Today’s Important Articles for Geography (03-01-2023)
Today’s Important Articles for Sociology (03-01-2023)
Today’s Important Articles for Pub Ad (03-01-2023)
- Ayes and nays: On remote EVMs for domestic migrants READ MORE
- Rethinking the Muslim law of inheritance: Why Muslims should rightfully be able to give their daughters an equal share in their properties through a will READ MORE
- Decoding the note ban verdict READ MORE
- Legal teeth for data protection & privacy needed READ MORE
- Data Protection Bill Is Riddled With Arbitrary Provisions That Violate the Right to Privacy READ MORE
WSDP Bulletin (03-01-2023)
(Newspapers, PIB and other important sources)
Prelim and Main
- MeitY releases Draft amendments to the IT (Intermediary Guidelines & Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 in relation to online gaming READ MORE
- Majority verdict finds no flaw in 2016 demonetisation process READ MORE
- RBI tags SBI, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank as Systemically Important Banks READ MORE
- What is the new delimitation exercise by Assam? READ MORE
- A new coronavirus variant on the block READ MORE
- For first time in many years, no rhinos poached in Assam in 2022 READ MORE
- States may push for debate on central schemes, cesses READ MORE
- Horn of Africa: 20 million children at risk of disease, thirst, starvation, says UNICEF READ MORE
Main Exam
GS Paper- 1
- For a new paradigm of growth: Groundwater crises of Arizona and Punjab show how things have gone wrong READ MORE
- Need to address root-causes of domestic violence READ MORE
- Women: Education, employment, empowerment READ MORE
GS Paper- 2
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
- Ayes and nays: On remote EVMs for domestic migrants READ MORE
- Rethinking the Muslim law of inheritance: Why Muslims should rightfully be able to give their daughters an equal share in their properties through a will READ MORE
- Decoding the note ban verdict READ MORE
- Legal teeth for data protection & privacy needed READ MORE
- Data Protection Bill Is Riddled With Arbitrary Provisions That Violate the Right to Privacy READ MORE
SOCIAL ISSUES
- Why EWS reservation defeats the purpose of reservation READ MORE
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
- India’s dilemmas in an Asian century: For status quoist India, the rise of the Asian century might turn out to be too seeped in harsh realpolitik for its comfort READ MORE
- Why China is happy with Nepal’s new PM READ MORE
- China’s growing influence in Nepal means India’s diplomacy and project delivery will need to improve READ MORE
- India must counter China economically READ MORE
GS Paper- 3
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
- GST buoyancy: On GST revenues in December READ MORE
- Demonetisation verdict: Six years later, farce after tragedy READ MORE
- It’s time to consider a wealth tax that may lessen Indian inequality READ MORE
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
- Loss of biodiversity and the new Global Biodiversity Framework READ MORE
SECURITY
- Combating the menace of narcotics consumption READ MORE
GS Paper- 4
ETHICS EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDY
Questions for the MAIN exam
- ‘Data Protection Bill is riddled with arbitrary provisions that violate the Right to Privacy’. Examine.
- ‘As the gap between women’s education and women’s employment continues to widen, the question arises if women are truly being empowered’. In light of the statement discuss how the discrimination against women at the workplace can be addressed?
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
- The growth and development of people is the highest calling of leadership.
- While the Bill takes several commendable steps to ensure that it complies with global standards of data protection, it nevertheless suffers from several infirmities that render its constitutionality questionable.
- A greater engagement with Constitution in our everyday workplaces and social conversations will go a long way in refining our understanding of the Constitution – so that in this upcoming cultural collision if you will, there is a collective sense of the constitutional idea of India.
- As the gap between women’s education and women’s employment continues to widen, the question arises if women are truly being empowered.
- Reservation on the basis of economic disadvantage can only be justified if the provision or policy attempts to eliminate the ingrained economic disadvantages that welfare measures cannot address.
- While the impact of domestic violence on the victim is worrisome, it can also have a traumatic effect on witnesses, especially kids.
- The pursuit of relentless growth of global and national GDP has become cancer that is sucking water out of the Earth.
- For status quo India, the rise of the Asian century might turn out to too seep in harsh realpolitik for its comfort
- Even the ECI had expressed doubts about the practicality of remote voting rights for migrants in the past. Meanwhile, there is also an active demand for voting rights for Non-Resident Indians. Higher turnout is worth striving for, but not without sufficient safeguards.
