Day-22 | Daily MCQs | UPSC Prelims | GEOGRAPHY
[WpProQuiz 26]
[WpProQuiz 26]
INDIAN ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: To boost exports, the government on Aug 17 announced rates of tax refunds under the export promotion scheme RoDTEP for 8,555 products, such as marine goods, yarn, dairy items.
Analysis:
Reference: Indian express
THE CONTEXT: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced the financial inclusion index (FI-Index) to capture the extent of financial inclusion in the country.
Analysis:
Reference: Live mint
THE CONTEXT: The Centre has argued that it cannot reduce taxes on petrol and diesel as it has to bear the burden of payments in lieu of oil bonds issued by the previous UPA government to subsidise fuel prices.
Analysis
WHY WERE OIL PRICES DEREGULATED, AND HOW HAS IT IMPACTED CONSUMERS?
HOW MUCH TAXES/DUTIES HAS THE GOVERNMENT COLLECTED?
TO WHAT EXTENT HAVE THE OIL BONDS BEEN SERVICED BY THE GOVERNMENT?
WHAT IS THE CURRENT GOVERNMENT’S BOND STRATEGY FOR BANKS?
NOTE: STUDENTS NEED TO REMEMBER ONLY MACRO TRENDS, GRANULAR DATA GIVEN TO PROVIDE CONTEXT.
Reference: Indian express
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Home Affairs has informed the Lok Sabha that Census 2021 has been postponed indefinitely.
Analysis:
WHAT WAS THE ORIGINAL TIMELINE OF THE CENSUS AND HOW IS IT BEING DELAYED?
HOW WILL THE DELAY AFFECT THE PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM?
WHAT OTHER WELFARE SCHEMES COULD BE AFFECTED BY THE DELAY?
HOW ABOUT CENSUS DATA ON MIGRATION?
Reference: The Hindu
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: As much as 32 per cent of India’s coastline underwent sea erosion and 27 per cent of it expanded between 1990 and 2018, according to a recent technical report by the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR) under the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences.
ANALYSIS:
ABOUT NCCR
Reference: Down to earth
THE CONTEXT: The Odisha Forest and Environment Department is set to begin ‘Island Odyssey’ and ‘Hirakud Cruise’ ecotourism packages for tourists to islands inside the reservoir when COVID-19 restrictions are lifted.
Analysis:
Reference: The Hindu
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: India on August 17 announced that it will issue an emergency e-visa to Afghan nationals
Analysis:
Reference: The Hindu
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The second United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC) will be organized by India in October next year.
Analysis:
ABOUT UNWGIC
Reference: PIB
Q 1. Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index) is launched recently. Consider the following statements about it:
1. It is launched by Ministry of finance.
2. The index will be released in the month of July every year.
3. Financial inclusion will be measured in a single value ranging between 0 and 100.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 3 only
d) 1, 2 and
Q.2 ‘Cattle Island” recently seen in the news is located near the vicinity of which of the following river?
a) Mahananda
b) Godavari
c) Mahanadi
d) d) None of the above.
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 17, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Q.1 Answer D. Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan are part of Golden Crescent infamous for illegal drug production and trafficking. Iraq is not part of it.
Q.2 Answer D. The Project BOLD (Bamboo Oasis on Lands in Drought) is an initiative of Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC). The project aims to boost the income of the tribal people and solve environmental concerns such as land desertification and land degradation by creating bamboo-based green patches in drylands.
[WpProQuiz 25]
INDIAN ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: The Project BOLD (Bamboo Oasis on Lands in Drought) of Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) has received Indian Army’s support in Leh
Analysis:
ABOUT KVIC
KVIC is a statutory body set under KVIC Act 1956 with the following objectives:
• The social objective of providing employment.
• The economic objective of producing saleable articles.
• The wider objective of creating self-reliance amongst the poor and building up of a strong rural community spirit.
Major schemes under KVIC:
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: The Employees’ State Insurance Corporation has notified a relief scheme for the dependents of ESI insured persons in case of their death due to COVID-19 that would give a minimum of 1,800 a month.
