TOPIC : AN ANALYSIS OF THE FIFTH ROUND OF THE NATIONAL FAMILY HEALTH SURVEY (NFHS-5)
The context: Recently, the National Report of the 2nd phase of the fifth round of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) was released. The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted on a representative sample of households throughout India. The following article would analyse the survey and highlight its findings from the UPSC perspective.
HISTORY OF NFHS
The main objective of each successive round of the NFHS has been to provide high-quality data on health and family welfare and emerging issues in this area.
NFHS-1:
The NFHS-1 was conducted in 1992-93.

NFHS-2:
The NFHS-2 was conducted in 1998-99 in all 26 states of India.
The project was funded by the USAID, with additional support from UNICEF.

The NFHS-3: carried out in 2005-2006
NFHS-3 funding was provided by the USAID, the Department for International Development (UK), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, UNICEF, UNFPA, and the Government of India.

The NFHS-4: Conducted in 2014-2015
In addition to the 29 states, NFHS-4 included all six union territories for the first time and provided estimates of most indicators at the district level for all 640 districts in the country as per the 2011 census.
NFHS-5: KEY IMPROVEMENTS FROM PREVIOUS VERSIONS
The NFHS-4 survey covered a range of health-related issues, including fertility, infant and child mortality, maternal and child health, perinatal mortality, adolescent reproductive health, high-risk sexual behaviour, safe injections, tuberculosis, and malaria, non-communicable diseases, domestic violence, HIV knowledge, and attitudes toward people living with HIV. The NFHS-5 has made certain improvements over the earlier versions.
ASPECT/CONTEXT
EXPLANATION
SCOPE OF NFHS-5
- NFHS-5 has expanded in respect of the earlier round of the survey (NFHS-4) by adding new dimensions:
o NFHS-5 includes some new topics, such as preschool education, disability, access to a toilet facility, death registration, bathing practices during menstruation, and methods and reasons for abortion.
o Also, NFHS-5 has additional components of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs), and an expanded age range for measuring hypertension and diabetes among all aged 15 years and above.
TRACKING SDGS
- NFHS-5 provides information on important indicators which are helpful in tracking the progress of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the country.
TRACKING SOCIAL STATUS
- The NFHS-5 report also provides data on socioeconomic and other background characteristics; useful for policy formulation and effective programme implementation.
INFLUENCING PUBLIC POLICIES
- Besides providing evidence for the effectiveness of ongoing programmes, the data from NFHS-5 help in identifying the need for new programmes with an area-specific focus and identifying groups that are most in need of essential services.
NFHS-5: KEY FINDINGS
DIMENSION
FINDING
USE OF FAMILY PLANNING METHODS
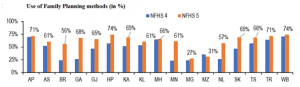
- Use of family planning methods increased; most states reduce their fertility rate, below the target of 2.1
- All states (except Mizoram) have seen an increase in the use of family planning methods. Goa (42%-point) and Bihar (32%-point) have seen the highest increase in the use of family planning methods.
FERTILITY RATES
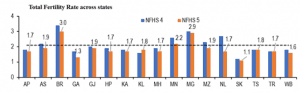
- Consequently, most states have seen a decrease in the total fertility rate (TFR). Bihar’s TFR has declined from 3.4 (in NFHS-4) to 3. All other media and large states in the survey (i.e., population above 1 crore) have a TFR below the replacement level rate of 2.1.
SEX RATIO AT BIRTH
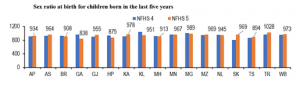
- The sex ratio at birth for children born in the last five years is below 950 for seven (of the 17) states. The sex ratio at birth is the number of female children born per 1,000 male children born. In three states, the ratio is below 900 (Goa: 838, Himachal Pradesh: 875, and Telangana: 894).
- The ratio has declined in seven states. The most notable decline was in Goa (from 966 to 838), and Kerala (from 1,047 to 951). Only Tripura has a sex ratio at birth above 1,000 (i.e., more females born than males).
