DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (AUGUST 04, 2022)
THE INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1.LOK SABHA PASSES CENTRAL UNIVERSITIES (AMENDMENT), BILL 2022
THE CONTEXT: Lok Sabha passed Central Universities (Amendment), Bill 2022 for conversion of the National Rail and Transportation Institute (NRTI), a Deemed to be University into Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya (GSV), a Central University.
THE EXPLANATION:
BILL HIGHLIGHTS:
The Bill amends the Central Universities Act, 2009, which provides for establishing central universities in various states. Key features of the Bill include:
- Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya: The Bill seeks to convert the National Rail and Transportation Institute, Vadodara (a deemed university) to the Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya, which will be a central university. The National Rail and Transportation Institute was declared a deemed university under the University Grants Commission Act, 1956. The Vishwavidyalaya will be sponsored and funded by the central government through the Ministry of Railways.
- Scope of education: The Bill provides that Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya will take measures to provide quality teaching, research, and skill development in disciplines related to transportation, technology, and management. If required, the University may also establish centres in India and abroad. According to the Statement of Objects and Reasons, establishment of the Vishwavidyalaya will address the need of trained talent in the transportation sector.
- Appointment of a new Vice-Chancellor (VC): The existing VC of the National Rail and Transportation Institute will hold office for: (i) six months from when the Act is notified, or (ii) until a new VC for the Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya is appointed, whichever is earlier.
What is PM Gati Shakti Master Plan?
- Prime Minister launched PM Gati Shakti – National Master Plan for Multimodal Connectivity in October 2021. This is a digital platform that aims to bring 16 Ministries including Education, Railways and Roadways together for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- It is learned that integrated and seamless connectivity for the movement of people, goods, and services from one mode of transport to another will be offered by this multi-modal connectivity. Also, last-mile connectivity of infrastructure will be facilitated to reduce travel time for people. Minister Sitharaman said in her Budget speech, “One product one railway station will be popularised, 400 new Vande Bharat trains to be introduced”.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2.EXPLAINED: COULD CHINA INVADE TAIWAN?
THE CONTEXT: After China announced military exercises in six sea zones close to Taiwan, the island’s defence ministry said it had no doubt what message Beijing wanted to send: “that they seek a cross-strait resolution by force instead of peaceful means.”
THE EXPLANATION:
Where is Taiwan?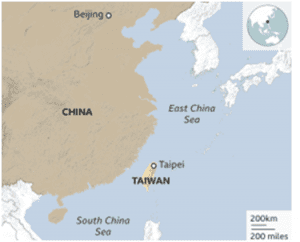
- Taiwan is an island that is roughly 100 miles from the Coast of South East China. Taiwan sits in the so-called ‘first island chain’, which includes a list of US-friendly territories that are also crucial to US Foreign Policy.
- If China was to take over Taiwan, some western experts have suggested that it could be freer to project power in the Western Pacific Region and could possibly even threaten US military bases as far away as Guam and Hawaii. However, China has insisted that its intentions are purely peaceful.
What is the origin of Taiwan-China Tussle?
- Taiwan, earlier known as Formosa, a tiny island off the east coast of China.
- The island is located in the East China Sea, to the northeast of Hong Kong, north of the Philippines and south of South Korea, and southwest of Japan.
- Taiwan is the unfinished business of China’s liberation under the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in 1949.
- The Guomindang (KMT) forces under Chiang Kai-shek lost the 1945-49 civil war to the Communist forces under Mao Zedong.
- Chiang Kai-shek retreated to the island of Taiwan and set up a regime that claimed authority over the whole of China and pledged to recover the mainland eventually.
- The Communists in turn pledged to reclaim what it regarded as a “renegade” province and achieve the final reunification of China.
- Taiwan (known as Republic of China – ROC) could not be occupied militarily by the newly established People’s Republic of China (Communist’s mainland China) as it became a military ally of the United States during the Korean War of 1950-53.
Why US-China are at loggerheads over Taiwan?
- The United States has been engaging in a delicate balancing act between Taiwan and China. Washington follows ‘One-China’ Policy, which recognizes Beijing but allows informal relations and defense ties with Taipei.
- US provides arms to Taiwan- it is by far the largest arms dealer for Taiwan- and follows a strategic ambiguity policy about how far it will be willing to go to defend Taiwan in the face of Chinese invasion.
- In recent times, tensions seem to have escalated between the US and China. In May, China made the second largest incursion into Taiwan’s air defence zone in 2022 with Taipei reporting 30 jets entering the area, including more than 20 fighters.