- Laws are an imperfect solution to social problems, but to clearly, loudly and unambiguously say something is not okay signifies something beyond itself. Some lines must be drawn, even if in the sand.
- As India debates the latest border clashes with China, Delhi should keep in mind that China has moved to security over economics mode, making a Chinese compromise less likely.
- A scheme such as MGNREGS needs to evolve while keeping its core idea of a demand-driven work allocation intact. Treating it as a burden will only hurt genuine beneficiaries.
ESSAY TOPIC
- The growth and development of people is the highest calling of leadership.
- Best way to predict future is to create it READ MORE
50-WORD TALK
- India’s China challenge has to be managed through trade and investment rather than by flexing military and diplomatic muscles. India has a diplomatic advantage over China because it is a more westernised country. But India has to find a more substantial way to deal with China, which lies in the economic sphere. India has to carve out its own niche in world affairs, but without using China as a reference point.
- We should gauge the import of the word ‘digital’ added to the present Data Protection Bill. In the digital realm, the magic is created by servers and phones. So, secure and robust data empowerment will happen if loopholes of both are plugged. Cyberspace and telecom platforms should have an overarching regulatory body. To begin with, the Grievance Appellate Committee can be merged with the Data Protection Board.
Things to Remember:
- For prelims-related news try to understand the context of the news and relate with its concepts so that it will be easier for you to answer (or eliminate) from given options.
- Whenever any international place will be in news, you should do map work (marking those areas in maps and exploring other geographical locations nearby including mountains, rivers, etc. same applies to the national places.)
- For economy-related news (banking, agriculture, etc.) you should focus on terms and how these are related to various economic aspects, for example, if inflation has been mentioned, try to relate with prevailing price rises, shortage of essential supplies, banking rates, etc.
- For main exam-related topics, you should focus on the various dimensions of the given topic, the most important topics which occur frequently and are important from the mains point of view will be covered in ED.
- Try to use the given content in your answer. Regular use of this content will bring more enrichment to your writing.
TOP 5 TAKKAR NEWS OF THE DAY (3rd JANUARY 2023)
INDIAN POLITY
1. DEMONETISATION VERDICT
TAGS: GS-II- INDIAN POLITY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, The Constitution bench of the Supreme Court in the majority opinion (4:1) upheld the Union Government’s demonetization order of 8th November 2016 to demonetize currency notes of Rs 500 and Rs 1,000.
THE EXPLANATION:
The majority of judges (4:1) accepted all arguments of the Union Government
- Section 26(2) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 gives the Union government the power to demonetize currency “on the recommendation of the Central Board” of the RBI.
- The majority view found that the word ‘recommendation’ would mean a consultative process between the Central Board and the Central Government.”
- The judges highlighted that it cannot be expected that the RBI and the Central Government acted in two isolated boxes. An element of interaction/consultation in such important matters cannot be denied.
- The majority verdict states that curbing fake currency, black money and terror funding are legitimate interests of the state and have a rational nexus with demonetization.
- The court said that the Centre is the best judge since it has all the inputs about fake currency, black money, terror financing & drug trafficking.
- The majority stated that the court cannot determine the effectiveness of the economic policy. It agreed with the Centre’s contention that the decision had to be made in secrecy and haste for it to be effective.
Justice B V Nagarathna disagreed with the reasoning and conclusions in the majority opinion
- The Justice stated that demonetization was a violation of Section 26(2) of the RBI Act as the recommendation for the demonetization originated from the Centre and not the RBI’s Central Board.
2. AMENDMENT RELATED TO ONLINE GAMING
TAGS: GS-II- INDIAN POLITY & GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology proposed an amendment to bring online gaming under the regulations of the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
The proposed model is similar to the rules in place for digital news sites and streaming services under the IT Rules, 2021.
- The Ministry highlighted that the proposed framework will;
o Boost the legitimate domestic online gaming industry.
o Ensure greater transparency.
o Promote Consumer protection and investor confidence. - The All India Gaming Federation (AIGF) stated that it would reduce the State-wise regulatory fragmentation that was a big challenge for the industry.
Online Gaming Market in India
- A 2019 survey by the U.S.-based Limelight Networks found that India had the second-largest number of gamers after South Korea.
- The revenue of the Indian mobile gaming industry is expected to exceed $1.5 billion in 2022 and is estimated to reach $5 billion in 2025.
- The industry in the country grew at a CAGR of 38% between 2017-2020, as opposed to 8% in China and 10% in the US.
