TOP 5 TAKKAR NEWS OF THE DAY (9th JANUARY 2023)
HEALTH ISSUES
1. LECANEMAB APPROVED FOR ALZHEIMER’S TREATMENT
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-II- HEALTH ISSUES
THE CONTEXT: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved lecanemab, a monoclonal antibody developed by Eisai and Biogen, for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Lecanemab is the second drug to receive approval for the treatment of Alzheimer’s and the first to slow cognitive decline in a clinical trial. However, the approval process has been controversial, with patient deaths and accusations that the FDA acted improperly when approving the first such drug, aducanumab.
Alzheimer’s Disease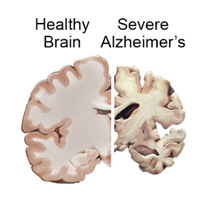
- Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by the accumulation of amyloid beta protein in the brain, leading to the formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.
- These abnormalities cause damage and death to brain cells, leading to memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. There is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s, and treatment options are limited to therapies that aim to slow the progression of the disease and improve symptoms.
Lecanemab
- Lecanemab is a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid beta protein. By binding to and neutralizing this protein, lecanemab aims to reduce the formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. In a clinical trial involving 1,800 patients with early-stage Alzheimer’s, lecanemab slowed cognitive decline by 27% over 18 months of treatment.
- The drug is administered intravenously and is intended to be used in the early stages of Alzheimer’s to allow individuals to “have more time to participate in daily life and live independently,” according to Joanne Pike, President and CEO of the Alzheimer’s Association in Washington DC.
Approval Process
- Lecanemab received approval through the FDA’s “accelerated approval” pathway, which is reserved for therapies for diseases with few treatment options and does not require phase III clinical trial data.
- However, lecanemab was granted approval on the basis of phase II data, rather than the more comprehensive phase III data, which were published in November 2021. The phase III data showed that lecanemab slowed cognitive decline by 27% in a clinical trial involving 1,800 patients with early-stage Alzheimer’s. The phase II data showed that lecanemab reduced plaques in the brains of 856 patients, but did not assess the effect on cognitive abilities.
Controversy
- The approval of lecanemab has been controversial, with some questioning the decision to grant approval on the basis of phase II data and concerns about patient deaths. Three patients enrolled in the lecanemab phase III trial died during the extended phase of the trial, when patients receiving placebo can ask to be given the drug.
- The deaths were attributed to complications involving brain bleeding and seizures, and researchers suspect that the antibody may have weakened blood vessels in the brain as it attacked amyloid plaques. All of the patients were taking anticoagulant drugs at the time of their deaths, and the FDA has stated that lecanemab should not be used in patients taking these medications.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
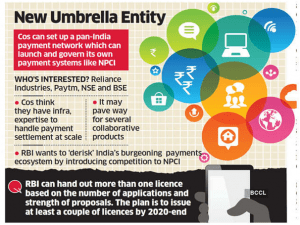
2. NEW UMBRELLA ENTITY (NUE) NETWORK
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS-III- BANKING
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is said to have put on hold licensing of the New Umbrella Entity (NUE) network, a fintech institution planned as a rival to the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
THE EXPLANATION:
Six groupings, which included Facebook, Google, Amazon, Flipkart and others, had applied for NUE licences and all of them have fallen short of the RBI’s expectations.
What is New Umbrella Entity (NUE)?
- As envisaged by the RBI, an NUE will be a non-profit entity that will set up, manage and operate new payment systems, especially in the retail space such as ATMs, white-label PoS; Aadhaar-based payments and remittance services.
- The entity formed shall be a company incorporated in India under the Companies Act, 2013. Currently, the umbrella entity for providing retail payments systems is NPCI, which is a non-profit entity, owned by banks.
- Promoters: A promoter will hold at least 25% and up to 40% of the operator. Only those entities that are owned and controlled by Indian citizens with at least three years of experience in the payments segment can become promoters of NUEs.
- Foreign investment: Foreign companies can own a maximum of 25%, so are teaming up with local players.
- Capital required: According to the RBI guidelines, the entity will have minimum paid-up capital of Rs 500 crore, with no single promoter group holding over 40 per cent investment in the capital.
- Governance structure: The new entity will have to abide by corporate governance norms and the ‘fit and proper’ criteria for persons to be appointed to the board.