- The president of the US Joe Biden raised eyebrows at China’s actions and said that the US would intervene militarily if Taiwan were attacked.
Why Taiwan is important for the rest of the world?
- Taiwan’s economy is hugely important. Much of the world’s everyday electronic equipment-from laptops, watches, and game consoles- is powered by computer chips that are made in Taiwan.
- By one measure, a single Taiwanese company- the Taiwan semiconductor manufacturing company or TSMC- has over half the world’s market. TSMC is a so-called ‘foundry’- a company that makes chips designed by consumers and military consumers. It is a vast industry that was worth almost $100 billion in 2021.
- A Chinese takeover in Taiwan can give Beijing some control over one of the world’s most important industries.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
3.INDIA ADDS 10 MORE WETLANDS DESIGNATED AS RAMSAR SITES TO MAKE TOTAL 64 SITES
THE CONTEXT: India adds 10 more wetlands designated as Ramsar sites to make total 64 sites covering an area of 12,50,361 ha in the country.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The 10 new sites include: Six (6) sites in Tamil Nadu and One (1) each in Goa, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha. Designation of these sites would help in conservation and management of wetlands and wise use of their resources.
- India is one of the Contracting Parties to Ramsar Convention, signed in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971. India signed it on 1st Feb 1982. So far 64 wetlands covering an area of 12,50,361 ha have been designated as Ramsar Sites of International Importance from India, till date.
- The sites are Koothankulam Bird Sanctuary, Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve,Vembannur Wetland Complex, Vellode Bird Sanctuary, Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary and Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary, all in Tamil Nadu, Satkosia Gorge in Odisha,Nanda Lake in Goa, Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary in Karnataka, and Sirpur Wetland in Madhya Pradesh.
- Until 2012, India had 26 Ramsar sites, with the last decade witnessing a meteoric rise. Ramsar wetlands now comprise around 10% of the total wetland area in the country.
- Being designated one, however, doesn’t necessarily invite extra international funds but that States —and the Centre — must ensure that these tracts of land are conserved and spared from man-made encroachment. Acquiring this label also helps with a locale’s tourism potential and its international visibility.
Criteria for declaring the wetlands
- “Ramsar Sites are designated because they meet the criteria for identifying wetlands of international importance. The first criterion refers to sites containing representative, rare or unique wetland types, and the other eight cover sites of international importance for conserving biological diversity. These criteria emphasize the importance the convention places on sustaining biodiversity,” the convention’s website states.
- The Pichavaram mangrove, for instance, which got the Ramsar tag on April 8, 2022 is one of the largest mangrove ecosystems in India with littoral and swamp forest habitats, located between the estuaries of the Vellar and Kollidam rivers. Trees here are permanently rooted under a few feets of water.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
4.INDIA’S TRADE DEFICIT SURGES TO OVER $31 BN – WHAT IS TRADE DEFICIT
THE CONTEXT: India’s trade deficit has widened to a record $31.02 billion in July 2022 to contracting merchandise exports and a rise in imports. This is a three-times increase from the $10.63 billion trade deficit reported in July last year (2021).
THE EXPLANATION:
What is trade deficit?
- Trade deficit or negative balance of trade (BOT) is the gap between exports and imports. When money spent on imports exceeds that spent on exports in a country, trade deficit occurs.
- It can be calculated for different goods and services and also for international transactions. The opposite of trade deficit is trade surplus.
What causes it?
There are multiple factors that can be responsible. One of them is some goods not being produced domestically. In that case, they have to be imported. This leads to an imbalance in their trade. A weak currency can also be a cause as it makes trade expensive.
Is it bad for a country’s economy?
- If trade deficit increases, a country’s GDP decreases. A higher trade deficit can decrease the local currency’s value.
- More imports than exports, according to economists, impact the jobs market and lead to an increase in unemployment. If more mobiles are imported and less produced locally, then there will be less local jobs in that sector.
Reasons of Surge in TD & CAD
- The surge in oil prices, amid a pickup in domestic demand, will significantly enhance India’s import bill.
- Aided by the broader rise in commodities and fertilizers.
- Anticipation that gold imports will remain high as investors look to hedge against market volatility and inflation.
- The situation is especially aggravated by the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
5.CENTRE INCREASES FAIR AND REMUNERATIVE PRICE ON SUGARCANE
THE CONTEXT: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, at its meeting chaired by Prime Minister, has approved Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for sugar season 2022-23 (October – September) at ₹305 per quintal. The amount is for sugarcane with a basic sugar recovery rate of 10.25%.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Centre has also announced a premium of ₹3.05 per quintal for each 0.1% increase in recovery of sugar over and above 10.25% and reduction in FRP by ₹3.05 per quintal for every 0.1% decrease in recovery.
