DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (APRIL 03 & 04, 2022)
THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. NEW CRIMINAL PROCEDURE (IDENTIFICATION) BILL, 2022
THE CONTEXT: According to the new provisions of the Criminal Procedure (Identification) Bill, it will allow police and prison authorities to collect, store and analyze physical and biological samples including the retina and iris scans of convicted, arrested, and detained persons.
THE EXPLANATION
What is the legislation about?
- The Bill seeks to repeal the Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920. The over 100-year-old Act’s scope was limited to capturing finger impressions, footprint impressions, and photographs of convicted prisoners and a certain category of arrested and non-convicted persons on the order of a Magistrate.
- The Statement of Objects and Reasons of the 2022 Bill said that new ‘‘measurement’’ techniques being used in advanced countries are giving credible and reliable results and are recognized the world over. It said that the 1920 Act does not provide for taking these body measurements as many of the techniques and technologies had not been developed then.
What are the major changes proposed?
It proposes four major changes.
- First, it would define ‘‘measurements’’ to include “signature, handwriting, iris and retina scan, physical, biological samples, and their analysis, etc.” It does not specify what analysis means, implying that it may also include storing DNA samples. The “etc.” mentioned in the text of the Bill could give unfettered powers to law enforcement agencies to interpret the law at their convenience, sometimes to the disadvantage of the accused.
- Second, it empowers the National Crime Records Bureau of India (NCRB), under the Union Home Ministry, to collect, store and preserve the record of measurements for at least 75 years. The NCRB will be able to share the data with other law enforcement agencies as well. Police is a State subject and NCRB works under the Union government, and experts contend this provision may impinge on federalism.
- Third, it empowers a Magistrate to direct any person to give vital details, which till now was reserved for convicts and those involved in heinous crimes.
- Fourth, it empowers police or prison officers up to the rank of a Head Constable to take details of any person who resists or refuses to do so.
What are some other changes?
- The Bill also seeks to apply to persons detained under any preventive detention law. The Bill also authorizes taking vital details of “other persons” for identification and investigation in criminal matters. It doesn’t define the “other persons”, implying its ambit extends beyond convicts, arrested persons, or detainees.
- The Bill’s stated objective is it provides legal sanction for taking such details and will make the investigation of crime more efficient and expeditious, and help in increasing the conviction rate.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. INDIA-AUSTRALIA ECONOMIC COOPERATION AND TRADE AGREEMENT (ECTA)
THE CONTEXT: India and Australia signed an Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (IndAus ECTA) which is set to provide zero-duty access to 96 percent of India’s exports to Australia including shipments from key sectors such as engineering goods, gems, jewelry, textiles, apparel, and leather.
THE EXPLANATION:
- ECTA encompasses cooperation across the entire gamut of bilateral economic and commercial relations between the two friendly countries and covers areas like Trade in Goods, Rules of Origin, Trade in Services, Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, Dispute Settlement, Movement of Natural Persons, Telecom, Customs Procedures, Pharmaceutical products, and Cooperation in other Areas.
- Goods: The ECTA between India and Australia covers almost all the tariff lines dealt in by India and Australia respectively. India will benefit from preferential market access provided by Australia on 100% of its tariff lines.
- This includes all the labor-intensive sectors of export interest to India such as Gems and Jewellery, Textiles, leather, footwear, furniture, food, agricultural products, engineering products, medical devices, and Automobiles.
- On the other hand, India will be offering preferential access to Australia on over 70% of its tariff lines, including lines of export interest to Australia which are primarily raw materials and intermediaries such as coal, mineral ores and wines, etc.
- Services: As regards trade in services, Australia has offered wide-ranging commitments in around 135 sub-sectors and Most Favoured Nation (MFN) in 120 sub-sectors which cover key areas of India’s interest like IT, ITES, Business services, Health, Education, and Audiovisual.
- Some of the keys offered by Australia in the services space include a Quota for chefs and yoga teachers; a Post-study work visa of 2-4 years for Indian students on a reciprocal basis; mutual recognition of Professional Services and Other licensed/regulated Occupations; and Work & Holiday visa arrangement for young professionals.
- On the other hand, India has offered market access to Australia in around 103 sub-sectors and Most Favoured Nation in 31 sub-sectors from the 11 broad service sectors such as ‘business services’, ‘communication services’, ‘construction and related engineering services, and so on. Both sides have also agreed to a separate Annex on Pharmaceutical products under this agreement, which will enable fast-track approval for patented, generic, and biosimilar medicines.
- India and Australia are partners in the trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) arrangement along with Japan which seeks to enhance the resilience of supply chains in the Indo-Pacific Region. Further, India and Australia are also members of the recently formed Quad, also comprising the US, and Japan, to further enhance cooperation and develop partnerships across several issues of common concerns.
- The India-Australia ECTA will further cement the already deep, close, and strategic relations between the two countries and will significantly enhance bilateral trade in goods and services, create new employment opportunities, raise living standards, and improve the general welfare of the peoples of the two countries.
Background:
- India-Australia bilateral trade for both merchandise and services is valued at US$ 27.5 billion in 2021. India’s merchandise exports to Australia consist primarily of a broad-based basket largely of finished products like gold jewelry, polished diamonds, etc. India’s merchandise imports consist largely of raw materials, minerals, and intermediate goods.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3. NFC TECHNOLOGY FOR INSTANT PAYMENTS
THE CONTEXT: Google Pay has recently launched a new feature in India, ‘Tap to pay for UPI’, in collaboration with Pine Labs. The feature makes use of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is NFC and how does it work?
- NFC is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows NFC-enabled devices to communicate with each other and transfer information quickly and easily with a single touch — whether to pay bills, exchange business cards, download coupons, or share a document.
