DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (SEPTEMBER 28, 2022)
INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. THE CASE OF NIKAH HALALA IN INDIA, AND A LONG COURT BATTLE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Public interest litigation (PIL) was filed seeking the annulment of halala marriage and polygamy.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The PIL was regarding the annulment of Section 2 of the Muslim Personal Law (Shariat) Application Act, 1937, to be declared arbitrary and in violation of Articles 14, 15, 21 and 25 of the Constitution.
• The litigant requested the court to ensure that provisions of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, apply to all Indian citizens.
• She contended that nikah halala is rape under IPC Section 375.
What is Nikah halala?
• Nikah halala is a law that requires a woman to marry and sleep with another man in order to return to her first husband.
• In Islam, ‘halala’ is a term that finds its roots in ‘halal’ that translates to something that is permissible, and therefore ‘lawful’.
• In the context of marriage then, it means that a divorced woman can become ‘halal’ (lawful) for her husband again after nikah halala is complete.
What is the procedure?
• Islam dictates that a Muslim man has the liberty to divorce and remarry the same woman twice.
• However, if he decides to dissolve the marriage for the third time, he can only remarry the same woman if she first marries another man, consummates the marriage, and only if the man dies or willingly asks for divorce, can the woman go back to her first husband and remarry him.
• Usually, nikah halala stems from instant triple talaq and ends with it.
Quranic justification:
• Halala, the way the Koran speaks of it, empowers women to take independent decisions.
• It saves women from temperamental husbands who divorce in a fit of anger, then cancel it, then divorce again, unleashing an endless cycle of marriage and divorce.
Global scenario:
• In Saudi Arabia, where divorces are on the rise, no cases of halala have been reported.
• No case has been reported from the UAE, Kuwait and Yemen either.
Indian Law on Nikah Halala:
• In India, the Muslim Women’s Protection of Rights on Marriage, passed after invalidation of triple talaq by the Supreme Court, is silent on nikah halala.
• The Act made instant triple talaq a criminal offence but steered clear of halala which takes place as a consequence of triple talaq.
Issues:
In modern India, nikah halala has been manipulated and misused.
• Rapes: There are cases of rapes on women by keens on the name of Halala.
• Websites offering halala marriage: In the midst of this, several websites and social media pages have emerged offering halala marriage services to women who’ve been divorced by their first husbands.
• Blackmailing and extortion: Many women who approach these services are either blackmailed or taken advantage of. Many are asked to pay large sums of money.
HEALTH ISSUES
2. KHOSTA-2: NEW VARIANT OF CORONAVIRUS
THE CONTEXT: Recently,Khosta-2 variant of coronavirus found in Russian bats in Sochi National Park.
THE EXPLANATION:
• A team of American researchers have found the Khosta-2 in Russian bats.The zoonotic virus is capable of infecting humans.
• This is unlike the Khosta-1, which is also found in Russian bats but cannot easily spread to humans.Khosta-2 has been classified as sarbecovirus, a member of the coronavirus family.
• It is related to SARS-CoV-2, which is causing a worldwide pandemic.Khosta-2 was discovered in bat samples obtained from Sochi National Park between March and October 2020, when the world was struggling to contain the spread of the SARS-CoV-2.
• The pathogen is capable of infecting human cells similar to SARS-CoV-2. It attaches to the ACE-2 entrance enzyme, which is located on the surface of the human cells with a spike-like protein on the surface.
• While its method of infection is similar to SARS-CoV-2, Koshta-2 is not effective.
• Scientists have combined the Khosta-2 with serum obtained from individuals vaccinated against COVID-19. They found that the antibodies in the serum were not able to neutralize the pathogen.
• Similar results were found when the virus was combined with the serum from people who have recently recovered from Omicron infection.It is also found to be completely resistant to all coronavirus vaccines currently available on the market.
• It does not have the genes that can increase the severity of the disease like the Omicron Variant. However, this can eventually change if it mixes with the genes of the SARS-CoV-2.
About sarbecovirus
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus or sarbecovirus is an enveloped positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that enters the host cells by latching on to the ACE2 receptor. It is capable of infecting humans, bats and other mammals.
VALUE ADDITION:
About Sochi National Park
Sochi National Park is UNESCO world heritage site in Russia. Established in 1983, it is the oldest national park in Russia. It is situated in Western Caucasus, close to the city of Sochi. It is bounded by rivers Shepsi and Magri in the northwest, Abkhazia in the southeast, Black sea coast and Main Caucasian ridge in the north and south.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
3. ADB TO PROVIDE 14 BILLION USD AID FOR FOOD SECURITY IN ASIA PACIFIC
THE CONTEXT: The Asian Development Bank announced a $14 billion assistance to fight food insecurity in Asia Pacific.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The funding to address food insecurity in Asia Pacific was announced as part of the 55th ADB annual meeting.