- It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% to reach Rs 153 billion in revenue by 2024. India’s percentage of new paying users (NPUs) in gaming has been the fastest growing in the world for two consecutive years, at 40% in 2020 and reaching 50% in 2021.
- According to a report by the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI), transaction-based games’ revenues grew 26% in India, with the number of paying gamers increasing by 17% from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021.
ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
3. ONE-HORNED RHINOS
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-III- ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Assam Chief Minister has recently announced that no rhinos were poached in the state in 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
Rhino Population
The park’s Rhino population has also increased. Under the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020), the Assam government decided to reintroduce rhinos in Manas National Park in 2005, and the first rhino was translocated to the park in 2006, from the Centre for Wildlife Rehabilitation and Conservation (CWRC) near Kaziranga National Park.
ABOUT ONE-HORNED RHINOS:
- Only the Great One-Horned Rhino is found in India.
- Also known as the Indian Rhino, it is the largest of the rhino species.
- It is identified by a single black horn and grey-brown hide with skin folds.
- They primarily graze, with a diet consisting almost entirely of grasses as well as leaves, branches of shrubs and trees, fruit, and aquatic plants.
- Conservation status:
- CITES Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I.
Types of Rhinos:
The Greater One-Horned Rhino is one among the five different species of Rhino. The other four are:
- Black Rhino: Smaller of the two African species. (IUCN: Critically Endangered)
- White Rhino: Recently, researchers have created an embryo of the northern white Rhino by using In-vitro Fertilization (IVF) process. (ICUN: Near Threatened)
- Javan Rhino: Critically endangered in IUCN Red List.
- Sumatran Rhino: Recently gone extinct in Malaysia, but Critically Endangered in IUCN Red List.
About Manas National Park
- Manas National Park is situated on the bank of the river men at the foothills of the Himalayas. The beautiful park is earlier known as North Kamrup wildlife sanctuary is spread over an area of 519.77 sq km and was declared a sanctuary on December 01, 1928. It was established as the core of the Manas Tiger Reserve in April 1973 and elevated to the position of a National Park status on September 7, 1990.
- The wildlife species found in the national park are Hispid Hare, Pigmy Hog, Golden Langur, Indian Rhinoceros, Asiatic Buffalo etc. Other commonly seen animals are elephants, Leopard, Clouded Leopard, Himalayan bears, Wild boars, Samber, Swamp Deer, Hog Deer etc.
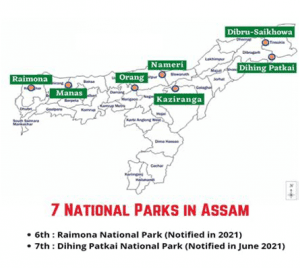
VALUE ADDITION:
INDIAN RHINO VISION 2020 (IRV 2020)
- Launched in 2005.
- The initiative is led by the Forest Department, Government of Assam, in partnership with WWF India, the International Rhino Foundation.
- The goal of IRV2020 was to increase the rhino population in Assam to 3,000by, by establishing populations in new areas.
- Rhinos are now found in four Protected Areas in Assam: Pobitora Wildlife Reserve, Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, Kaziranga National Park, and Manas National Park.
4. NEW TECHNOLOGY TO FILTER MICRO-PLASTICS FROM WATER
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-III- ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Scientists from South Korea have developed a new water purification system that can quickly and efficiently filter out microplastics. Crucially, the polymer used is relatively inexpensive with excellent adsorption performance and good photothermal properties.
THE EXPLANATION:
- In an experiment, over 99.9 per cent of contaminants were taken out of the water in just 10 seconds.
- Microplastics have inundated the world, finding their way into the human food chain . While some traditional carbon-based filters can filter out microplastics, they have limitations — the adsorption rate is slow and they are not energy-efficient.
- The Korean team’s breakthrough system requires lower levels of energy, making it ideal for solar-based use. This is particularly useful for developing countries where power supply is inconsistent.
The Problem of Microplastics in Water
- Microplastics, tiny plastic particles that are less than 5mm in size, have become a global problem. They have been found in water bodies, soil, and air, and have even made their way into the human food chain.
- The presence of microplastics in water can have negative impacts on aquatic life and potentially on human health.
VALUE ADDITION:
Measures taken by government:
- India has pledged to ban all single-use plastics by 2022.
- All offices of central and state governments and major PSUs have been told to prohibit single-use plastic products.
