DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (NOVEMBER 16, 2022)
HEALTH ISSUES
1. EXPERIMENTAL ALZHEIMER’S DRUG FROM ROCHE FAILS IN TRIALS
THE CONTEXT: According to a study by the pharmaceutical company, the Roche’s Alzheimer’s drug candidate could not be shown to slow dementia progression in two drug trials.
THE EXPLANATION:
The study
- According to the twin studies, known as Graduate 1 and 2, had not reached their main goal of showing that the drug gantenerumab could preserve abilities such as remembering, solving problems, orientation and personal care in patients suffering from early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The Swiss drugmaker conducted two identically designed studies, each with about 1,000 participants, who were examined and queried by physicians over more than two years. Within each study, volunteers were randomly assigned to receive either the injectable antibody drug gantenerumab or a placebo.
- The drug was associated with a relative reduction in clinical decline of 8 per cent in Graduate 1 and 6 per cent in Graduate 2 compared with the placebo, but those results were not statistically reliable.
- Gantenerumab is a fully human IgG1 antibody designed to bind with subnanomolar affinity to a conformational epitope on Aβ fibrils. It encompasses both N-terminal and central amino acids of Aβ. The therapeutic rationale for this antibody is that it acts centrally to disassemble and degrade amyloid plaques by recruiting microglia and activating phagocytosis.
VALUE ADDITION:
Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that causes the brain to shrink (atrophy) and brain cells to die.
- The disease is the most common cause of dementia – a continuous decline in thinking, behavioural and social skills that affect a person’s ability to function independently.
Caused by: Alzheimer’s disease is thought to be caused by the abnormal build-up of proteins in and around brain cells.
- One of the proteins involved is called amyloid, deposits of which form plaques around brain cells.
- The other protein is called tau, deposits of which form tangles within brain cells.
Vulnerability: Alzheimer disease most commonly affects older adults, but it can also affect people in their 30s or 40s.
Cases:
- According to WHO estimates for 2017, dementia affects approximately 50 million people worldwide, a number that is projected to grow to 82 million by 2030.
- In India, it is estimated that 5.3 million people (1 in 27) above the age of 60 have dementia in 2020. This is projected to rise to 7.6 million by 2030.
SOCIAL ISSUES AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
2. UNITED NATIONS POPULATION FUND REPORT
THE CONTEXT: The United Nations recently revealed that the world population has reached 8 billion mark. India is the largest contributor to the milestone, having added 177 million people.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The UN also noted that China, which added 73 million people, the projection is its contribution to the next billion in the global population is to be in the negative. This means the most populous country would now contribute in negative to the world population.
- the UN’s World Population Prospects 2022 report has also specified tat eight countries will be the biggest contributors in the next billion mark population rise. This includes India, Pakistan, Egypt, Congo, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Philippines, and Tanzania.
- According to a report half of the population still lives in just seven countries: China, India, the US, Indonesia, Pakistan, Nigeria and Brazil. While the world’s population will continue to grow to around 10.4 billion in the 2080s, the overall rate of growth is slowing down.
- The UN warned that India may soon surpass China to become the most populated country in the world. However, the UN also stated that the population growth in India is stablising than understood previously.
- “The good news is that India’s population growth appears to be stabilising. The Total Fertility Rate — more or less the average number of children born per woman — has declined from 2.2 to 2.0 at the national level”.
- Population growth has become increasingly concentrated among the world’s poorest countries, most of which are in sub-Saharan Africa.
Good record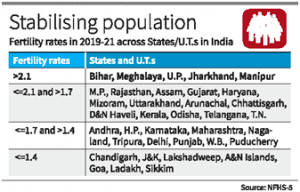
- A total of 31 States and Union Territories (constituting 69.7% of the country’s population) have achieved fertility rates below the replacement level of 2.1, it said.
- The main reasons for the decline in fertility include increase in adoption of modern family planning methods (from 47.8% in 2015-16 to 56.5% in 2019-21) and a reduction in unmet need for family planning by four percentage points over the same period. “This indicates significant improvements in access to family planning related information and services. In summary, it shows that India’s national population policies and health systems are working”.
