DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (JULY 26, 2022)
THE INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1.THE LATEST GUIDELINES ON ARRESTS AND BAIL ORDERS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a division bench of the Supreme Court of India in Satender Kumar Antil vs CBI laid down fresh guidelines on arrests in order to have strict compliance with the provisions of Section 41 and 41A of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973.
THE EXPLANATION:
- These guidelines are in addition to the earlier ones which the apex court had already laid down in the case of Arnesh Kumar vs State of Bihar (2014). The Court in the present case has also emphasised upon separate legislation on the law relating to bail and has also issued specific directions in this regard.
- Also, recently the Chief Justice of India (CJI) cautioned against “hasty and indiscriminate arrests”. He further commented on the delay in bails and the plight of undertrial prisoners.
How is a person arrested?
- Arrest in its simplest form is defined as, “when one is taken and restrained from his liberty”. The police has wide powers to arrest under the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. In the Joginder Kumar (1994) verdict, the Court had stated that “arrest and detention in police lock-up of a person can cause incalculable harm to the reputation and self-esteem of a person”.
- Further, in the case of Arnesh Kumar, the apex Court had rightly observed that “arrest brings humiliation, curtails freedom and cast scars forever”. In recent times, there have been several controversies regarding the arrest and subsequent bail of accused persons.
What are Sections 41 and 41A of the Code of Criminal Procedure?
- Section 41 of the Code provides for the circumstances in which arrest can be made by the police without a warrant and mandates for reasons to be recorded in writing for every arrest and non-arrest.
- Section 41A of the Code provides for the requirement of a notice to be sent by the investigating agencies before making an arrest in certain conditions prescribed by the Code. The Court stated that any dereliction on the part of the agencies has to be brought to the notice of the higher authorities by the court followed by appropriate action.
The Bench further said that the courts will have to satisfy themselves on the compliance of Section 41 and 41A. Any non-compliance would entitle the accused for grant of bail.
What are the guidelines with respect to bail?
- As part of the new guidelines, it is clearly stated that there need not be any insistence on a bail application while considering the application under Sections 88, 170, 204 and 209 of the Code. The Court said that “there needs to be a strict compliance of the mandate laid down in the judgment of this court in Siddharth”( Siddharth vs State of U.P., 2021).
- It is a clear direction of the Court that bail applications ought to be disposed of within a period of two weeks except if the provisions mandate otherwise — the exception being an intervening application. The Court also said that “applications for anticipatory bail are expected to be disposed of within a period of six weeks with the exception of any intervening application”.
VALUE ADDITION:
Types of Bail in India
Depending upon the sage of the criminal matter, there are commonly three types of bail in India:
- Regular bail- A regular bail is generally granted to a person who has been arrested or is in police custody. A bail application can be filed for the regular bail under sections 437 and 439 of CrPC.
- Interim bail– This type of bail is granted for a short period of time and it is granted before the hearing for the grant of regular bail or anticipatory bail.
- Anticipatory bail– Anticipatory bail is granted under section 438 of CrPC either by session court or High Court. An application for the grant of anticipatory bail can be filed by the person who discerns that he may be arrested by the police for a non-bailable offence.
What is default bail?
- Also known as statutory bail, this is a right to bail that accrues when the police fail to complete the investigation within a specified period in respect of a person in judicial custody. This is enshrined in Section 167(2) of the Code of Criminal Procedure where it is not possible for the police to complete an investigation in 24 hours, the police produce the suspect in court and seek orders for either police or judicial custody. This section concerns the total period up to which a person may be remanded in custody prior to the filing of the charge sheet.
- For most offences, the police have 60 days to complete the investigation and file a final report before the court. However, where the offence attracts a death sentence or life imprisonment, or a jail term of not less than 10 years, the period available is 90 days. In other words, a magistrate cannot authorise a person’s judicial remand beyond the 60-or 90-day limit.