Analysis:
ABOUT ESIC
Reference: The Hindu
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Only 23 states have implemented the Decentralized Procurement Scheme (DCP) so far — 15 to procure rice and eight to procure wheat — despite the scheme being in place for 23 years according to the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Food, Consumer affairs and Public Distribution
Analysis:
KEY OBSERVATIONS OF THE REPORT
Reference: Down to earth
THE CONTEXT: The central government is facing opposition to the Electricity Amendment Bill 2021 even before it is introduced in Parliament.
Analysis:
KEY CHANGES PROPOSED IN THE BILL
WHAT IS ARE THE OBJECTIONS TO DELICENSING OF POWER DISTRIBUTION?
WHAT ARE OTHER KEY CONCERNS?
Reference: Indian express
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Pollution control bodies of most Indian states shared no or partial information on public hearings of development projects online, a new study found.
Analysis:
NOTE: STUDENTS NEED NOT REMEMBER THE GRANULAR DATA. THEY ARE GIVEN TO PROVIDE CONTEXT.
Reference: Down to earth
6. WHY HAITI IS PRONE TO DEVASTATING EARTHQUAKES?
THE CONTEXT: Earthquakes have been wreaking havoc in Haiti since at least the 18th century and the powerful quake on 14 August has killed hundreds and injured thousands. Analysis
WHAT MAKES HAITI PRONE TO EARTHQUAKES?
WHY CAN EARTHQUAKES IN HAITI BE SO DEVASTATING?
Reference: Indian express
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: The anti-drug law enforcement agencies are suspecting a steep surge in cross- border
trafficking of heroin and crystal methamphetamine with the rapid Taliban takeover in
Afghanistan.
Analysis:
Reference: The Hindu
THE CONTEXT: More than 28,000 children died from cancer in sub-Saharan Africa amid the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic in 2020, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Analysis:
• COVID-19 affected treatment of children with cancer as they need to travel a lot every month for up to two-three years
• Travel restrictions meant that many failed to reach hospital on time
• A significant backlog in screening and treatment for COVID-19 likely led to delayed diagnoses and treatment and a significant increase in the number of avoidable cancer deaths, according to Cancer Control 2020 Survey.
• There was limited infrastructure, scarce cancer care centres and only a few established satellite cancer treatment centres in Ethiopia.
• In Kenya, cancer facilities were open only for a few hours every day. It disrupted care for patients who needed to travel to urban areas for treatment.
• In Nigeria, the pandemic made a significant impact on cancer care: Access to care was disrupted, cost for treatment and care rose and cancer screening activities were suspended
• Cancer survival rate among children in Africa is around 20 per cent; it is over 80 per cent in high-income countries.
• A review of cancer clinical trials in Africa found that only 20 of 54 African countries surveyed hosted clinical trials for children with cancer.
• A majority of such trials were carried out only in four African countries: Egypt, South Africa, Algeria and Kenya.
• In 2018, the WHO announced Global Initiative for Childhood Cancers, which aims to achieve a survival rate of 60 per cent among children with cancer. It aims to reduce suffering from cancer for all children by 2030.
Reference: Down to earth
Q 1. Which of the following country is not part of ‘Golden Crescent’ group of countries associated with illegal drugs production trade?
a) Pakistan
b) Afghanistan
c) Iran
d) Iraq
Q.2 Project BOLD recently seen in the news is ?
a) A policing initiative for strengthening women security in the national capital
b) An environmental protection initiative by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
c) An Indian Army initiative to train college students in self defence
a) d) None of the above.
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 15&16, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Answer: C
Explanation: Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary is actually a Bird Sanctuary located near the Jhajjar district in Haryana. Thol Lake Wildlife Sanctuary and Wadhvana Wetland are located in Gujrat. Sultanpur National park is in Haryana.
[WpProQuiz 24]
INDIAN HISTORY
THE CONTEXT: Google paid a tribute to activist and author Subhadra Kumari Chauhan’s 117th birth anniversary with a creative doodle. With the doodle, the New Zealand-based guest artist, Prabha Mallya, hopes people find the courage to follow their dreams. The doodle shows Chauhan holding a pen – surrounded by several notes, the queen of Jhansi and people taking part in a protest.