- India has banned imports of solid plastic waste.
- India has passed the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 and introduced the Extended Producer Responsibility.
Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- It aims to increase minimum thickness of plastic carry bags from 40 to 50 microns.
- Expand the jurisdiction of applicability from the municipal area to rural areas, because plastic has reached rural areas also.
- Extended Producer Responsibility: To bring in the responsibilities of producers and generators, both in plastic waste management system and to introduce collect back system of plastic waste by the producers/brand owners, as per extended producers responsibility
- Introduced collection of plastic waste management fee through pre-registration of the producers, importers of plastic carry bags/multilayered packaging and vendors selling the same for establishing the waste management system
- Promote use of plastic waste for road construction as per Indian Road Congress guidelines or energy recovery, or waste to oil etc. for gainful utilization of waste and also address the waste disposal issue.
GOVERNMENT INTERVENTIONS
5. ‘SMART’ (SCOPE FOR MAINSTREAMING AYURVEDA RESEARCH IN TEACHING PROFESSIONALS) PROGRAM
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS-II- GOVERNMENT INTERVENTIONS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM) and Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS) under Ministry of Ayush launched ‘SMART’- scope for mainstreaming ayurveda research in teaching professionals programme.
THE EXPLANATION:
About ‘SMART’ (Scope for Mainstreaming Ayurveda Research in Teaching Professionals) Program:
- It is aimed to boost scientific research in priority healthcare research areas through Ayurveda colleges and hospitals.
- The proposed initiative is conceptualised with an objective to identify, support and promote innovative research ideas in healthcare research areas including Osteoarthritis, Iron Deficiency Anaemia, Chronic Bronchitis, Dyslipidemia, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Psoriasis, Generalised Anxiety Disorder, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- The eligible Ayurveda academic institutions may apply by 10 January, 2023.
- All details regarding contact information, eligibility criteria and application process has been shared to all recognized academic institutions and hospitals through NCISM.
- The ‘SMART’ program will motivate teachers for taking up projects in designated areas of healthcare research and create a large database.
Day-351 | Daily MCQs | UPSC Prelims | POLITY
[WpProQuiz 396]
TOPIC : THE LAUNCH OF 5G IN INDIA: ADVANTAGES AND CHALLENGES
THE CONTEXT: 5G, the next-generation network service was launched in India by the Prime Minister at the sixth edition of India Mobile Congress (IMC) held on 1 October 2022 in New Delhi. With the launch of 5G services, India joins the list of around 70 countries with the next generation of the telecom standards.
ABOUT 5G TECHNOLOGY FOR MOBILE DEVICES.
BASICS: 5G cellular networks are up to 100 times faster than 4G. Faster connectivity speeds, ultra-low latency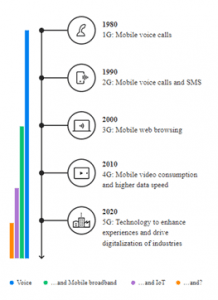 (time taken between performing an action and getting a response) and greater bandwidth are helping in advancing societies, transforming industries and enhancing day-to-day experiences.
(time taken between performing an action and getting a response) and greater bandwidth are helping in advancing societies, transforming industries and enhancing day-to-day experiences.
5G EVOLUTION:
- The 1G era was defined by briefcase-sized phones and short conversations between a relatively small number of professional people.
- During 2G era, the demand for mobile services grew and never slowed down.
- Phones that could fit in your pocket, SMS and mobile internet access were hallmarks of the 3G world.
- 4G is the era of smartphones, app stores and YouTube.
- 5G will completely reshape both our professional and personal lives by enabling new use cases like connected vehicles, Augmented Reality and enhanced video and gaming.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN 4G AND 5G MOBILE NETWORK TECHNOLOGY
4G TECHNOLOGY
- Uses lower reading frequencies of 700 MHz to 2500 MHz.
- Low speed with less data transfer.
- Latency: the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction.
- Higher latency as compared to 5G that is about 20-30 milliseconds.
- Supports a lesser number of devices (about 4,000 devices per square kilometre).
- Has led to more congestion and lesser coverage.
5G TECHNOLOGY
- Uses much higher radio frequencies of 28 GHz.
- Faster speeds with more data transfer.
- Has lower latency which is predicted to be below 10 milliseconds, and in best cases around 1 millisecond.
- Uses a millimetre-wave spectrum which enables more devices to be used within the same geographic area supporting around one million per square kilometre.
