TOP 5 TAKKAR NEWS OF THE DAY (3rd APRIL 2023)
1. THE COMPREHENSIVE AND PROGRESSIVE AGREEMENT FOR TRANS-PACIFIC PARTNERSHIP (CPTPP)
TAGS: GS- II-INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS AND PRELIMS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the United Kingdom has agreed to join an 11-country trans-Pacific trade pact to deepen ties in the region and build its global trade links after leaving the European Union.
THE COMPREHENSIVE AND PROGRESSIVE AGREEMENT FOR TRANS-PACIFIC PARTNERSHIP (CPTPP)
About:
- CPTPP is a free trade agreement (FTA) that was agreed in 2018 between 11 countries – Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore and Vietnam.The U.K will become the 12th member and the first to join since the partnership since its inception.
- It is the successor to the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), which was a key plank in the Obama administration’s “Pivot to Asia” strategy that aimed to create an economic counterweight to China’s regional influence.It emerged after the former US president Donald Trump withdrew the country from the TPP in 2017, soon after taking office.
- Also, it is important to note that, In September 2021, China submitted a formal application to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). But for the entry, there must be a consensus among all 11 members.
- The CPTPP commission 2023 is currently chaired by New Zealand.

Objectives:
- The agreement mandates the duty-free entry of commercial samples having almost negligible value and printed advertising material from the territory of a signatory party.
- CPTPP covers virtually all sectors and aspects of trade in order to eliminate or reduce barriers. It establishes clear rules that help create a consistent, transparent and fair environment to do business in CPTPP markets.
- It eliminates tariffs and reduces barriers for 98% of exports to CPTPP member countries.
- It also includes trade-related technical cooperation among CPTPP members, including with respect to small and medium-sized enterprises, regulatory coherence and economic development.
Significance:
- The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) will offer exporters a competitive advantage over exporters from other countries that do not have a free trade agreement with countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Once fully implemented, CPTPP will form a trading bloc representing 500 million consumers and 13.5% of global GDP, providing preferential access to key markets in Asia and Latin America.
2. IMF’S $15.6 BILLION LOAN FOR UKRAINE
TAGS: GS-II-INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has approved a loan program worth $15.6 billion for Ukraine as part of a larger $115 billion package to aid its war-torn economy. With one-third of Ukraine’s population displaced, the IMF’s support comes as a crucial aid in reconstructing the country’s economy.
THE EXPLANATION:
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy expressed gratitude to the IMF for the support and called it an essential help in the fight against Russian aggression.
Two-Phase Loan Program for Ukraine
- The IMF’s loan program for Ukraine will span four years and run in two phases. The first phase aims to close Ukraine’s massive budget deficit and stabilize disinflation. The IMF’s support will ease the pressure on government spending by providing immediate financial assistance of $2.7 billion. Ukraine is required to focus on financial stability and undertake ambitious structural reforms, particularly in the energy sector.
- The second phase of the loan program will begin once active combat subsides and will focus on reforms to improve growth in the medium to long term. The IMF’s overarching goals are to sustain economic and financial stability at a time of exceptionally high uncertainty and promote reforms for Ukraine’s post-war accession to the European Union.
Requirements for the Loan Program
- The IMF’s loan program is designed to support Ukraine’s struggles in meeting its payments arising from the large exogenous shock of the war. Ukraine is required to meet stringent IMF targets while financing its possibly decisive spring counteroffensive, which is expected to commence in April, 2023.
- The program mandates Ukraine to develop independent and effective anti-corruption institutions to help mitigate corruption risks and boost donor confidence.
3. PIEZOELECTRIC EFFECT IN LIQUIDS
TAGS: GS-III- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, researchers have discovered that this effect can also occur in liquids, opening up a host of novel applications. Let’s take a closer look at this discovery and what it means.
THE EXPLANATION:
The piezoelectric effect is a phenomenon whereby certain materials, such as quartz crystal, generate an electric current when subjected to mechanical stress.
The Piezoelectric Effect and Liquid Composition
- The piezoelectric effect in solids is well known, with quartz crystal being one of the most famous examples. Quartz crystal is composed of silicon and oxygen arranged in an organized structure. When squeezed, the crystal generates an electric current due to the displacement of charges from the centre.
- In liquids, however, the piezoelectric effect has not been observed until now. Two liquids, one normal and one ionic, were studied to investigate this effect. The liquids were subjected to mechanical stress, and the resulting electric current was measured. The researchers found that both liquids exhibited the piezoelectric effect, with strengths of 16 mV/N and 17 mV/N, respectively.
The Structure of the Body and the Piezoelectric Effect
- The significance of the structure of the body in the piezoelectric effect is that it needs to have an organized structure. Quartz crystal is an excellent example of this, as the organized structure allows for the displacement of charges from the centre when squeezed.