- At the end of this period, if the investigation is not complete, the court shall release the person “if he is prepared to and does furnish bail”.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
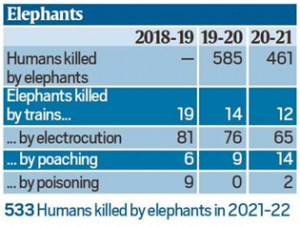
2.TOLL OF HUMAN-ANIMAL CONFLICT ON TIGERS, ELEPHANTS AND PEOPLE
THE CONTEXT: According to the Ministry of Environment, forest, and climate change between 2018-19 and 2020-21, 222 elephants were killed by electrocution across the country, 45 by trains, 29 by poachers and 11 by poisoning. Among tigers, too, 29 were killed by poaching between 2019 and 2021, while 197 tiger deaths are under scrutiny.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Among human casualties of conflict with animals, elephants killed 1,579 humans in three years — 585 in 2019-
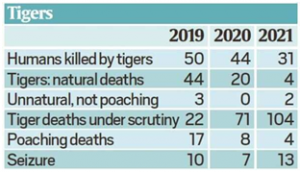 20, 461 in 2020-21, and 533 in 2021-22. Odisha accounted for the highest number of these deaths at 322,followed by Jharkhand at 291 (including 133 in 2021-22 alone), West Bengal at 240, Assam at 229, Chhattisgarh at 183, and Tamil Nadu at 152.
20, 461 in 2020-21, and 533 in 2021-22. Odisha accounted for the highest number of these deaths at 322,followed by Jharkhand at 291 (including 133 in 2021-22 alone), West Bengal at 240, Assam at 229, Chhattisgarh at 183, and Tamil Nadu at 152. - Tigers killed 125 humans in reserves between 2019 and 2021. Maharashtra accounted for nearly half these deaths, at 61. For tiger deaths caused by human activity.
- Among the 222 elephant deaths caused by electrocution, Odisha accounted for 41, Tamil Nadu for 34 and Assam for 33. Odisha (12 out of 45) also had the highest number of elephant deaths caused by trains, followed by West Bengal (11) and Assam (9). Poaching deaths were highest in Meghalaya (12 out of 29) while poisoning deaths were highest in Assam (9 out of 11, including 8 in 2018-19 alone).
- As a result of concerted efforts made for protection and conservation of wildlife, the population of several
 wildlife species like Tigers, Elephants, Asiatic Lion, Rhino etc. in the country has increased”.
wildlife species like Tigers, Elephants, Asiatic Lion, Rhino etc. in the country has increased”. - “Assessments of human-wildlife conflicts indicate that the main causes of human wildlife conflict include habitat loss, growth of population of wild animals, changing cropping patterns that attract wild animals to farmlands, movement of wild animals from forests area to human dominated landscapes for food and fodder, movement of human beings to forests for illegal collection of forest produce, habitat degradation due to growth of invasive alien species, etc.
VALUE ADDITION:
About Project REHAB:
- Project RE-HAB stands for Reducing Elephant-Human Attacks using Bees. It is an initiative of the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC).
- The project has been launched as a sub-mission of KVIC’s National Honey Mission.

- It intends to create “bee fences” to thwart elephant attacks in human habitations using honeybees.
- Bee boxes have been placed on the ground as well as hung from the trees.
- The boxes are connected with a string so that when elephants attempt to pass through, a tug causes the bees to swarm the elephant herds and dissuade them from progressing further.
- This idea stems from the elephants’ proven fear of the bees.
- The project aims to mitigate Human– elephant conflicts in the country.
- It was launched as a pilot project launched on the periphery of Nagarhole National Park in Karnataka.
National Honey Mission:
- Launched by Khadi and Village Industries Commission(KVIC)
- To provide sustainable employment and income to rural and urban unemployed youth.
- To conserve the honeybee habitat and tapping untapped natural resources.
- Promote beekeeping for increasing crop productivity and pollination services avenue for beekeepers and farmers.