- NFC transmits data through electromagnetic radio fields, to enable communication between two devices. Both devices must contain NFC chips, as transactions take place within a very short distance. NFC-enabled devices must be either physically touching or within a few centimeters from each other for data transfer to occur.
How will this technology work with the recently launched feature, ‘Tap to pay for UPI’?
- Google Pay has been the first among UPI apps to bring the Tap to Pay feature working on POS terminals. It will allow users with UPI accounts configured on Google Pay to make payments just by tapping their NFC-enabled Android smartphones on any Pine Labs Android POS terminal.
- Once users tap their phones on the POS terminal, it will automatically open the Google pay app with the payment amount pre-filled. Users can then verify the amount and merchant name and authenticate the payment, using their UPI PIN. They will be notified once the payment is successful.
- The process is much faster compared to scanning a QR code or entering the UPI-linked mobile number which has been the conventional way till now.
What are the other applications of NFC technology?
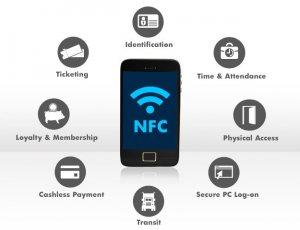
How safe is this technology?
- NFC technology is designed for an operation between devices within a few centimeters from each other. This makes it difficult for attackers to record the communication between the devices compared to other wireless technologies which have a working distance of several meters.
- The user of the NFC-enabled device determines by the touch gesture which entity the NFC communication should take place with, making it more difficult for the attacker to get connected. The security level of NFC communication is by default higher compared to other wireless communication protocols.
- The NFC Forum has also added Peer to Peer communication which is a mechanism to cipher all exchanged data to avoid external interpretation of recorded communication. Since the receiving device reads your data the instant you send it, NFCs also reduce the chance of human error.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN THE NEWS
4. IDEX INITIATIVE
THE CONTEXT: Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) framework was launched by the Government to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace Sector by engaging Industries including MSMEs, startups, individuals innovators, R&D institutes, and academia and promoting self-reliance.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Government has approved a central sector scheme for iDEX with budgetary support of Rs. 498.78 crore for the next 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Aim: to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace Sector by engaging Industries including MSMEs, startups, individual innovators, R&D institutes, and academia and promote self-reliance.
About Innovations for Defence Excellence (IDX):
- The Government has approved a central sector scheme for iDEX with budgetary support of Rs. 498.78 crore for the next 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective of the scheme: to provide financial support to nearly 300 Startups/ MSMEs/individual innovators and about 20 Partner incubators through the Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO).
- For the current financial year 2021-2022, Rs. 45 crore have been released by the Government to iDEX-DIO.
- The iDEX framework and establishment of the DIO by the Department of Defence Production (DDP) is aimed at promoting innovation and indigenization in the aerospace and defense sector at the start-up level.
- iDEX will be funded and managed by a “Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO)‟ formed as a “not for profit‟ company as per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 for this purpose.
- It aims at empowering a culture of technology co-creation and co-innovation in the sector and boosts innovation among the start-ups and encourages them to be a part of the ecosystem.
THE HEALTH AND COVID CORNER
5. WHO RECORDS THE NEW SARS-COV-2 VARIANT
THE CONTEXT: The World Health Organization (WHO) has flagged the emergence of a new variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the XE recombinant, in the United Kingdom, and with a possibly higher rate of transmission.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The WHO, in its recent epidemiological update, said the recombinant was detected in the United Kingdom on January 19, 2022, and over 600 sequences have been reported and confirmed since.
- It also added, “the early-day estimates indicate a community growth rate advantage of about 10% as compared to BA.2, however, this finding requires further confirmation.”
- The U.K. Health Security Agency (UKHSA), which tracks SARS-CoV-2 variants, analyzed three recombinants, known as XF, XE, and XD. Of these, XD and XF is recombinant of Delta and Omicron BA.1, while XE is a recombinant of Omicron BA.1 and BA.2.
- According to WHO, While XE only accounts for a small fraction of the cases, its extremely high transmissibility could mean that it becomes the most dominant strain shortly.
- A recombinant variant occurs when an individual becomes infected with two or more variants at the same time, leading to a mixing of genetic material in the human body. Several such recombinants have emerged in the past during the pandemic.
- The UKHSA has stated that in the United Kingdom, only 38 cases of XF recombinant have been identified, though none since mid-February 2022.
- The new variant is 10 percent more transmissible than the most contagious BA.2 subvariant.
THE DATASHEET
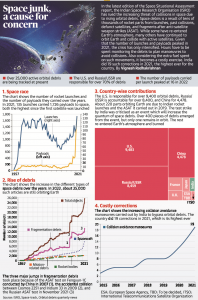
6. THE SPACE JUNK, A CAUSE OF CONCERN
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. UNEP hosts a secretariat of which of the following?
- Convention on Migratory Species
- Minamata Convention
- Convention on Biodiversity
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of them
ANSWER FOR 2ND APRIL 2022
Answer: B
Explanation:
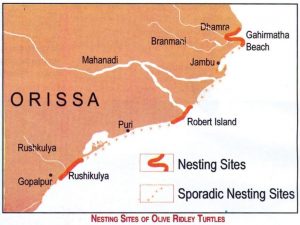
- Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea) are migratory species visiting Indian coasts for nesting.
- These turtles travel all the way from the South Pacific Ocean to breed on the coast of Gahirmatha.
- Their mass nesting phenomenon is called arribadas.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- They have the highest degree of protection as they are included in Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The turtle eggs normally take 45 days to hatch. After this, tiny hatchlings come out and make their way to the sea.
- Threats: Heavy predation of eggs by dogs and wild animals, indiscriminate fishing with trawlers and gill nets, and beach soil erosion.