- The same appears to be true for liquids, with the discovery of the piezoelectric effect suggesting that there is some manner of organization in ionic liquids that is not seen in normal liquids.
Dielectric Materials and Ionic Liquids
- Dielectric materials are materials that don’t conduct electricity but are mildly affected by an electric field. Ionic liquids, on the other hand, are made of ions instead of molecules and can be recycled with fewer environmental issues.
- The difference between normal and ionic liquids is that they respond very differently at the molecular level when an electric charge is imposed on them.
The Piezoelectric Constant in Liquids
- The piezoelectric constant is a measure of how strongly a material exhibits the piezoelectric effect. The piezoelectric constant calculated for the liquids tested in the study was lower than that of quartz by a factor of 10.
- This suggests that the piezoelectric effect in liquids may not be as strong as in solids, but it is still a significant discovery.
Applications of the Piezoelectric Effect in Liquids
- The discovery of the piezoelectric effect in liquids opens up a whole new avenue of research for novel applications.
- One potential use of the inverse piezoelectric effect, which is the distortion of liquids when an electric charge is applied, is to control how liquids bend light passing through them. Another possible use is in developing room-temperature ionic liquids for use in batteries and other electronic devices.
4. NEVADO DEL RUIZ VOLCANO
TAGS: PRELIMS-PLACES IN NEWS
THE CONTEXT: Nevado del Ruiz is a stratovolcano located in the central part of Colombia. It is considered one of the most active and dangerous volcanoes in the country, with a history of generating destructive lahars and pyroclastic flows. In this article, we will delve into the facts and information about the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
THE EXPLANATION:
Geographical Location and Composition
- Nevado del Ruiz is situated in the Andes mountain range, approximately 129 km (80 mi) from the capital city of Bogotá. It is part of the Los Nevados National Natural Park, which is home to other volcanic peaks and glaciers.
- The volcano’s composition consists of layers of lava, volcanic ash, and pyroclastic rocks, which have built up over approximately two million years of volcanic activity.
Types of Eruptions and Hazards
- The Nevado del Ruiz volcano has a history of generating explosive eruptions, ranging from Vulcanian to Plinian. The eruption in 1985 caused the deadliest lahar in recorded history, known as the Armero tragedy.
- The lahar, which was triggered by the melting of snow and ice on the volcano’s summit during the eruption, swept away the town of Armero and claimed the lives of over 23,000 people.
Current Status and Risk Assessment
The Volcanic and Seismic Observatory of Manizales constantly monitors the Nevado del Ruiz volcano. The current status of the volcano is an orange alert due to an increase in seismic activity, which indicates a heightened risk of volcanic activity. Up to 500,000 people could be at risk from lahars and other hazards in the event of future eruptions.
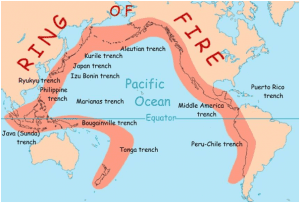
The Ring of Fire
Nevado del Ruiz is situated in the Ring of Fire, a belt of intense seismic activity that encircles the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire is known for its numerous active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
5. WHAT IS UTKALA DIBASA?
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Odisha Day, also known as Utkala Dibasa, is a significant day for the Indian state of Odisha. Celebrated on 1 April every year, the day commemorates the formation of the state as a separate entity out of Bihar and Orissa Province. This article delves deeper into the history behind Odisha Day and how it has become an essential part of the state’s cultural identity.
THE EXPLANATION:
Origins of Odisha Day
- Odisha’s history dates back to ancient times when it was known as Kalinga. It was ruled by several dynasties, including the Mauryas, Satavahanas, and Guptas. However, the state lost its political identity completely in 1568 after the defeat and demise of the last king, Mukunda Dev. For centuries, Odisha was ruled by different empires, including the Mughals and the British.
- In the early 20th century, Odisha witnessed a linguistic movement that aimed to establish a separate province based on the Odia language. The movement culminated in the formation of a separate state under British rule on 1 April 1936.
The Main Revolution
- The main revolution in this separate state continued for three decades, starting from the very day of the formation of Utkal Sammilani. The movement turned more intense under the leadership of Utkala Gouraba Madhusudan Das and other notable leaders such as Utkala mani Gopabandhu Das, Maharaja SriRam Chandra Bhanj Deo, and more.
- The leaders fought for the rights and development of Odisha and its people. They demanded a separate province based on the Odia language, which would help preserve and promote the state’s rich culture and heritage. Their efforts led to the creation of a politically separate state on April 1, 1936.
Role of the Public
The public played a significant role in supporting the leaders during the Odisha movement. They participated in protests, rallies, and demonstrations, demanding a separate state for Odisha. Their support and solidarity gave the leaders the strength and motivation to continue the struggle for their rights.