ABOUT SUBHADRA KUMARI CHAUHAN
Reference: Indian express
THE CONTEXT: The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi has said that in memory of the struggles and sacrifices of our people, 14th August will be observed as Partition Horrors Remembrance Day.

Reference: PIB
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Addressing the nation from the Red Fort in the national capital on India’s 75th Independence Day Prime Minister laid out the plan for the next 25 years before the nation.
THE KEY TAKEAWAYS FROM PM INDEPENDENCE DAY SPEECH
Reference: Live Mint
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Four more wetlands from India get recognition from the Ramsar Secretariat as Ramsar sites. These sites are Thol and Wadhwana from Gujarat and Sultanpur and Bhindawas from Haryana.
ANALYSIS:
ROLE OF WETLANDS
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: In TRIFED to make available eco-friendly Pankhas for eminent dignitaries and guests who will attend the Independence Day Celebrations at the Red Fort.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: Nearly 6,800 people lost their lives in the country over the past three years due to hydro meteorological calamities such as flash floods, landslides and cyclones and West Bengal has recorded the highest deaths among all States, The details were provided by the Home Ministry.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: The Hindu
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: Taliban insurgents now control all of Afghanistan’s major cities apart from Kabul, after making rapid advances against local forces who are largely fending for themselves as foreign troops withdraw. Talks between the Taliban and the Afghan government on a political understanding that could lead to a peace deal, backed by the United States and its allies, have failed to make significant progress.
SOME OF THE MAJOR MILESTONES IN THE ISLAMIST MILITANT MOVEMENT’S ADVANCE IN RECENT MONTHS
April 14 – President Joe Biden announces U.S. troops will withdraw from Afghanistan starting on May 1 and ending on Sept.11, bringing America’s longest war to a close. It was an extension of the previous withdrawal deadline of May 1 agreed between the United States and the Taliban.
May 4 – Taliban fighters launch a major offensive on Afghan forces in southern Helmand province. They also attack in at least six other provinces.
May 11 – The Taliban capture Nerkh district just outside the capital Kabul as violence intensifies across the country.
June 7 – Senior government officials say more than 150 Afghan soldiers are killed in 24 hours as fighting worsens. They add that fighting is raging in 26 of the country’s 34 provinces.
June 22 – Taliban fighters launch a series of attacks in the north of the country, far from their traditional strongholds in the south. The UN envoy for Afghanistan says they have taken more than 50 of 370 districts.
July 2 – American troops quietly pull out of their main military base in Afghanistan – Bagram Air Base, an hour’s drive from Kabul. It effectively ends U.S. involvement in the war.
July 5 – The Taliban say they could present a written peace proposal to the Afghan government as soon as August.
July 21 – Taliban insurgents control about a half of the country’s districts, according to the senior U.S. general, underlining the scale and speed of their advance.
July 25 – The United States vows to continue to support Afghan troops with intensified airstrikes to help them counter Taliban attacks.
July 26 – The United Nations says nearly 2,400 Afghan civilians were killed or wounded in May and June in escalating violence, the highest number for those months since records started in 2009.
Aug. 6 – Zaranj in the south of the country becomes the first provincial capital to fall to the Taliban in years. Many more are to follow in the ensuing days, including the prized city of Kunduz in the north.
Aug. 13 – Four more provincial capitals fall in a day,including Kandahar, the country’s second city and spiritual home of the Taliban. In the west, another key city, Herat, is overrun and veteran commander Mohammad Ismail Khan, one of the leading fighters against the Taliban, is captured.
Aug. 14 – The Taliban take the major northern city of Mazar-i-Sharif and, with little resistance, Pul-e-Alam, capital of Logar province just 70 km (40 miles) south of Kabul. The United States sends more troops to help evacuate its civilians from Kabul as Afghan President Ashraf Ghani says he is consulting with local and international partners on next steps.
Aug. 15 – The Taliban take the key eastern city of Jalalabad without a fight, effectively surrounding Kabul.
