ECONOMIC SURVEY 2021-22: CHAPTER 6- SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND CLIMATE CHANGE
THE INTRODUCTION: In 2020-21, India progressed further on achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In 2021, India continued exercising significant climate leadership at the international stage under the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), and Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT Group). The chapter discusses several initiatives taken in the area of sustainable finance by the Ministry of Finance, RBI, and SEBI.
INDIA’S PROGRESS ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
- India has been making strides towards achieving the social, economic, and environmental goals covered under SDGs.
- This achievement gains further significance in the face of the considerable human and economic costs imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has set countries back on their developmental goals and created serious impediments to the attainment of the SDGs, the world over.
GOAL WISE PERFORMANCE OF INDIA AS A WHOLE: NITI AAYOG SDG INDIA INDEX REPORT AND DASHBOARD 2020-21
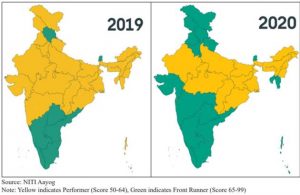
- India’s overall score on the NITI Aayog SDG India Index & Dashboard improved to 66 in 2020-21 from 60 in 2019-20 and 57 in 2018-19, showing progress in India’s journey towards achieving the SDGs.
- Despite 2020-21 being a pandemic year, India performed well on eight of the 15 SDGs measured by the NITI Aayog SDG India Index.
- These included – goal 3 (good health and well-being), goal 6 (clean water and sanitation), goal 7 (affordable and clean energy), goal 10 (reduced inequalities), goal 11 (sustainable cities and communities), goal 12 (responsible consumption and production), goal 15 (life on land) and goal 16 (peace, justice, and strong institutions).
PERFORMANCE OF STATES AND UTS ON THE NITI AAYOG SDG INDIA INDEX, 2021
- The number of Front Runners (scoring 65-99) increased to 22 states and UTs in 2020-21 from 10 in 2019-20. All remaining states and UTs were Performers (scoring 50- 64).
- Amongst states, additions to the Front Runner category in 2020-21 included Uttarakhand, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Mizoram, Punjab, Haryana, and Tripura. Amongst us, additions to the Front Runner category included Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, and Lakshadweep.
STATE OF THE ENVIRONMENT
- Sustainable development requires balancing rapid economic growth with conservation, ecological security, and environmental sustainability. This section explores the state of the environment across the land, water, and air.
LAND FORESTS
- Russia, Brazil, Canada, USA, and China were the top five largest countries by forest area in 2020, while India was the tenth-largest country by forest area.
- The top 10 countries account for 66 percent of the world’s forest area.
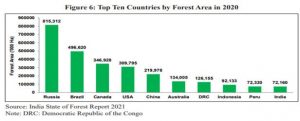
- Forests covered 24 percent of India’s total geographical area accounting for two percent of the world’s total forest area in 2020.
- India has increased its forest area significantly over the past decade. It ranks third globally in an average annual net gain in forest area between 2010 to 2020, adding an average of 2,66,000 ha of additional forest area every year during the period, or adding approximately 0.38 percent of the 2010 forest area every year between 2010 to 2020.
- Madhya Pradesh (11 percent of India’s total forest cover) had the largest forest cover in India in 2021, followed by Arunachal Pradesh (9 percent), Chhattisgarh (8 percent), Odisha (7 percent), and Maharashtra (7 percent).
- Mizoram (85 percent), Arunachal Pradesh (79 percent), Meghalaya (76 percent), Manipur (74 percent), and Nagaland (74 percent) were the top five states in terms of the highest percent of forest cover w.r.t. total geographical area of the state in 2021
PLASTIC WASTE MANAGEMENT AND ELIMINATION OF IDENTIFIED SINGLE-USE PLASTICS
- India is committed to mitigating pollution caused by littered single-use plastics.
- In 2018, the Hon’ble Prime Minister announced that India would phase out single-use plastic by 2022.
- The Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016 as amended regulate the import of identified plastic waste into the country by SEZ and EOUs.
- The regulation of import of plastic waste prevents dumping of plastic waste by other countries in the country and allows for recycling of plastic waste generated in the country.
- The following domestic regulatory actions have been taken in 2021:
- In August 2021, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India, notified the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021 prohibiting identified single-use plastic items, which have low utility and high littering potential, by 2022.
- The plastic packaging waste, which is not covered under the phase-out of identified single-use plastic items.
- In October 2021, the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change notified the draft Regulations on the Extended Producer Responsibility for plastic packaging under Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
WATER
GROUNDWATER
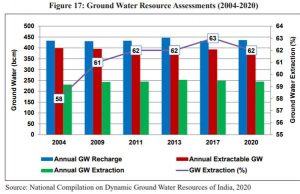
- Ground Water Resources Assessment of states/UTs is carried out jointly by state groundwater/ nodal departments and Central Ground Water Board at periodic intervals, and the Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India is published by compiling the state/UT wise groundwater resources assessed.