- India is a youthful nation with the largest cohort of young people anywhere in the world, with major potential to achieve its demographic dividend. While many parts of the world are ageing, India’s youthful population can be a global resource to solve global problems.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
3. EAST TIMOR TO BECOME 11TH MEMBER OF ASEAN
THE CONTEXT: The AEAN members agreed in principle to admit East Timor as the 11th member of the bloc.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is ASEAN?
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional bloc founded on August 8, 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand. Its member states are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. East Timor was added as a new member of this regional grouping.
About East Timor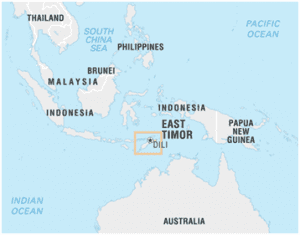
- Timor Leste or East Timor is a half-island nation in the eastern Lesser Sunda Islands. It is situated at the southern extreme of the Malay Archipelago. It occupies the eastern half of the Island of Timor. It is bounded by the Timor Sea to the southeast, the Wetar Strait to the north, the Ombai Strait to the northwest and the western Timor (part of Indonesian territory) to southwest.
- East Timor that was previously part of Indonesian territory. Indonesia occupied the island nation in 1976. Hundreds of thousands have died on the island while resisting the annexation of Indonesia. Due to the global pressure, the Indonesian government authorized a referendum in 1999 to determine future of East Timor. In the UN-supervised referendum, the country voted to secede from Indonesia. It was recognized by the United Nations in 2002. This makes it the youngest democracy in Asia.
East Timor and ASEAN
East Timor started applying for ASEAN membership in 2011. The ASEAN decided to admit the island nation as its 11th member more than a decade after Timor-Leste requested membership. This decision was made at Cambodia’s capital, Phnom Penh, where the 40th and 41st ASEAN and related summits officially began recently. East Timor was granted observer status at ASEAN meetings, including summit plenaries, until it is formally inducted into the regional bloc.
4. EAST ASIA SUMMIT
THE CONTEXT: Vice President recently addressed the East Asia Summit on the last day of his visit to Cambodia, as the three-day Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) summit concluded.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is the East Asia Summit?
- Beginning in 2005, 16 participating countries comprised this grouping, with their first meeting in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. These members were the 10 ASEAN countries,Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, and the Republic of Korea.
- ASEAN’s 10 member countries are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The United States and the Russian Federation joined at the 6th East Asia Summit in 2011.
- The EAS is an ASEAN initiative and refers to the annual Meeting of Heads of States/Governments of these countries, where they are able to discuss common concerns and interests
- Its creation was based on the idea of enhancing cooperation among East Asian countries and those in the neighbouring regions. Six priority areas of cooperation were identified – environment and energy, education, finance, global health issues and pandemic diseases, natural disaster management, and ASEAN Connectivity.
- In the past, the issues of claims over the South China Sea, the United Nations Convention on the Law Of the Sea, terrorism, the actions of North Korea and the conflict situation in Myanmar have been discussed by the countries.
What are the EAS’s links with India?
- This (2022) year marks the 30th anniversary of ASEAN-India relations and is being celebrated as the ASEAN-India Friendship Year.
- In a joint statement, ASEAN-India acknowledged the deep civilisational linkages, maritime connectivity, and cross-cultural exchanges between Southeast Asia and India which have grown stronger over the last 30 years, providing a strong foundation for ASEAN-India relations.
- Vice President announced an additional contribution of USD 5 million to the ASEAN-India science and technology fund to enhance cooperation in sectors of public health, renewable energy and smart agriculture.
- According to a 2021 statement by the Prime Minister’s website, “ASEAN-India Strategic Partnership stands on a strong foundation of shared geographical, historical and civilizational ties. ASEAN is central to our Act East Policy and our wider vision of the Indo-Pacific.”
ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
5. GLOBAL SHIELD AGAINST CLIMATE RISKS INITIATIVE
THE CONTEXT: The Global Shield Against Climate Risks initiative was launched on November 14, 2022 by the Vulnerable Twenty (V20) countries and G7 countries. While V20 countries represent 58 countries that are vulnerable to climate change, the G7 represent seven of the world’s most industrialized countries.
THE EXPLANATION:
About the initiative
- The Global Shield Against Climate Risks initiative was launched at the 27th Conference of Parties
 (COP27) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt.
(COP27) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt. - It is a social protection and insurance-based finance mechanism for loss and damage outside the UNFCCC process.
- It will provide pre-arranged financial aid that can be rapidly deployed to respond to disasters like the devastating flood that occurred in Pakistan in August 2022.
- It will help expand the financial protection instruments for governments, communities, businesses and households.
- These instruments will minimise the impacts of disasters by helping vulnerable economies become more resilient, ensure sustainable development and protect lives and jobs.
How will the initiative be implemented?
- The initiative will be implemented in a way that it aligns with the vulnerable country’s financial and economic strategies so that the financing gaps are removed. This initiative will support countries in ensuring livelihood protection, social protection systems, livestock and crop insurance, property insurance, business interruption insurance, risk-sharing networks and credit guarantees. The support will be provided at the level of government, humanitarian agencies and non-profits so that the finances are present whenever necessary.
- Pakistan, Bangladesh, Costa Rica, Fiji, Senegal, Philippines and Ghana will be the first to receive assistance under this initiative. The initial contributions for this initiative are provided Germany, Denmark, Ireland and Canada. The US, which is also part of this initiative, is providing funding for the African Risk Capacity – an insurance and disaster risk solutions company. Other countries like the UK and the international organizations like the UNDP and the UN Office of Disaster Risk Reduction are also backing this initiative.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES IN NEWS
6. POSOCO RENAMED AS “GRID CONTROLLER OF INDIA LIMITED”
THE CONTEXT: India’s national grid operator Power System Operation Corporation Limited (POSOCO) was renamed as Grid Controller of India Limited.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Grid Controller of India Limited (Grid-India)
- The Grid Controller of India Limited (Grid-India) is a wholly owned central government enterprise that comes under the aegis of the Ministry of Power.
- Previously, it was a fully owned subsidiary of the Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (Powergrid) – the central public sector undertaking (PSU) owned by the Union Power Ministry.
- It was set up in March 2009 to take care of the power management functions of the PGCIL.
- It was later made a separate company, with PGCIL being involved only in setting up transition link.
- Grid-India, as a separate company, was given the load despatch functions. It oversees the operations of the national load despatch centre (NLDC) and 5 regional load despatch centres (RLDCs). The NLDC is the apex body that ensures the integrated operation of national power system.
- Grid-India currently works as the nodal agency for major reforms in the power sector like the implementation and operation of Green Energy Open Access Portal, Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) Mechanism, transmission pricing, short-term open access in transmission, deviation settlement mechanism, Power System Development Fund (PSDF) and others.
Why was the name changed?
- The name was changed to reflect the important role played by the grid operators in ensuring integrity, reliability, resilience and sustainable operation of the Indian electricity grid. It also points to the unique position held by the Grid-India in connecting people to energy they use. The name reflects the functions performed by the grid managers in India at the national and state levels.
- It also explains the role played by the Grid-India in the country’s transition towards renewable energy. It also reflects the vision of the PSU to become a “global institution of excellence for reliable and resilient power systems, fostering efficient electricity markets, promoting economy and sustainability”.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTION
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. Consider the following statements about Atal Tunnel:
1. It is located near Baralacha La pass in Himachal Pradesh.
2. It provides all weather connectivity from Manali to Lahaul and Spiti valley.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
Atal Tunnel:
- It is located near Rohtang pass in Himachal Pradesh.
- It provides all weather connectivity from Manali to Lahaul and Spiti valley.