WSDP Bulletin (11/03/2024)
(Newspapers, PIB and other important sources)
Prelim and Main
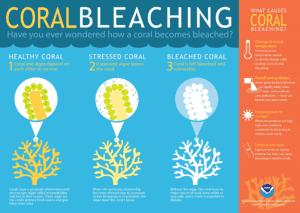
1. In Frames | A flurry of feathers in a drying lake READ MORE
2. 16 years, 21 rounds of talks: India-EFTA free trade agreement a reality READ MORE
3. Centre issues directive to curb tailgating at e-gates for Digi Yatra passengers READ MORE
4. PM Modi unveils bronze statue of Ahom general in Assam: Who was Lachit Borphukan? READ MORE
5. India’s first museum dedicated to cooperatives is coming up in Kozhikode READ MORE
6. Report turns spotlight on India’s ‘zero-food children’ READ MORE
7. India’s golden langur population estimated at 7,396 READ MORE
8. Meet Pi, the world’s ‘friendliest’ chatbot powered by the new Inflection-2.5 LLM READ MORE
9. Yaounde Declaration: Health ministers of 11 African countries commit to end malaria deaths READ MORE
Main
GS Paper- 1
1. Challenging colonial patriarchy and cultural hegemony READ MORE
2. Gig workers suffer from lack of social security, regulations: study READ MORE
3. Ocean temperature hit record high in February 2024, EU scientists say READ MORE
4. Crisis of time: On parched Karnataka and its water woes READ MORE
5. Bengaluru’s water crisis decoded READ MORE
GS Paper- 2
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. Arun Goel’s Resignation: What is the Established Law on the Appointment of Election Commissioners? READ MORE
2. EC exit no big worry READ MORE
3. We need limits on election campaign spending READ MORE
4. Voter must know who funds political parties. This is the right that Supreme Court has protected READ MORE
5. The case for disclosure of judicial assets READ MORE
6. Protect dignity of women in custody READ MORE
SOCIAL ISSUES
1. Post-Cold War era and Great Power competition: Implications and options for India READ MORE
2. India and the Greater Indo-Pacific: Balancing geopolitical equations READ MORE
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
1. Boosting India-US ties: Strategic move to counter Chinese challenge READ MORE
2. Maldives’ Muizzu is making a mistake READ MORE
GS Paper- 3
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
1. India must act fast on free trade agreements READ MORE
2. The practice of offering freebies must stop READ MORE
3. Urban Employment Programmes: A Catalyst for Female Labour Force Participation READ MORE
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
1. RBI and the net-zero transition — A road map for green India READ MORE
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1. India needs an enforceable AI regime READ MORE
2. How women are navigating challenges and taking centre stage in the AI-powered technology landscape READ MORE
INTERNAL SECURITY
1. Not law, nor duty: On ‘safe military jobs’ and Indians in war zones READ MORE
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
1. Mitigating risks in infrastructure development READ MORE
GS Paper- 4
ETHICS EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDY
1. Law Commission Recommends Whistleblower Protection, Says Amendments May Be Brought To Mandate Test Data Disclosure READ MORE
2. Chandigarh Police fastest in country with emergency response time of 7.03 minutes READ MORE
Questions for the MAIN exam
1. The voter’s right to information includes the right to know financial contributions to a political party because of its influence on electoral politics and on governmental decisions. Comment.
2. The Supreme Court has struck down the electoral bonds scheme that will remove opacity in legal donations but this is akin to putting a band-aid on a bullet wound as the majority of the funding continues to be in unaccounted cash. Analyse.
3. Urban employment programmes must go beyond being safety nets, to imbibe not just protective and preventive measures, but transformative measures that address women’s labour force participation. Comment.
4. The future of Indo-Pacific peace and stability hinges on the tranquility of the Greater Indo-Pacific, where India’s pivotal role as a voice of the Global South and global power can effectively recalibrate regional geopolitics. Discuss.
5. Gender equality is not just a matter of social justice; it is also a prerequisite for sustainable development. Comment.
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
- Justice demands that no one should do more ruling than being ruled, but that all should have their turn.
- Climate change is a crisis of time. It precipitates non-linear changes that lead to disproportionate, and sometimes irreversible, outcomes, forcing underprepared governments to mount rapid responses to forces that have been festering for decades.
- The voter’s right to information includes the right to know financial contributions to a political party because of its influence on electoral politics and on governmental decisions.
- In a democratic country, it is essential for a government to spread awareness about its schemes and policies.
- It is the opaque nature of most of the donations coupled with the distribution of cash for votes that weakens the process of free and fair elections in India.
- The Supreme Court has struck down the electoral bonds scheme that will remove opacity in legal donations but this is akin to putting a band-aid on a bullet wound as the majority of the funding continues to be in unaccounted cash.
- Challenging gender norms requires more than legislation and material resources; it also takes community mobilisation and a long-term commitment.
- Under all circumstances, war is to be regarded not as an independent thing but as a political instrument.
- The mismatch between the availability of funds and the requirement will make the Scheme prone to the use of discretion, corruption and nepotism in choosing the beneficiaries.
- There are concerns regarding judicial accountability, which makes a strong case for the disclosure of assets by judges in the higher judiciary.
- Section 24 in both Acts (pari-materia) allows the central government to frame rules only for the purpose of these Acts. Unfortunately, the purpose for accountability is nowhere to be seen in these Acts as of now.
- Women’s activists point out that the causes of custodial sexual offences include patriarchal norms, abuse of power by the authorities, lack of gender sensitivity and training for police and other officials, and the social stigma attached to victims.
- The culture of impunity and victim blaming within the law enforcement machinery hinders survivors from seeking justice.
- India has had multi-member election commissions in operation since 1993, with decision-making power by majority vote. With Arun Goel’s resignation as election commissioner, the Election Commission has been reduced to one-man commission.
- As the world prepares for an emerging three-power strategic situation, India needs to tread carefully to secure its well-deserved place on the global high table without any knee-jerk actions.
- The future of Indo-Pacific peace and stability hinges on the tranquility of the Greater Indo-Pacific, where India’s pivotal role as a voice of the Global South and global power can effectively recalibrate regional geopolitics
ESSAY TOPIC
- Gender equality is not just a matter of social justice; it is also a prerequisite for sustainable development.
50-WORD TALK
- Supreme Court has rightly used strong words to quash the ‘waging war’ case against the Maharashtra professor who merely updated his WhatsApp status criticising abrogation of Article 370. It has called for educating the police about free speech and democracy. This is key to preventing citizen harassment by the authorities.
Things to Remember:
- For prelims-related news try to understand the context of the news and relate with its concepts so that it will be easier for you to answer (or eliminate) from given options.
- Whenever any international place will be in news, you should do map work (marking those areas in maps and exploring other geographical locations nearby including mountains, rivers, etc. same applies to the national places.)
- For economy-related news (banking, agriculture, etc.) you should focus on terms and how these are related to various economic aspects, for example, if inflation has been mentioned, try to relate with prevailing price rises, shortage of essential supplies, banking rates, etc.
- For main exam-related topics, you should focus on the various dimensions of the given topic, the most important topics which occur frequently and are important from the mains point of view will be covered in ED.
- Try to use the given content in your answer. Regular use of this content will bring more enrichment to your writing.