• It will be used to combat food crisis caused by climate change and Russian war in Ukraine.
• The financial aid will be provided for the period of 2022-2025.
• While 3.3 billion USD will be spent in 2022, 10.7 billion USD will be used from 2023 to 2025.
• In 2022, USD 2.5 billion of this assistance will be used to repurpose and strengthen the existing projects and launch new projects in agriculture, natural resources and rural development.
• 800 million USD will be used by private sector for finance operations of trade and supply chain, direct agribusiness lending, micro financing programmes and lending to financial institutions.
• This comprehensive initiative will ensure long-term food security in Asia and Pacific by strengthening food systems and making them resilient to climate crisis and biodiversity degradation.
• The latest funding would complement the existing aids targeting food security in the region.
Food security situation in Asia Pacific
• The food insecurity in the region is being exacerbated by floods, droughts, global warming, diseases and other factors that are adversely impacting the food production. Currently, around 1.1 billion people do not have access to healthy diets because of scarcity and food inflation in the region.
• Some countries in Asia Pacific are vulnerable to food shocks because of their high dependence on imported staples and fertilizers. This makes nutritious food unaffordable in several of low-income countries in the region. The Russian invasion of Ukraine has disrupted the supply of these vAital goods and worsened the situation.
About Asian Development Bank
Asian Development Bank is a Manila-based regional development bank established in 1966. Its aim is to promote the social and economic development of Asia and the Pacific. It is owned by 68 members, of which 49 are from Asia Pacific region.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
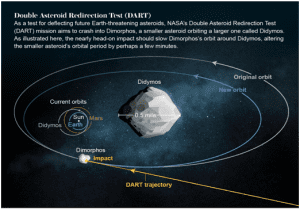
4. NASA’S DOUBLE ASTEROID REDIRECTION TEST (DART)
THE CONTEXT: Recently, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) successfully crashed into Dimorphous.
THE EXPLANATION:
The Humanity’s first planetary defence test:
• With the collision, the test has been completed successfully in a mission that went exactly as planned without any hitches.
Reason for test:
• The impact should have nudged the asteroid slightly and subtly changed its orbit around Didymos, the larger asteroid.
• Telescopes on Earth and in space are going to take measurements of this change to see how the change measures up to computer-generated simulations.
Why Dimorphos?
• Didymos is a perfect system for the test mission because it is an eclipsing binary which means it has a moonlet that regularly orbits the asteroid and it can be seen when it passes in front of the main asteroid.
• The Didymos system is not an Earth-crossing asteroid, and there is no possibility that the deflection experiment could create an impact hazard.
• Earth-based telescopes can study this variation in brightness to understand how long it takes Dimorphos to orbit Didymos.
About the DART Mission
It is a planetary defence-driven test of technologies for preventing an impact on Earth by a hazardous asteroid.
Objectives:
• DART is the first technology demonstration of the kinetic impactor technique that could be used to mitigate the threat of an asteroid hitting Earth.
• The kinetic impactor mitigation technique is the impulsive deflection of the asteroid through the sudden addition of momentum. In simpler terms, DART is being sent to collide with an asteroid to change its orbital period.
VALUE ADDITION:
ABOUT ASTEROIDS
• Asteroids, sometimes called minor planets, are rocky, airless remnants left over from the early formation of the solar system about 4.6 billion years ago.
• Most of this ancient space rubble can be found orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter within the main asteroid belt.
o Some asteroids go in front of and behind Jupiter, which are called Trojans.
o Asteroids that come close to Earth are called Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) for short. NASA keeps close watch on these asteroids.
• Asteroids range in size from Vesta (the largest at about 329 miles in diameter) to bodies that are less than 33 feet across. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is less than that of Earth’s Moon.
• Asteroids are not all round like planets. They have jagged and irregular shapes.
5. HONEYBEES CAPABLE OF PARITY CATEGORIZATION
THE CONTEXT: A new study has shown that honeybees can learn odd and even number categorisation — also called parity classification.
THE EXPLANATION:
• Parity classification is the categorization of numbers as either odd or even.
• It is used when dealing with real-world objects that can be paired. If an element cannot be paired in a group, then the number of objects are odd.
• Previous studies have shown that honeybees are capable of learning the order of quantities, performing simple addition and subtraction, matching symbols with quantities and relate size and number concepts.
• A new research has found that they were also capable of parity classification.
• Till date, only humans were found to be capable of this task.
• Honeybees were successfully trained to undertake this task as part of an experiment.
