HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDEX (HDI)
TAG: GS 3: ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: After a drop in 2021, India’s HDI value increases from 0.633 to 0.644 in 2022, placing the country in the medium human development category.
India has been ranked 134 out of 193 countries in Human Development Index.
EXPLANATION:
- The Human Development Index is published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- The Human Development Index (HDI) is a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, being knowledgeable and having a decent standard of living.
- The HDI is the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of the three dimensions.
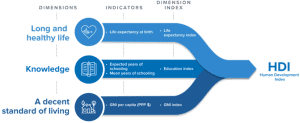
More specifically, these three dimensions are measured with four indicators:
- A long and healthy life: measured by life expectancy at birth.
- Knowledge: measured by expected years of schooling (for children of school entering age) and average years of schooling (for adults aged 25 and older)
- A decent standard of living: measured by Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
- The index is then calculated by normalizing and aggregating these three indicators. First, the indicators are brought onto the same scale, ranging from 0 to 1. This is done by setting minimum and maximum values for each indicator, and a country at or below the minimum value receiving a score of 0, and a country at or above the maximum value receiving a score of 1.
- Second, the indicators are combined. This is done by calculating the arithmetic mean of the knowledge indicators and then calculating the geometric mean across the three dimensions.
- The resulting HDI scores each country on a spectrum from 0 to 1. It covers almost all countries since 1990.
Highlights of the report:
- With a Gender Inequality Index value of 0.437 in 2022, India has shown progress and fares better than the global average of 0.462 and the South Asian average of 0.478.
- Global HDI is projected to reach record highs in 2023. However, this progress is uneven. Rich countries are experiencing record levels of human development, while half of the world’s poorest countries remain below their pre-crisis level.
- This uneven progress is leaving the poorest behind, exacerbating inequality, and stoking political polarization on a global scale. The result is a dangerous gridlock that must be urgently tackled through collective action.
- The report stated that while India ranked 135 in 2021, it had moved up to 134 in 2022. A total of 193 countries were ranked in 2022 and 191 countries in 2021.
- India’s southern neighbour Sri Lanka has been ranked much ahead at 78, while China is ranked 75, both categorised under the High Human Development category.
- India also ranks below Bhutan that stands at 125 and Bangladesh, which is in the 129th position.
- India, Bhutan and Bangladesh are all in the Medium Human Development category. Switzerland has been ranked number one.
- Nepal (146) and Pakistan (164) have been ranked lower than India.
- India’s life expectancy at birth has slightly improved from 67.2 years in 2021 to 67.7 years in 2022.
- There is an overall increase (5.88%) in expected years of schooling (EYS) from 11.9 years to 12.6 years, leading to an improvement of 18 places when the EYS aspect was considered.
- The Gross National Income (GNI) per capita also improved from $6,542 to $6,951