- The FRP for last season was ₹290 per quintal with a basic recovery rate of 10%. While the Centre claimed the increase will protect the interest of sugarcane farmers, the farmers’ organisations said the FRP is too low when compared to the increase in input cost and the increase of 0.25% in recovery rate is a blow to them. The Centre has also decided that there shall not be any deduction in case of sugar mills where recovery is below 9.5%. “Such farmers will get ₹282.125 per quintal for sugarcane in ensuing sugar season 2022-23 in place of ₹275.50 per quintal in current sugar season 2021-22”.
- It added that the A2 + FL (actual paid out cost plus imputed value of family labour) cost of production of sugarcane for season 2022-23 is ₹162 per quintal. “This FRP of ₹305 per quintal at a recovery rate of 10.25% is higher by 88.3% over cost of production, thereby ensuring the promise of giving the farmers a return of more than 50% over their cost. The FRP for sugar season 2022-23 is 2.6% higher than current sugar season 2021-22. The decision is based on a recommendation by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
VALUE ADDITION:
Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP)
- CACP is an expert body that recommends minimum support prices (MSPs) to the Government (CCEA) by taking into account the cost of production, trends in domestic and international prices.
- It is a statutory panel under the Ministry of Agriculture, established in January 1965.
- It makes recommendations for MSPs for 23 Kharif and rabi crops
- However, its suggestions are not binding on the government.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
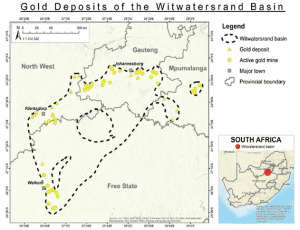
6.PLACES IN NEWS:WITWATERSRAND BASIN: ARTISANAL GOLD MINING IN SOUTH AFRICA IS OUT OF CONTROL
THE CONTEXT: The Illegal and unregulated artisanal gold mining on the Witwatersrand Basin, located south of South Africa’s Gauteng province, is an increasing threat to community, industrial and state security. Reports on turf wars between rival gangs, or shootouts between illegal miners and security officers are commonplace.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The recent incidents point to a spike in the scale of illegal activity, conflict and criminality.
- In October 2021, approximately 300 illegal miners, known as “zama zamas”, attacked and shot at police and security officers when the officers tried to prevent them from delivering food parcels to underground miners. In June 2022, about 150 illegal miners stormed gold miner Sibanye-Still water’s mothballed Cooke shaft near Randfontein in an attempt to gain control. And since last week, South Africans have been reeling at the horrific robbery and gang rape of a film crew at a mine dump close to West Village, a multi-racial suburb of Krugersdorp on the West Rand.
What is meant by artisanal mining?
Artisanal and small-scale mining, or ASM, is a largely informal economic sector that includes workers around the world who use basic tools to extract from the earth everything from gold and gemstones to vital metals such as cobalt, tin, tungsten and tantalum.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY
Q.Consider the following pairs:
RAMSAR SITES STATE
- Koothankulam Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Nanda Lake – Telangana
- Vembannur Wetland Complex – Kerala
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 3 only
ANSWER FOR THE PRACTICE QUESTION
ANSWER: A
EXPLANATION:
India adds 10 more wetlands designated as Ramsar sites to make total 64 sites covering an area of 12,50,361 ha in the country.
- The 10 new sites include: Six (6) sites in Tamil Nadu and One (1) each in Goa, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha. Designation of these sites would help in conservation and management of wetlands and wise use of their resources.
- India is one of the Contracting Parties to Ramsar Convention, signed in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971. India signed it on 1st Feb 1982. So far 64 wetlands covering an area of 12,50,361 ha have been designated as Ramsar Sites of International Importance from India, till date.
- The sites are Koothankulam Bird Sanctuary, Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve,Vembannur Wetland Complex, Vellode Bird Sanctuary, Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary and Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary, all in Tamil Nadu, Satkosia Gorge in Odisha,Nanda Lake in Goa, Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary in Karnataka, and Sirpur Wetland in Madhya Pradesh.
- The 10 new sites include: Six (6) sites in Tamil Nadu and One (1) each in Goa, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha. Designation of these sites would help in conservation and management of wetlands and wise use of their resources.
 atmosphere. These soot particles have a far larger impact on the climate than all other sources of soot combined, as BC particles are almost 500 times more efficient at retaining heat.
atmosphere. These soot particles have a far larger impact on the climate than all other sources of soot combined, as BC particles are almost 500 times more efficient at retaining heat. world economy.
world economy.