Reference: The Hindu
Q 1. Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
Wetlands Region
1. Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary Rajasthan
2. Sultanpur National Park Haryana
3. Thol Lake Wildlife Sanctuary Maharashtra
4. Wadhvana Wetland Gujarat
Select the correct answer using code given below:
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) 1, 2 , 3 and 4
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 13, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Answer: d)
Explanation:
Q2. ANSWER: b)
Explanation:
[WpProQuiz 22]
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs launched ‘SonChiraiya’ – (A brand and logo)- for marketing of urban Self-Help Group (SHG) products. While launching the brand and logo, he said that helping women to become financially empowered and live a dignified life is one of the priority areas of the Government.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment to Flag-Off ‘Operation Blue Freedom – Land World Record at Siachen Glacier ‘Trained by a team of Armed Forces veterans, the selected people with disabilities will undertake an expedition to Siachen.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: PIB
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Government notified the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021, prohibiting identified single use plastic items by 2022.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: In a first, Bihar has decided to tag endangered greater adjutant storks (Leptoptilos dubius), locally known as ‘Garuda’, with GPS trackers to monitor their movement as a part of efforts to conserve them.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: Down to Earth
THE CONTEXT: Government released “IndiGau’, India’s first Cattle Genomic Chip for the conservation of pure varieties of indigenous cattle breeds like, Gir, Kankrej, Sahiwal, Ongole etc.
ANALYSIS:
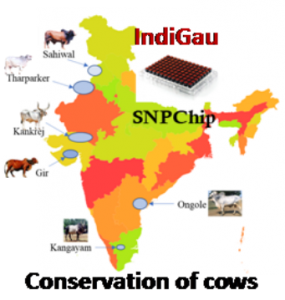
Reference: PIB
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Bharat Biotech’s BBV154 intranasal vaccine has become the first of its kind to receive the regulatory approval for phase 2/3 trials.
ANALYSIS:
Reference: The Hindu
Q 1. ‘Son Chiraiya’ is a brand and logo for marketing of products by?
a) Minority groups
b) Prisoners
c) Primitive Tribal groups
d) Self-Help Groups
Q2. Recently in news, the term “IndiGau ” is related to ?
a) New Scheme to cows
b) Cattle Genomic Chip
c) Growth Hormone to improve productivity
d) Indigenous cattle breed
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 13, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Answer: c)
Explanation:
1. ‘AL– Mohed AL–Hindi’ – Saudi Arabia
2. ‘Zayed Talwar’ – UAE
3. ‘Varuna’ – France
Q2. ANSWER: c)
Explanation:
ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: It was inscribed recently as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
ANALYSIS:
ARCHITECTURE
REFERENCE: The Hindu
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Despite highest disruption since 2014, the no. of bills passed per day during this session in Rajya Sabha was the 2nd highest since 2014 (i.e. 1.1 bills per day passed). The time lost due to interruptions / an adjournment (till Aug 11) was 76 Hours 26 Minutes and the highest average time per day lost due to interruptions / adjournments since the 231st session of Rajya Sabha in 201 was 4 Hours 30 Minutes.
DETAILS OF THE MONSOON SESSION
1. The Monsoon Session, 2021 of Parliament which commenced on Monday, 19th July, 2021 has been adjourned sine die on the 11th of August, 202 The Session provided 17 sittings spread over a period of 24 days.
2. The Session, which was originally scheduled to have 19 sittings from 19th July till 13 August, 2021, was curtailed due to continuous disruptions in both the Houses and completion of essential government business.
3. During the Session, 22 Bills were passed by both the Houses of Parliament which includes two appropriation Bills relating to the Supplementary Demands for Grants for 2021-22 and the Demands for Excess Grants for 2017-2018 which were passed by Lok Sabha, transmitted to Rajya Sabha and are deemed to have been passed under Article 109(5).
4. Four Bills replacing the Ordinances, namely, the Tribunals Reforms (Rationalisation and Conditions of Service) Ordinance, 2021, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2021, the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas Ordinance, 2021 and the Essential Defence Services Ordinance, 2021 which were promulgated by the President before Monsoon Session, were considered and passed by the Houses.
