DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (OCTOBER 18, 2022)
SOCIAL ISSUES AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
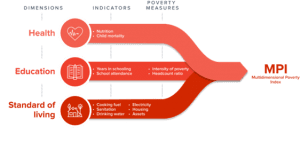
GLOBAL MULTIDIMENSIONAL POVERTY INDEX (MPI) 2022
THE CONTEXT: Recently a study was released by the research centre Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) which states that India is among many countries that have reduced poverty significantly faster.
REPORT HIGHLIGHTS:
- It is the first time that the report highlights a special section on India, giving information on 15 years of trends in the country.
- The number of poor people in India dropped by about 415 million over the last 15 years, the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index report has revealed. However, the country still has the highest number of poor people and children worldwide.
- About 71 per cent of the data for the country from the Demographic and Health Survey was obtained in 2019 before the pandemic and the rest in 2021.
- The poorest states reduced poverty the fastest and deprivations in all indicators fell significantly among poor people.
- Poverty among children fell faster, it indicated. However, India has the world’s highest number of poor children, amounting to a total of 97 million or about 21.8 per cent of the Indian children population between the ages 0 and 17 years.
- Half of the poor people in India, accounting for about 593 million are children under 18 years of age. This means that one in every three children lives in poverty compared to the one in seven ratio among adults.
- About 140 million exited poverty since 2015-16 as per the Demographic and Health Survey for India. Also, the MPI value and incidence of poverty more than halved from 0.283 in 2005-06 to 0.122 in 2015-16 and reduced again to 0.069 in 2019-21.
- Meanwhile, the incidence of poverty dropped from 55.1 per cent to 16.4 per cent over 15 years.
- Nationally, the relative drop between 2015-16 and 2019-21 was faster at the rate of 11.9 per cent annually compared with 8.1 per cent per year between 2005-06 and 2015-16.
About Global Multidimensional Poverty Index
Definition: The global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) is an international measure of acute multidimensional poverty covering over 100 developing countries.
- It complements traditional monetary poverty measures by capturing the acute deprivations in health, education, and living standards that a person faces simultaneously.
Developed by: The global MPI was developed by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) with the UN Development Programme (UNDP) for inclusion in UNDP’s flagship Human Development Report in 2010.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
HOW DOES TOKENISATION PREVENT ONLINE CARD FRAUD?
THE CONTEXT: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated the tokenisation of credit/debit cards for online merchants from October 1. Till then, card details for online purchases were stored on the servers of these merchants in order to help customers avoid keying in their details every time they shopped with that merchant.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is tokenisation?
- As per the RBI’s FAQ on tokenisation updated late last month, tokenisation “refers to the replacement of actual card details with an alternative code called the ‘token’, which shall be unique for a combination of card and the token requestor (i.e. the entity which accepts the request from the customer for tokenisation of a card and passes it on to the card network to issue a corresponding token).”
Why is tokenisation necessary?
- When you visit a restaurant, or even an ATM machine, it is possible for card thieves to clone your card with a skimmer, a gadget that quietly reads the magnetic strip at the back of your card.
- Similarly, hackers can also break into online websites and mobile apps that store your credit card details. Such data breaches could give con artists access to millions of cards in one go which are then sold on the dark web.
- To help lessen the chances of such fraud, some banks have mandated the use of an OTP delivered to your registered mobile number to withdraw cash at ATMs. Other banks have enabled the use of their mobile app to allow cash withdrawal without the physical use of cards.
- Some credit card-issuing banks allow limits that you can set up yourself, per day, per transaction, etc on the bank’s app. The tokenisation mandate of the RBI is a similar exercise in caution.
What are the benefits of tokenisation?
- According to RBI, a tokenised card transaction is safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant.
- Even if a hacker/scammer were to get their hands on one’s token number, they would not be able to make indiscriminate use of it.
- The token generated upon request for a specific merchant is unique to a specific card number and is usable only on that particular site or mobile app.
- The token is useless outside of that merchant’s ecosystem.” The “new mandate is only for the use of credit/debit cards online. For offline merchants, users would continue to swipe the cards on the POS machines as per previously existing guidelines.”
- Popular card network Visa further explains the concept of tokenisation through the example of a metro train ticket. It is useful only for that route and not on any other. Similarly, the unique token generated for a specific site is only applicable on that site and nowhere else.
- And if an undesirable third-party gains access to that specific token and shops within that specific website, the chances of identifying the party are more as their login and phone details would be with the site.
ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
WHAT ARE GREEN CRACKERS & HOW DO WE IDENTIFY THEM?
THE CONTEXT: According to the National Green Tribunal (NGT), green crackers are only allowed in cities and towns where air quality is poor or moderate and helps to reduce sound emissions.
THE EXPLANATION:
Difference between green and traditional crackers:
- Both green and traditional crackers cause pollution, and people should refrain from using either. The only difference is that green crackers cause 30 per cent less air pollution than traditional ones.
- Green crackers reduce emissions substantially, absorb dust, and don’t contain any hazardous elements such as barium nitrate. Toxic metals in traditional crackers are replaced with less dangerous compounds in green crackers. According to the National Green Tribunal (NGT), green crackers are allowed only in cities and towns where air quality is poor or moderate.
What are the toxic metals released from conventional crackers?
- Crackers release many toxic metals that can be harmful to health. The white colour emitted through crackers is aluminium, magnesium and titanium, while the orange colour is carbon or iron.