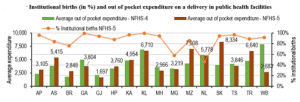
INSTITUTIONAL BIRTHS
- In 7 states, more than 90% of the births in the last five years were institutional births. In Kerala, nearly 100% of the births were institutional births. Only 46% of the births in Nagaland were institutional births.
- The average out-of-pocket expenditure on delivery in a public health facility increased in 8 of the 17 states. Note that in West Bengal, the average expenditure on deliveries declined by Rs 5,236 per delivery (66% of the cost in 2015-16), and the proportion of institutional births increased from 75% to 92%.
INFANT MORTALITY RATE & NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF CHILDREN
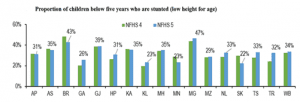
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) has declined across states; however, malnourishment among children is increasing. IMR has marginally declined in nearly all states. Assam has seen one of the largest drops in IMR, from 48 deaths (per 1,000 live births) to 32 deaths. IMR remains high in Bihar (47 deaths per 1,000 live births).
- However, the nutritional status of children below 5 years of age is worsening. Stunting or chronic malnutrition (i.e., low height with respect to age) has increased in 11 of the 17 states.
- The proportion of severely wasted children has increased in 13 of the 17 states. Wasting or acute malnutrition refers to low weight with respect to height. Children who are stunted or wasted are more vulnerable to diseases and illness.
- The proportion of children who are underweight (low weight with respect to age) has increased in 11 of the 17 states. In Bihar and Gujarat, 40% or more of the children under the age of five years are underweight.
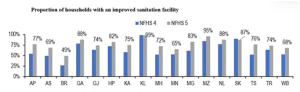
ACCESS TO ELECTRICITY, IMPROVED SOURCE OF DRINKING WATER AND SANITATION
- The proportion of households with electricity and improved drinking water source has increased across all states. Households with improved sanitation facilities have also increased across all states. 99% of households in Kerala have an improved sanitation facility, while only 49% of households have it in Bihar.
- Similarly, the proportion of households using clean fuel for cooking has also increased across nearly all states. Telangana has seen a nearly 25%-point increase in access to improved sanitation facilities and clean cooking fuel as compared to NFHS-4.
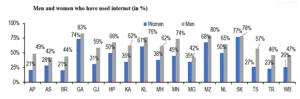
DISTRIBUTION OF INTERNET ACCESS
- More women using mobile phones across all states; however, many of them do not have access to the internet
- The proportion of women who have a mobile phone has increased across all states. However, only about 50% of women own and use a mobile phone in Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat, and West Bengal.
- The Survey also measured the proportion of men and women (15-49 years of age) who have ever used the internet. Across all states, the proportion of men who have used the internet was higher than women, with the difference being higher than 25%-point in states such as Telangana, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh. In Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, and Tripura, less than 25% of women have used the internet.
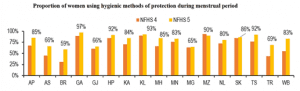
ACCESS TO MENSTRUAL HYGIENE
- The use of hygienic methods of protection during the menstrual period has increased across states
- The Survey measured the proportion of women (15-24 years) who are using hygienic methods of protection during their menstrual period. This has increased across almost all states. The largest increase was seen in Bihar and West Bengal (28%-point). However, it still remains low in Bihar (59%), Assam and Gujarat (66%).
NFHS: AN OVERVIEW AND ANALYSIS
FINDING
CRITICAL ANALYSIS
Contraceptive use:
Only 50.7 percent of women in the lowest wealth quintile used modern contraceptives, compared to 58.7 percent of women in the highest quintile.
- While the data shows that the knowledge of contraceptives is pretty much universal (99 percent of married men and women in both rural and urban India knew of them), only a little over 50 percent of the currently married population opts for contraceptives.
- Their usage is also determined by employment status and income level.
The onus of family planning:
37.9 per cent of married women between the ages of 15 to 49 underwent female sterilisation. This is nearly 2 percent more than in 2015-16.
- The onus of family planning still heavily leans on women, and far from modern contraceptives easing the burden of female sterilisation, the practice has only gone up.