5. Some important Bills, passed by Houses of Parliament are as under: –
A. ECONOMIC SECTOR/EASE OF DOING BUSINESS MEASURES
B. TRANSPORT SECTOR REFORMS
C. EDUCATIONAL REFORMS
D. SOCIAL JUSTICE REFORMS
REFERENCE: PIB
THE CONTEXT: The Delhi government has launched an ambitious “faceless” transport initiative.
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE: IE
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: The total installed renewable energy capacity in India, excluding large hydro, has crossed the mile-stone of 100 GW. Today India stands at 4th position in the world in terms of installed RE capacity, 5th in solar and 4th in wind in terms of installed capacity.
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE: PIB
THE CONTEXT: On World Elephant Day (August 12th), Government declared that from December, India will move to a system that will count tigers and elephants as part of a common survey. The tiger survey is usually held once in four years and elephants are counted once in five years.
ANALYSIS:
THE CONTEXT: Madhya Pradesh’s commercial capital Indore has been declared as India’s first ‘water plus’ city under the Swachh Survekshan 2021.
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE:INDIA TODAY
THE CONTEXT: India is all set to import 15 lakh tonnes of genetically modified (GM) soyameal after the Union Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change and the Food Safety and Standard Authority of India (FSSAI) gave their nod to it. This would be the first time that India would import GM soya meal in view of the demand by the poultry industry
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE: IE
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: India’s attempt to place a geoimaging satellite (GISAT-1) with its GSLV-F10-EOS-3 mission did not succeed. The GSLV-F10 rocket of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), which blasted off from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota with the purpose of launching the Earth Observation Satellite EOS-3 into space, failed in its mission due to a ‘performance anomaly’.
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE:THE HINDU
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: The maiden bilateral naval exercise between India and Saudi Arabia named ‘AL– Mohed AL–Hindi’ got under way.
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE: THE HINDU
THE CONTEXT: Kabul handed a proposal to Taliban negotiators in Qatar offering a power-sharing deal in return for an end to fighting. The Taliban had been given an offer about a “government of peace” without providing more specifics.
ANALYSIS:
REFERENCE: THE HINDU
Q 1. Which of the following pairs of Naval exercises of Indian Navy, are correctly matched?
1. ‘AL– Mohed AL–Hindi’ – Saudi Arabia
2. ‘Zayed Talwar’ – Oman
3. ‘Varuna’ – France
Select the correct answer using code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Q2. Which city has been declared as India’s first ‘water plus’ city under the Swachh Survekshan 2021.
a) Hyderabad
b) Bhopal
c) Indore
d) Raipur
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 12, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Answer: b)
Explanation:
Q2. ANSWER: b)
Explanation:
[WpProQuiz 21]
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Parliament passed National Commission for Homoeopathy (Amendment) Bill, 2021
THE CONTEXT: Parliament passed National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (Amendment) Bill, 2021.
THE CONTEXT: At least 14 States and Union Territories have reopened or plan to reopen schools partially this month.
Analysis:
Reference: The Hindu
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has formulated a scheme “SMILE – Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise”, which includes sub-scheme – ‘Central Sector Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of persons engaged in the act of Begging’.
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: Quality of Life for Elderly Index was released by Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM). The Index has been created by the Institute for Competitiveness at the request of EAC-PM and it sheds light on an issue often not mentioned- problems faced by the elderly.
Analysis:
KEY HIGHLIGHTS FROM THE REPORT
Reference: PIB
THE CONTEXT: In a unique initiative Ministry of Tribal Affairs in partnership with The Art of Living Foundation, Aurangabad, Maharashtra launched Vrushka Bandhan Project where 1100 tribal women are creating Rakhis for Raksha Bandhan with seeds of indigenous trees, which is a unique contribution to increasing forest cover & combating climate change.
ABOUT THE PROJECT
Reference: PIB
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Kaziranga has become the first National Park in India to have been equipped with satellite phones.
Analysis:

Reference: The Hindu
THE CONTEXT: NASA has created a visualization tool that makes data on future sea level rise from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) accessible to the public.