- It uses a new digital technology that improves coverage, speed, and capacity.
5G NETWORK ARCHITECTURE: A mobile network has two main components, the ‘Radio Access Network’ and the ‘Core Network’.
The Radio Access Network:
- It consists of various types of facilities, including small cells, towers, masts and dedicated in-building and home systems that connect mobile users and wireless devices to the main core network.
- Small cells will be a major feature of 5G networks, particularly at the new millimetre wave (mmWave) frequencies where the connection range is very short. To provide a continuous connection, small cells will be distributed in clusters depending on where users require connection which will complement the macro network that provides wide-area coverage.
- 5G Macro Cells will use MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) antennas that have multiple elements or connections to send and receive more data simultaneously. The benefit to users is that more people can simultaneously connect to the network and maintain high throughput.
The Core Network: It is the mobile exchange and data network that manages all of the mobile voice, data and internet connections. For 5G, the ‘core network’ is being redesigned to better integrate with the internet and cloud based services and also includes distributed servers across the network improving response times (reducing latency). Many of the advanced features of 5G including network function virtualization and network slicing for different applications and services, will be managed in the core. The pictorial representation given below shows local cloud servers providing faster content to users and low latency applications for vehicle collision avoidance systems.
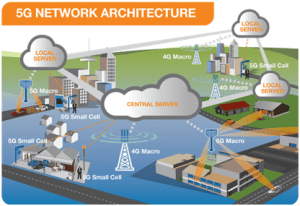
Example of a local server in a 5G network providing faster connection and lower response times
- Network Slicing: enables a smart way to segment the network for a particular industry, business or application. For example emergency services could operate on a network slice independently from other users.
- Network Function Virtualization (NVF): It is the ability to instantiate network functions in real-time at any desired location within the operator’s cloud platform. NVF is crucial to enable the speed, efficiency and agility to support new business applications and is an important technology for a 5G ready core.
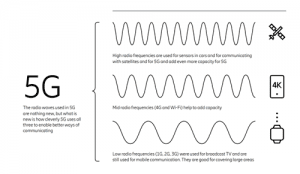
Different Bands of 5G
5G primarily operates across three bands: low, mid, and high-frequency spectrums, each with its benefits and drawbacks.
- Low Band Spectrum: The maximum speed of Internet and data exchange is limited to 100 Mbps in terms of coverage and speed (Megabits per second). This means that telecom companies can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high-speed Internet. However, the low band spectrum may not be optimal for the industry’s specialised needs.
- Mid-Band Spectrum: It has faster speeds than the low-band spectrum, but it has restrictions regarding coverage area and signal penetration. Industries and specialised production units could utilise this band to create captive networks that can be tailored to their specific demands.
- High Band Spectrum: The fastest speed of all three bands, but its coverage and signal penetration intensity are severely limited. This band significantly improves future 5G technology applications such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and innovative technologies, although it has significant infrastructure requirements.
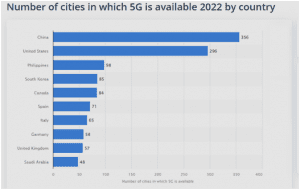
5G AROUND THE WORLD: Since being launched in 2019, 5G is introduced in around 70 countries as of June 2022. China and the United States are the countries with the most 5G cities. But on a regional basis, the Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) region has surpassed the Asia Pacific region (including China) in terms of deployed 5G networks. The graph given below depicts the countries with the most number of cities with 5G technologies in the world.
ADVANTAGES OF 5G TECHNOLOGY:
- With very high speed, 5G allows access to high-bandwidth multi-media such as HD videos, movies and games, which can be downloaded in seconds.
- It enables high-speed data services that have industrial applications and also supports critical applications like financial transactions and healthcare.
- It will help incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) into our daily lives. It will enable cloud systems to seamlessly stream software updates, music, and navigation data to driverless cars. It will also facilitate vehicle-vehicle communications to keep a safe distance from each other leading to fewer car accidents and less traffic congestion.
- Broadband Internet of Things (IoT) takes things up a level.This will allow for: The use of drones for everyday activities such as the delivery of retail goods or medical supplies; Tracking of traffic patterns in relation to an organisation’s delivery schedules; Smarter electricity grids for greatly reduced carbon emissions.
