DISCOVERY OF MELANOCHLAMYS DROUPADI
TAG: GS 3: ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) recently unveiled a groundbreaking discovery, a new species of head-shield sea slug named Melanochlamys droupadi.
EXPLANATION:
- This unique marine creature has been christened in honor of President Droupadi Murmu and was found along the coasts of West Bengal and Odisha.
- The discovery is highlighted in a scientific paper authored by ZSI researchers.
Taxonomy and Morphological Characteristics:
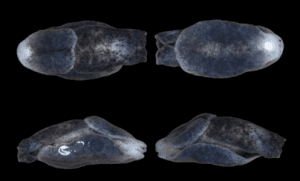
- Melanochlamys droupadi belongs to the Melanochlamys genus.
- It distinguishes itself with a short, blunt, and cylindrical body.
- Its dorsal surface is smooth and adorned with two shields – the anterior cephalic and posterior shield.
- Notably, the species features a captivating ruby red spot, a characteristic not observed in any other known sea slug.
- The detailed study reveals that Melanochlamys droupadi engages in continuous secretion of transparent mucus, forming a protective sheath to prevent sand grains from entering its parapodial space.
- The discovery sites for Melanochlamys droupadi are Digha of West Bengal coast and Udaipur of Odisha coast.
- The species, measuring up to a maximum length of 7 mm, is characterized by its brownish-black coloration and hermaphroditic nature.
- Notably, it leaves crawl marks on sandy beaches as it moves along the intertidal zone.
- The confirmation of the species has been affirmed through a meticulous examination of morphological, anatomical, and molecular characteristics.
Behavior and Reproduction:
- According to the ZSI statement, Melanochlamys droupadi exhibits intriguing behaviors.
- The sea slug crawls beneath smooth sand, forming a moving capsule where its body is rarely visible.
- Reproduction for this species is noted to occur between November and January, adding to its unique biological characteristics.
Type Specimens and Conservation Status:
- The type specimens of Melanochlamys droupadi have been deposited in the Marine Aquarium and Regional Centre, Digha, and the Estuarine Biology and Regional Centre, Gopalpur.
- This scientific documentation not only contributes to the understanding of marine biodiversity but also aids in conservation efforts for this newly discovered species.
Global Distribution and Comparative Analysis:
- While species of the Melanochlamys genus are generally found in temperate regions of the Indo-Pacific Oceanic realm, Melanochlamys droupadi stands out as one of the truly tropical distributed species.
- This uniqueness is emphasized by the fact that it joins the ranks of only three species within the group that are found in tropical regions.