- Such groundwater assessments have been undertaken in 2004, 2009, 2011, 2013, 2017, and 2020.
- The annual groundwater recharge, annual extractable groundwater resources, annual groundwater extraction, and the stage of total groundwater extraction of India during 2004-2020.
- Overall, the annual groundwater extraction has been in the range of 58-63 percent during this period.
RESERVOIRS
- Reservoirs are an important source of water resources for the country. However, they are particularly prone to seasonality and are greatly impacted by rainfall and temperature patterns.
- The capacity at full reservoir levels in 138 monitored reservoirs of India along with the live storage during June-December 2021, June 2020–May 2021, and the ten-year average during June – May.
- It may be seen that reservoir live storage is at its peak during monsoon months and lowest in summer months, requiring careful planning and coordination of storage, release, and utilization of reservoirs.
RIVERS
- The Ganga River Basin is the largest in India, covering more than a quarter of the country’s land area, hosting about 43 percent of its population and contributing 28 percent of India’s water resources.
- The Government of India launched the Namami Gange Mission in 2014 as an integrated and multi-sectoral mission for the conservation of Ganga and its tributaries.
Namami Gange Mission
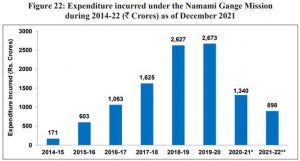
- The total expenditure incurred under the Namami Gange Mission from 2014-15 to December 2021. Lower expenditure incurred in 2020-21 and 2021-22 needs to be viewed in the context of the COVID pandemic and recent changes in accounting norms.
- Under the Gyan Ganga (Research and Knowledge Management) component, the Ganga Knowledge Centre was set up to create a state-of-the-art center to support the NMCG and create a comprehensive knowledge base on Ganga.
- The Centre for Ganga Management & Study was set up at IIT Kanpur for long-term basin studies and technology development.
AIR
- The Government of India launched the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) in 2019 to tackle the air pollution problem comprehensively, with a target to achieve 20-30 percent reduction in particulate matter (PM) concentrations by 2024 across the country keeping 2017 as the base year for the comparison of concentration.
- The NCAP is implemented in 132 cities, of which 124 cities have been identified based on non-conformity with national ambient air quality standards for five consecutive years.
- This includes 34 million-plus cities / urban agglomerations identified by the Fifteenth Finance Commission (XV-FC).
- In addition, NCAP also covers eight other million-plus cities, which fall under the XV-FC grant for receiving performance-based grants for air quality improvement. Figure 26 shows the funds released under the NCAP in 2019-20 and 2020-21.
- In 2019-20, the highest funds were released to Uttar Pradesh, followed by Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh while in 2020-21, the highest funds were released to Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, and West Bengal.
- Several steps are being taken to control and minimize air pollution from various sources in the country, which inter alia include:
- Vehicular Emission: India has leapfrogged from BS-IV to BS-VI norms for fuel and vehicles since April 2020.
- Industrial Emission: Stringent emission norms for coal-based thermal power plants have been introduced.
- Air Pollution due to dust and burning of waste: Six waste management rules covering solid waste, plastic waste, e-waste, bio-medical waste, construction, and demolition waste, and hazardous waste have been notified.
- Monitoring of Ambient Air Quality: The air quality monitoring network of manual as well as continuous monitoring stations, under programs such as the National Air Monitoring Programme, have been expanded.
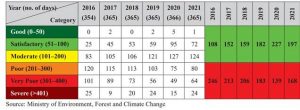
AVERAGE ANNUAL AIR QUALITY INDEX, DELHI (2016-2021)
CLIMATE CHANGE
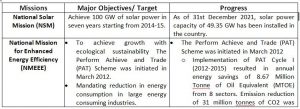
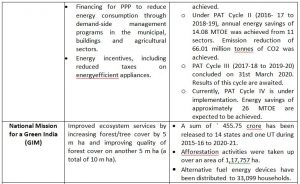
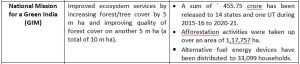
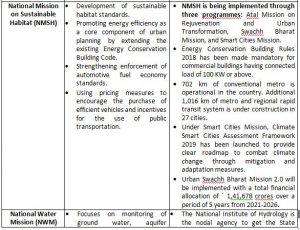
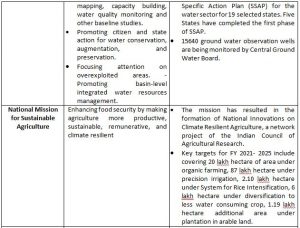
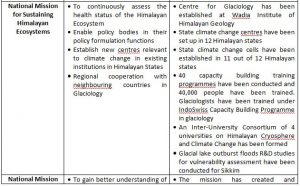
India launched the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) in 2008, establishing eight National Missions to advance action on the country’s climate priorities.