Reference: DTE
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: India has successfully tested the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)-developed Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile off the coast of Odisha’s Balasore district.
Analysis:
Reference: TOI
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: According to a new book by the journalists, National Security Advisor (NSA) Ajit Doval and the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW) exchanged messages with top Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) officials as part of a unique back channel connection between the two countries that involved two foreign journalists Adrian Levy and Cathy Scott-Clark in 2018-2019, including after the Pulwama attack.

August 12, 2021 Prelim Practice Questions
Q 1. Consider the following National Parks of Assam:
1. Dibru-Saikhowa NP
2. Kaziranga NP
3. Manas NP
4. Nameri NP
Arrange them in East-West direction of their location and select the correct answer from code given below:
a) 1-2-3-4
b) 1-2-4-3
c) 1-3-2-4
d) 1-3-4-2
Q2. Quality of Life for Elderly Index was released by
a) NITI AAYOG
b) Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)
c) Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
d) Ministry of Health
Answer for August 11, 2021 Prelims Practice Questions
Q1 ANSWER: C)
Explanation
Q2. ANSWER: A)
Explanation:
CONTEXT: India is currently pursuing multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) or drones programme in an attempt to arm its three services with weapons that would play a critical role in future wars.
Reference: The Print
CONTEXT: Yogita K Adlakha, an Inspire Faculty Fellow, has developed human-based models to study neuron development and neuro developmental disorders such as autism, which can help design treatment strategies for such brain disorders.
Reference: The Week
CONTEXT: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch an Earth Observation Satellite on August 12 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, SHAR, at Sriharikota.
Analysis:
Reference: The Hindu
CONTEXT: India strongly rejected a statement on Jammu and Kashmir by the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) and asked it to refrain from allowing vested interests to exploit its platform for comments on internal affairs of the country. The strong comments by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) came in response to the statement issued by the General Secretariat of the OIC on the second anniversary of the withdrawal of the special status of Jammu and Kashmir.
Reference: The Week
CONTEXT: Mauritius has denied a report that it has allowed India to build a military base on the remote island of Agalega.
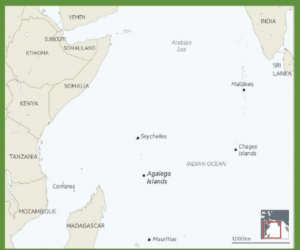
CONTEXT: Finance and Corporate Affairs Minister introduced the Taxation Laws (Amendment) Bill in the Lok Sabha to nullify the relevant retrospective tax clauses that were introduced in 2012 to bring past indirect transfer of Indian assets under the ambit of taxation.
Reference: The Hindu
CONTEXT: parliament on Thursday approved a bill that seeks to set up a commission for air quality management in the National Capital Region and its adjoining areas
Reference: India Today
CONTEXT: Indian Council of Scientific and Industrial Research’s Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-CMERI), Durgapur, recently inaugurated a “naturally ventilated polyhouse facility” and laid the foundation stone of “retractable roof polyhouse” its Ludhiana centre.
Reference: Down to Earth
CONTEXT: The Scheme for PMKSY-HKKP was valid till March, 2021. The extension of the scheme for the period 2021-26 is under consideration of the Government. The targets for this period shall be firmed up based on approval of the scheme for the period 2021-26.
Reference: PIB
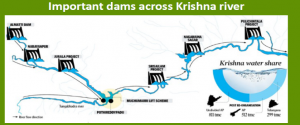
CONTEXT: One of the radial gates of KL Rao Sagar Pulichintala Project was washed away, causing floods in nearby villages.
Reference: The Hindu
CONTEXT: A comprehensive initiative called PM e-VIDYA has been initiated as part of Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan in 2020, which unifies all efforts related to digital/online/on-air education to enable multi-mode access to education.
The initiative includes:
Reference: PIB
CONTEXT: In a new study, scientists reveal how Earth’s inner core is growing faster on one side than the other, which could help explain how old the inner core is, and the intriguing history of Earth’s magnetic field
Reference: Earth’s inner core