, ENVIRONMENT AND HEALTH (UNU-INWEH)
TAGS:GS-II & III- HEALTH ISSUES- ENVIRONMENT AND CLIMATE CHANGE
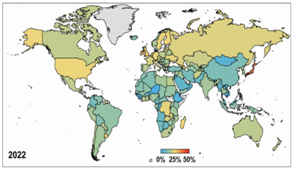
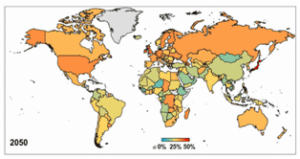
THE CONTEXT:A report was recently released by United Nations Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH) that stated that world will lose 26% storage by 2050 to trapped sediment.
THE EXPLANATION:
Key findings of the report:
- About 50,000 large dams across the world will lose 24-28 % water storage capacity by 2050 due to sediment trapped in them.
- These water reservoirs have already lost about 13-19 % capacity to sedimentation.
- Sedimentation is caused when a river carrying eroded soil is blocked by a dam at its watershed.
- Sediment helps to maintain the aquatic ecosystem.
- Poor management Sedimentation can lead to nutritional disbalances causing eutrophication, damages in habitations downstream, choke of dam and turbine system.
- Shallow water formed due to sedimentation also reduces the recreational value of the reservoirs.
- United Kingdom, Panama, Ireland, Japan and Seychelles will experience highest water storage losses by 2050 losing between 35% and 50% of their original capacities.
- Bhutan, Cambodia, Ethiopia, Guinea and Niger will be five least-affected countries losing less than 15 % by 2050.
- Dredging can be costly and only temporary.
- PT POINTERS: Dredging– to clear the mud from the bottom of a river, canal, etc. using a special machine.
Major highlights of the report in the Asia-Pacific region:
- Asia has 35,252 large dams, making it the world’s most heavily dammed region.
- Region has 60% of the world’s population and water storage is crucial for sustaining water and food security.
- In 2022, region will lose 13% of its initial dam storage capacity.
- It will lose nearly a quarter (23%) of initial storage capacity by 2050.
- Loss of storage capacity of Japan’s 3,052 dams is most acute in the region.
- India’s Central Water Commission reported in 2015 that-
- Among 141 large reservoirs that are over 50 years old, one-quarter had already lost at least 30% of their initial storage capacity.
- UNU-INWEH estimates that India’s 3,700 large dams will have lost on average 26% of their initial total storage by 2050.
- China, world’s most heavily dammed nation has lost about 10% of its storage and will lose a further 10% by 2050.
VALUE ADDITION:
About UNU-INWEH:
- UNU-INWEH was established in 1996 as subsidiary body of the United Nations University (UNU) institutes and an academic arm of the UN.
- Its operations are secured through long-term host-country and core-funding agreements with the Government of Canada.
- The Institute is located in Hamilton, Canada; its facilities are supported by McMaster University.
- It specializes on water for development, working, primarily with countries in the Global South, and addressing water issues of global significance.
- It is the UN Think Tank on Water created by the UNU Governing Council.
- UNU-INWEH is the only Institute in UNU that focuses entirely and solely on water issues.
- It is also the only entirely water-focused UN entity in Canada.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
3. BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS (BIS)
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT:Union Minister for Commerce recently launched many initiatives to improve the quality of standards in India on the occasion of 76th Foundation Day of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
THE EXPLANATION:
- BIS is the National Standard Body of India established under the BIS Act 2016 for the harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking and quality certification of goods and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- BIS has been providing traceability and tangibility benefits to the national economy in a number of ways –
- providing safe reliable quality goods;
- minimizing health hazards to consumers;
- promoting exports and imports substitute;
- control over proliferation of varieties etc. through standardization, certification and testing.
- BIS has its Headquarters at New Delhi and its 05 Regional Offices (ROs) are at Kolkata (Eastern), Chennai (Southern), Mumbai (Western), Chandigarh (Northern) and Delhi (Central).
- Keeping in view, the interest of consumers as well as the industry, BIS is involved in various activities as given below:
- Standards Formulation
- Product Certification Scheme
- Compulsory Registration Scheme
- Foreign Manufacturers Certification Scheme
- Hall Marking Scheme
- Laboratory Services
- Laboratory Recognition Scheme
- Sale of Indian Standards
- Consumer Affairs Activities
- Promotional Activities
- Training Services, National and International level and
- Information Services
4. DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY (DMD)
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, IIT Jodhpur, Dystrophy Annihilation Research Trust (DART) and AIIMS Jodhpur are working on developing an affordable treatment for a rare and incurable genetic disorder called Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)?
- It is the most common and fatal type of muscular dystrophy marked by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness due to alterations of a protein called “dystrophin” that helps keep muscle cells intact.
- Patients (usually children) have reduced bone density and an increased risk of developing fractures.
- India has over 5 lakh patients in the country suffering from DMD and the condition is predominantly seen in boys, but in rare cases, it can also affect girls.
- It can begin as early as age 2 or 3, first affecting the proximal muscles (those close to the core of the body) and later affecting the distal limb muscles (those close to the extremities).
- Symptoms: Enlargement of calves, a waddling gait, and lumbar lordosis (an inward curve of the spine)
- The current therapeutic options available to treat DMD are minimal and highly expensive treatment and are mostly imported from abroad.
5. BASMATI RICE
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, For the first time in the country, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has specified the identity standards for Basmati Rice.
THE EXPLANATION:
- As per these standards, Basmati rice shall possess natural fragrance characteristics of basmati rice and be free from artificial colouring, polishing agents and artificial fragrances.
- It was issued to Brown Basmati Rice, Milled Basmati Rice, Parboiled Brown Basmati Rice and Milled Parboiled Basmati Rice.
- The standards are aimed at establishing fair practices in the trade of Basmati rice and protecting consumer interest, both domestically and globally. These standards will be enforced from 1st August 2023.
What is the Uniqueness of Basmati Rice?
- It is cultivated in the Himalayan foothills of the Indian sub-continent and is universally known for its long grain size, fluffy texture and unique inherent aroma and flavour.
What are the Climatic conditions required for rice cultivation?
- Temperature: Between 22-32°C with high humidity.
- Rainfall: Around 150-300 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep clayey and loamy soil.
- Top Rice Producing States: West Bengal > Punjab > Uttar Pradesh > Andhra Pradesh