CHALLENGES FOR THE ADOPTION OF 5G TECHNOLOGY FOR INDIA
DIGITAL DIVIDE
- 5G will not necessarily bridge the digital divide among the rural and urban areas in the short term, rather increase it as the business case of 5G, even in urban areas does not have maximum accessibility. Therefore, it will not be easily available in rural areas too.
SECTOR-SPECIFIC
- The rollout of 5G technology will be different from the one seen in 4G; it will be introduced in specific sectors and areas in the initial phases and will be a niche service unlike 3G and 4G, which were pervasive services. 5G will get intensified over a comparatively longer period of time.
INROADS OF 4G
- The consumers are still grappling with basic network issues like call drops and interrupted data services. We still have areas where 4G networks have not stabilised causing frequent disruptions in internet services. It is important to meet the quality of service parameters of existing 4G networks before embarking on a new 5G platform.
CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE
- 5G will require a fundamental change to the core architecture of the communication system. The major flaw of data transfer using 5G is that it can’t carry data over longer distances. Hence, even 5G technology needs to be augmented to enable infrastructure.
GOVERNMENT SUBSIDIES
- The likelihood of government subsidies is low as is evident from the history of high reserve prices set by the governments for spectrum auctions amid ongoing fiscal deficits.
FINANCIAL LIABILITY
- For the transition from 4G to 5G technology, one has to upgrade to the latest cellular technology, thereby creating financial liability on consumers as well as service providers.
CAPITAL INADEQUACY
- Lack of adequate capital with suitable telecom companies (like Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea) is delaying the 5G spectrum allocation.
THREATS FROM THE 5G TECHNOLOGY
DATA HACKING
- The increased risk of hacking of data is one of the immediate concerns of 5G. Hackers can use mobile and external IP networks for spying and stealing data.
- The use of common Internet protocols such as HTTP and TLS in 5G also lowers the entry barrier for hackers. This could be a potential means for cyberattacks.
- The risk also increases as more and more poorly secured IoT devices are used.
NATIONAL SECURITY
- From a national security perspective, potential targets in 5G networks include critical information infrastructure (CIIs) and mission-critical and nationally important networks.
- The proliferation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) – commonly known as drones – is a sure-shot consequence of the 5G rollout. The threat of automotive cyber-attacks through 5G networks will also rise.
INTERFERENCE WITH AIR TRAFFIC
- 5G also interferes with airplanes’ radio altimeters, which give readings of the height above the ground during a flight’s approach. This is critical during poor visibility and for aircraft flying at low altitudes.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- Domestic production and internal security:
- Domestic procurement shall be made mandatory for all 5G equipment. The inclusion of 5G in the PLI scheme will also enable domestic procurement.
- India needs to adopt the requisite standard for 5G services to address security concerns. The Mandatory Testing and Certification of Telecommunication Equipment (MTCTE), under which Indian OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) get certified by the government, should be extended to 5G equipment as well.
- To encourage that the spirit of Atmanirbhar Bharat is followed when it comes to the 5G rollout, there is a need to work closely with startups/MSMEs, academia, telecom service providers and the industry in the setting up of R&D Centres.
- Bridging the Rural-urban Gap: The low band spectrum range is much longer, which is helpful in the long distance communications and for rural and far-off places. 5G shall be deployed at different band spectrums which will benefit the rural areas and enhance the wide coverage in lesser time.
- Band Spectrums: The government has complete control over the 5G band spectrum. By managing the design of the spectrums, the government can control the price to be paid by the people. The government can also support the telecom companies to roll out networks that are sustainable and affordable for the public.
- As the deployment of the 5G network is expensive, both the Central and State governments may need to consider measures that aid fibre investment, attract investment through public-private partnerships (PPPs), and facilitate investment funds on a nominal interest basis. The government shall also consider allowing 100% foreign direct investment in the telecom sector along with other policy reforms which will attract investment into the sector.
- Level playing field: The imminent 5G networks demand massive investment and upgradation of sophisticated operations. A level playing field for the relevant operators and honest incentives shall be provided to operators to embrace new technology.
THE CONCLUSION: 5G Technology has ushered in a new era in the technology sector around the world. As far as the nationwide deployment of the technology is concerned, India still has a long way to go. Bringing down the spectrum prices and bridging the rural-urban gap by increasing the accessibility of networks to hinterlands are a few key areas which the government shall focus upon from making the technology a niche.
Mains Practice Questions:
- Discuss the advantages and challenges of 5G technology for India.
- With the advent of the 5G technologies, the data is at risk. What measures the government should adopt for the protection of critical data?