- There isn’t much difference in this as far as rural and urban sphere are concerned.
Low fertility rates:
The trends in fertility of residence (TFR) are down across communities, however, the fall in TFR among Muslims has been the sharpest at 2.36 children per woman as compared to 2.62 kids per woman in 2015-16.
- The numbers are lower, yet vary across caveats of religious groups, communities, and states.
- The decline continues the downward trend in India’s fertility rate over the last few decades.
Anaemia remains a major concern:
57 percent of all women aged 15-49 years were found to be anaemic, whereas 25 percent of men in the same age group have anaemia.
- While there has been a 4 percent rise in anaemia in women compared to 2015-16, there has been a 3 percent rise among men.
- India has not been effectively able to tackle the burden of anaemia and remains a concern across age groups, sexes and social strata. The government will have to prioritize a more aggressive approach to tackle this issue going forth.
Obesity is on the rise:
24 percent of women and 22.9 percent of men were found to be overweight or obese (BMI ≥25.0 kg/m2), which is 4 percent higher than in 2015-16.
- While obesity seems to have gone up in both men and women, fewer people in the same age groups are underweight as compared to 2015-16.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- Considering the huge population size and profound demographic diversity in the country, context-specific policy and programmes will be needed for states, passing through different stages of the demographic transition. There must be a more focused approach towards aspects like eliminating anaemia and providing easy access to contraceptives.
- There has to be an accelerated coverage of national programmes such as Jan Dhan Yojana, Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY), Swachh Bharat Abhiyaan, Ujjawala Scheme, PMMVY (Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana), and Beti Bachao Beti Padhao mission.
- Lower TFR usually comes with economic development and greater education, particularly those policies that pave the way for women’s education and employment. States like Kerala have recorded declining TFR due to this, and thus, it becomes a role model for states like Bihar which hasn’t fared well as compared to its southern counterparts.
THE CONCLUSION: While there is much to celebrate in the NFHS-5 data, especially the fact that the Total Fertility Rate has come down to 2.0, our focus should now be to reach the unreached. We must do more for the marginalized sections of society, who may be underprivileged on the basis of class, identity or geography.
QUESTIONS TO PONDER
- Discuss a few significant findings of the fifth round of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) in the context of health and inclusivity of women in India.
- “While there is much to celebrate in the NFHS-5 data, we must do more for the marginalized sections of the society, who may be underprivileged on the basis of class, identity or geography.” Examine critically in the context of the fifth round of the National Family Health Survey.

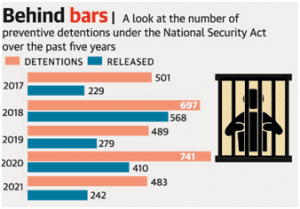 detained as of 2021-end — the highest since 2017 when the NCRB started recording this data.
detained as of 2021-end — the highest since 2017 when the NCRB started recording this data.
 to 6 tear gas shells and dropped on the target area.
to 6 tear gas shells and dropped on the target area.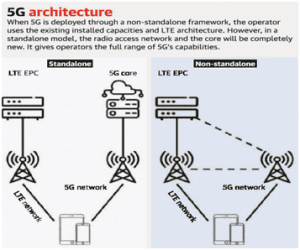 coverage and speed (Megabits per second). This means that telecom companies can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high-speed Internet. However, the low band spectrum may not be optimal for specialised needs of the industry.
coverage and speed (Megabits per second). This means that telecom companies can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high-speed Internet. However, the low band spectrum may not be optimal for specialised needs of the industry.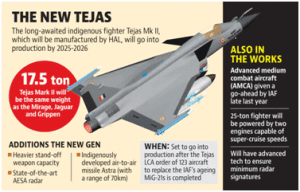 opposed to the Mark IA’s 62 per cent), but will incorporate more advanced technologies to be manufactured in India. Tejas is a single-engine and highly maneuverable multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft manufactured by state-run Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
opposed to the Mark IA’s 62 per cent), but will incorporate more advanced technologies to be manufactured in India. Tejas is a single-engine and highly maneuverable multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft manufactured by state-run Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).