• The scientists separated honeybees into two groups.
• One group trained to associate even numbers with sugar water and odd numbers with quinine (bitter-tasting liquid).
• Another group was trained to associate odd numbers with sugar water and even number with quinine.
• The training was given using comparisons of odd versus even numbers with cards presenting 1 to 10 printed shapes.
• The group that associated odd number with sugar water learned more quickly than the other group.
• This shows that honeybees’ learning bias is different from humans, who categorize even numbers more quickly.
• The bees were then tested with new numbers that were not shown during the training.
• They were able to categorize the new numbers of 11 or 12 elements as odd or even with 70 per cent accuracy.
• They may have been able to achieve this feat either by finding unpaired element, performing division calculations or counted each element and applied odd or even categorization rule to the total number of elements.
• This novel experiment, if used in other animal species, would help improve the understanding on how mathematics and abstract thoughts emerged in humans.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
6. BATHUKAMMA: STATE FESTIVAL OF TELANGANA
THE CONTEXT: Bathukamma is being celebrated in Telangana from September 25 to October 3 this year.
THE EXPLANATION:
• Bathukamma is observed as the state festival of Telangana since the state’s inception in 2014.It is a flower festival celebrated mainly in Telangana and several parts of Andhra Pradesh.
• This 9-day festival is celebrated based on Sathavahana calendar and it usually falls on September or October, during the latter half of monsoon, before the onset of winter.
• This festival begins with Mahalaya Amavasya, also known as Engili Poola Bathukamma.
• Bathukamma means ‘Goddess of Life’. It is a collection of flowers stacked one layer at a time and rising in a series of concentric circles like the gopuram in South Indian temples.
• It is made using locally grown flowers like Gunugu puvvu (Celosia), Thangedu puvvulu (Cassia auriculata), Gummadi puvvulu (Cucurbita), Vaama puvvulu (Ajwain), Banthi puvvu (Marigold), Chamanthi puvvulu (Chrysanthemum) etc.
• During the first seven days of this festival, women make symbolic images of Bodemma (Goddess Gauri) using clay and small Bathukamma.
and small Bathukamma.
• The final day of this festival, called Saddula Bathukamma, involves the preparation of huge Bathukamma on a special plate and womenfolk singing and dancing around it.
• Bathukamma are then taken out in a procession to be immersed a river or any nearby waterbody.
• The flowers used in Bathukamma are capable of purifying water in ponds and tanks.
• The festival concludes a day before the Dasara Festival.
• The Union Ministry of Culture has announced that this festival would be celebrated at the India Gate for the first time.
• The celebrations will be in line with the Telangana/Hyderabad Liberation Day celebrations that were organized earlier this month, when the national flag was hoisted in Hyderabad by Home Minister.
• Meanwhile, the Telangana government has started the distribution of 1 crore Bathukamma sarees for this festive occasion.The initiative was started by the Telangana government in 2017 to support weavers in the state.
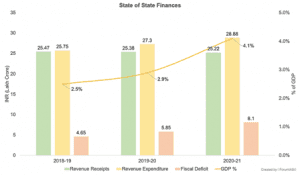
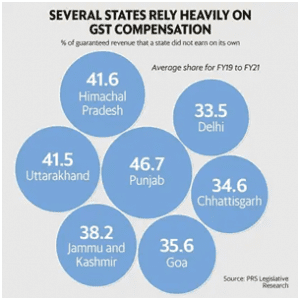
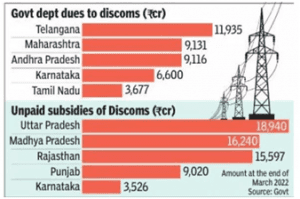
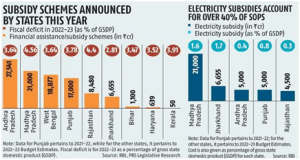
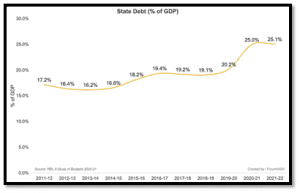 its fiscal situation and a predicted debt-to-GSDP ratio that would reach 45% in 2026–2027. By 2026–2027, it is anticipated that Rajasthan, Kerala, and West Bengal will have debt-to-GSDP ratios higher than 35%. To stabilize their debt levels, these states will need to take major remedial action.
its fiscal situation and a predicted debt-to-GSDP ratio that would reach 45% in 2026–2027. By 2026–2027, it is anticipated that Rajasthan, Kerala, and West Bengal will have debt-to-GSDP ratios higher than 35%. To stabilize their debt levels, these states will need to take major remedial action.