- Similarly, the yellow colour emits sodium compounds, while blue and red are copper compounds and strontium carbonates. The green agent is barium monochloride salts, barium nitrate, or barium chlorate.
What damage can these chemicals do when people are exposed to them? Who is vulnerable to them?
- Crackers can impact the nervous system, while copper triggers respiratory tract irritation, sodium causes skin issues, and magnesium leads to mental fume fever.
- Cadmium not just causes anaemia but also damages the kidney, while nitrate is the most harmful that causes cognitive impairment. The presence of nitrite irritates mucous membranes, eyes and skin.
- Experts added that the most vulnerable population are infants, children, pregnant women, the elderly and people with underlying medical conditions. Yet no one remains untouched by the harm these chemicals cause.
5TH ASSEMBLY OF INTERNATIONAL SOLAR ALLIANCE (ISA)
THE CONTEXT: Recently 5th Assembly of International Solar Alliance (ISA) began in New Delhi under India’s presidentship. Participants from 109 countries will be sharing their experiences towards a low-carbon economy through the promotion of solar energy.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Assembly is the apex decision-making body of the International Solar Alliance makes decisions concerning the implementation of the ISA’s Framework Agreement.
- The Assembly meets annually at the ministerial level at the ISA’s seat.
About International Solar Alliance (ISA)
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was presented by the leaders of the two countries at the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
- Headquarters: India
- The Assembly is the apex decision-making body of the ISA. It meets annually at the Ministerial level at the seat of the ISA.
- Membership: A total of 80 countries have signed and ratified the ISA Framework Agreement and 101 countries have only signed the agreement.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN THE NEWS
PRADHAN MANTRI BHARTIYA JAN URVARAK PARIYOJANA – ONE NATION ONE FERTILISER
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Prime Minister launched Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Urvarak Pariyojana – One Nation One Fertiliser.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Under the scheme, all fertiliser companies, State Trading Entities (STEs) and Fertiliser Marketing Entities (FMEs) will be required to use a single “Bharat” brand for fertilisers and logo under the PMBJP.
- All subsidised soil nutrients – urea, di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), Muriate of Potash (MoP), and NPK – will be marketed under the single brand Bharat across the nation.
- With the launch of this scheme, India will have a common bag design across the country like Bharat urea, Bharat DAP, Bharat MOP, Bharat NPK, and so on.
- The new “Bharat” brand name and PMBJP logo will cover two-thirds of the front of the fertiliser packet
- The manufacturing brands can only display their name, logo, and other information on the remaining one-third space.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE SCHEME:
The government introduced a single ‘Bharat’ brand for all subsidised fertilisers because:
- There are some 26 fertilisers (inclusive of urea), on which government bears subsidy and also effectively decides the MRPs.
- Apart from subsidising and deciding at what price companies can sell, the government also decides where they can sell. This is done through the Fertiliser (Movement) Control Order, 1973.
- When the government is spending vast sums of money on fertiliser subsidy (the bill is likely to cross Rs 200,000 crore in 2022-23), plus deciding where and at what price companies can sell, it would obviously want to take credit and send that message to farmers.
| PM- Kisan Samruddhi Kendras (PM-KSK):
· The Union government also intends to convert more than 3.3 lakh fertiliser retail shops in the country into PM- Kisan Samruddhi Kendras (PM-KSK) in a phased manner. · The PM-KSK will supply agri-inputs like seeds, fertilisers, and farm implements. It will also provide testing facilities for soil, seeds and fertilisers. · Information about government schemes will also be provided. |
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
NATIONAL MARITIME HERITAGE COMPLEX AT LOTHAL
THE CONTEXT: Recently the Prime Minister reviewed the site work progress of the National Maritime Heritage Complex at Lothal in Gujarat.
THE EXPLANATION:
- It would be developed as an international tourist destination, where the maritime heritage of India from ancient to modern times would be showcased.
- The idea is to create an edutainment (education with entertainment) approach for this destination that would be of great interest for the visitors.
- It is going to cover an area of 400 acres, with structures such as Heritage Theme Park, National Maritime Heritage Museum, Lighthouse Museum, Maritime Institute, eco-resorts, and more.
- There will also be many pavilions where all coastal states in India and union territories can showcase their artifacts and maritime heritage.
- The unique feature of NMHC is the recreation of ancient Lothal city, which is one of the prominent cities of the ancient Indus valley civilization.
| LOTHAL:
· Lothal was one of the southernmost cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization located in Gujarat. · Construction of the city began around 2400 BCE. · According to the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), Lothal had the world’s earliest known dock, which connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati river on the trade route between Harappan cities in Sindh and the peninsula of Saurashtra. |
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTION
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. With reference to culture of India, ‘pahandi’ refers to –
a) Annual Rath Yatra at Jagannath puri temple.
b) Kanwariyas travel during Kanwar Yatra.
c) Vaishno Devi Yatra
d) Char Dham Yatra
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Puri temple is famous for its annual Ratha yatra, or chariot festival, in which the three principal deities (Jagannath, Balabhadra and Subhadra are a trio of deities) are pulled on huge and elaborately decorated temple cars.
- At Jagannath Puri temple, annually, three deities are taken out in a chariot procession called Rath Yatra covering 3 kms along the Grand Road connecting the 12th century Shri Jagannath temple and the Mausi Maa temple. Servitors carry huge wooden idols from temple swaying them rhythmically in a ritual described as pahandi.