ENVIRONMENT- INFRASTRUCTURE
3. FLOATOVOLTAICS
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS-III-ENVIRONMENT- ENERGY RESOURCES
THE CONTEXT: Covering 10% of the world’s hydropower reservoirs with ‘floatovoltaics’ would install electrical capacity equivalent to that provided by all electricity-generating fossil fuel plants in operation worldwide.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Floatovoltaics, floating solar plants, or FSPV (floating solar photovoltaic) are panel structures that are installed on water bodies like lakes, basins, and reservoirs instead of on solid structures like a roof or terraces.
- The biggest impetus behind the rise of large-scale FSPV has been that it doesn’t take up any land space, which could be then used for construction and agriculture.
The world’s first large-scale FSPV system was installed in 2011, in Napa Valley, California.
India:
- In recent years, floating solar power plants have become part of India’s plans of solar expansion.
- According to a 2020 study by TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute) reservoirs cover 18000 square Kilometer in India and can generate 280 GW through floating solar panels.
- Currently less than 1% of solar installations are floating.

- The largest floating solar power plant in India is currently the Ramagundam in Peddapalli district of Telangana, with a capacity of 100 MW.
- Currently a plant is being built on the Narmada’ Omkareshwar Dam in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh is being built with a capacity of 600 MW, which will soon be the largest floating solar power plant in the world.
What are the benefits of floating solar panels?
- The water’s cooling effect makes them more efficient than land-based ones;
- They don’t interfere with desert ecosystems; and
- They keep precious water from evaporating.
- Even though reservoirs are artificial ecosystems, they provide habitats for wildlife.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES IN NEWS
4. ‘SPRINT’ INITIATIVE
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GOVERNMENT SCHEMES
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Navy has recently announced a collaboration with Sagar Defence Engineering Private Limited for the development of armed autonomous boat swarms as part of the “SPRINT” initiative.
THE EXPLANATION:
- It was launched by Prime Minister in July 2022, SPRINT (Supporting Pole-Vaulting in R&D through Innovations for Defence Excellence) aims to promote the development and usage of indigenous defense technologies by domestic companies. The task of developing this technology is one of the 75 challenges introduced by the Indian Navy under the “Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav” celebrations.
India’s First Armed Autonomous Unmanned Boat
- Sagar Defence Engineering has stated that it possesses the know-how to develop India’s first armed autonomous unmanned boat with swarming capabilities. According to the company, the platform will be able to conduct a variety of navy and security tasks, including high-speed interdiction, surveillance, constabulary operations, and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
Indian Navy Plans to Order 12 Systems
- The collaboration with Sagar Defence Engineering is the 50th contract signed under the SPRINT initiative, and the Indian Navy plans to place an order for 12 systems once the construction of the weaponized autonomous unmanned boat is completed. The agreement is part of the Defense India Start-up Challenge (DISC 7) SPRINT initiative.
SPRINT Initiative Aims to Induct 75 New Technologies by 2023
- As part of the “Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav” celebrations and in an effort to achieve self-reliance in defense, the Naval Innovation and Indigenisation Organisation (NIIO) aims to induct at least 75 new indigenous technologies/products into the Indian Navy through the SPRINT initiative.
- In March 2022, the Indian Navy also signed a memorandum of understanding for a knowledge partnership with BharatShakti.in and the Society for Indigenous Defence Manufacturing (SIDM) as a step towards encouraging innovation and self-reliance in defense in the country.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. PARSHURAM KUND FESTIVAL
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Arunachal Pradesh government informed that Parshuram Kund Festival (PKF), is to be celebrated from 12 to 16 January 2023.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Parshuram Kund Festival:
- It is a Hindu pilgrimage site situated on the Brahmaputra plateau in the lower reaches of the Lohit River and 21 km north of Tezu in the Lohit district of Arunachal Pradesh, India.
- Devotees and sadhus take a holy dip in its water each year on the occasion of Makar Sankranti, in January.
- It is also known as the Kumbh of the Northeast.
- Religious significance: It is dedicated to a mythological figure sage Parshuram. This popular festival attracts pilgrims from Nepal, from across India, and from nearby states of Manipur and Assam.
- The project “Development of Parasuram Kund is sanctioned under the Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive’ (PRASHAD) Scheme of the Ministry of Tourism.