NATIONAL MISSIONS UNDER NAPCC

MAJOR DECISIONS AT THE COP26 CLIMATE SUMMIT, GLASGOW
- The COP26 adopted outcomes on all pending issues of the “Paris Rule Book”, which is the procedures for implementation of the Paris Agreement, including market mechanisms, transparency, and common timeframes for NDCs.
- The “Glasgow Climate Pact” emphasizes adaptation, mitigation, finance, technology transfer, capacity-building, loss, and damage.
- The decision urges the developed country Parties to fully deliver on the USD 100 billion mobilization goal urgently and through till 2025 and emphasizes the importance of transparency in the implementation of their pledge.
- COP26 also welcomed the launch of a comprehensive two-year Glasgow–Sharm el-Sheikh work program on the global goal of adaptation. The Glasgow Dialogue between Parties, relevant organizations, and stakeholders on loss and damage was established to explore the ways to fund loss and damage due to climate change.
India’s NDC and its voluntary commitment to enhanced climate action.
India submitted its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement on a “best effort basis” keeping its developmental imperatives in mind. India committed to
- Reduce the emission intensity of GDP by 33 to 35 percent by 2030 as compared to the 2005 level.
- Create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030.
- Achieve about 40 percent cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel energy resources by 2030.
FINANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
DEALING WITH FINANCIAL RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH CLIMATE CHANGE:
To assess the progress of its regulated entities in managing climate risk, RBI is preparing a consultative discussion paper covering, inter alia,
- Governance
- Strategy
- Risk management
- Disclosure
AUGMENTING FINANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT:
- India is actively contributing to the global efforts towards green finance.
- RBI joined the Central Banks and Supervisors Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) as a member on April 23rd, 2021, and has begun participating in the workstreams of the NGFS.
INDIA’S INITIATIVES AT THE INTERNATIONAL STAGE
Lifestyle for Environment (LIFE):
- In November 2021, the Hon’ble Prime Minister proposed a One-Word Movement in the context of climate: LIFE – Lifestyle for Environment, at the COP 26 in Glasgow.
International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- In November 2021, the Hon’ble Prime Minister launched the joint Green Grids Initiative One Sun One World One Grid (GGI –OSOWOG) at the World Leaders’ Summit in Glasgow.
Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure:
- India’s call for promoting disaster resilience of infrastructure through the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) has been receiving global attention.
- Since CDRI’s launch in September 2019, its membership has expanded to 28 countries and seven multilateral organizations, with several member countries committing to provide technical assistance and financial resources.
Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT Group):
- LeadIT was launched by India and Sweden, with the support of the World Economic Forum at the UN Climate Action Summit in New York in September 2019, as one of the nine action tracks identified by the UN Secretary-General to boost climate ambitions and actions to implement the Paris Agreement.
CONCLUSION: Going forward, there is a need to further improve forest and tree cover. Social forestry could also play a significant role in this regard. States/UTs need to improve management of their groundwater resources through improving its recharge and by stemming its over-exploitation and preventing the critical and semi-critical assessment units from further worsening. There is a greater thrust on climate action following the announcement of India’s target of becoming Net-Zero by 2070. Climate finance will remain critical to successful climate action by developing countries, including India.
HIGHLIGHTS
- India’s overall score on the NITI Aayog SDG India Index and Dashboard improved to 66 in 2020-21 from 60 in 2019-20 and 57 in 2018-19.
- Number of Front Runners (scoring 65-99) increased to 22 States and UTs in 2020-21 from 10 in 2019-20.
- In North-East India, 64 districts were Front Runners and 39 districts were Performers in the NITI Aayog North-Eastern Region District SDG Index 2021-22.
- India has the tenth largest forest area in the world.
- In 2020, India ranked third globally in increasing its forest area from 2010 to 2020.
- In 2020, the forests covered 24% of India’s total geographical, accounting for 2% of the world’s total forest area.
- In August 2021, the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021, was notified which is aimed at phasing out single-use plastic by 2022.
- Draft regulation on Extended Producer Responsibility for plastic packaging was notified.
- The Compliance status of Grossly Polluting Industries (GPIs) located in the Ganga main stem and its tributaries improved from 39% in 2017 to 81% in 2020.
- The consequent reduction in effluent discharge has been from 349.13 million liters per day (MLD) in 2017 to 280.20 MLD in 2020.
- The Prime Minister, as a part of the national statement delivered at the 26th Conference of Parties (COP 26) in Glasgow in November 2021, announced ambitious targets to be achieved by 2030 to enable further reduction in emissions.
- The need to start the one-word movement ‘LIFE’ (Lifestyle for Environment) urging mindful and deliberate utilization instead of mindless and destructive consumption was underlined.