3.CLEARANCE OF GENETIC ENGINEERING APPRAISAL COMMITTEE (GEAC) MANDATORY FOR THE ENVIRONMENTAL RELEASE OF GENETICALLY MODIFIED (GM) CROPS
THE CONTEXT: According to the Ministry of Environment, Ecology and Climate Change the Clearance of Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) Mandatory for the Environmental Release of Genetically Modified (GM) Crops.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) is the statutory committee constituted under the “Rules for the Manufacture, Use/Import/Export and Storage of Hazardous Micro Organisms/Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells (Rules, 1989)” framed under Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Applications are considered by GEAC as per the provisions of the Rules, 1989 and amendments thereafter. Every set of application has specific form and pre-requisite documents along with recommendations, wherever needed.
About the Clearance:
- Clearance of Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) is mandatory for the environmental release of Genetically Modified (GM) crops. As per the ‘’Rules 1989’’, State/UT Biotechnology Coordination Committees and District Level Committees are responsible for monitoring instances of illegal cultivation of GM crops and taking appropriate action under Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- The Chief Secretary of State/UT is the Chairperson for the State Biotechnology Coordination Committee (SBCC). Any complaints that come to the notice of GEAC secretariat are sent to the Chief Secretary.
- For the consideration of any application related to confined field trials of Genetically Modified (GM) crops by GEAC, NOC from the State/UT Government is required.
For Genetically Modified Crop
- Bt cotton is the only GM crop which has been approved for commercial cultivation in India. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) conducted study during (2012 -2015) on impact of Bt cotton on 2700 cotton growing farmers belonging to 18 major cotton growing districts of Maharashtra and it was observed that the average seed cotton yield increased after the adoption of Bt Cotton.
- Also, ICAR has done the feeding studies of Bt cotton on various animals viz., broiler chickens, lambs, cows and goat which was found to be safe.

4.INDIA DESIGNATES 5 NEW RAMSAR SITES
THE CONTEXT: India has designated five (5) new wetlands of International importance, which include three wetlands (Karikili Bird Sanctuary, Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest & Pichavaram Mangrove) in Tamil Nadu, one (Pala wetland) in Mizoram and one wetland (Sakhya Sagar) in Madhya Pradesh, making a total of 54 Ramsar sites in the country. The Ramsar sites have been increased from 49 to 54 Ramsar sites.
THE EXPLANATION:
- India has the largest number of Ramsar sites in Asia, according to data available with the Environment Ministry. A wetland is an ecosystem flooded by water, seasonally or permanently.
- Under the Ramsar Convention, an intergovernmental treaty for the conservation of wetlands, contracting parties are expected to identify and place suitable wetlands onto the ‘list of wetlands of international importance’, also known as the Ramsar List.
- The convention has several mechanisms to help parties designate their most significant wetlands as Ramsar Sites, and to take the steps necessary to manage them effectively by maintaining their ecological character.
Criteria for declaring the wetlands
- “Ramsar Sites are designated because they meet the criteria for identifying wetlands of international importance. The first criterion refers to sites containing representative, rare or unique wetland types, and the other eight cover sites of international importance for conserving biological diversity. These criteria emphasize the importance the convention places on sustaining biodiversity,” the convention’s website states.
- The Pichavaram mangrove, for instance, which got the Ramsar tag on April 8, 2022 is one of the largest mangrove ecosystems in India with littoral and swamp forest habitats, located between the estuaries of the Vellar and Kollidam rivers. Trees here are permanently rooted under a few feets of water.

THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5.THE PRIVATE SECTOR BOOST IN INDIA’S SPACE INDUSTRY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Principal Scientific Advisor stated earlier this month that the government would soon come up with a new space policy that could initiate the rise of India’s own “SpaceX-like ventures”.
THE EXPLANATION:
- He also stated that the proposed move would increase private sector participation in the industry. Consultations have already been held and the final version of the policy would soon be referred to the Empowered Technology Group for further examination.
- According to him, India has not tapped into its complete potential in this sector. “In 2022, the space sector is witnessing what the information technology sector experienced in the 1990s. We will have our own SpaceX (SpaceX is Elon Musk’s private space transportation company) in the next two years”.
Why is development in the space sector important?
- Enhancing space technology would be beneficial to bolster connectivity and combat climate-related implications through a more secure and effective means.
- Satellites provide more accurate information on weather forecasts and assess (and record) long-term trends in the climate and habitability of a region. For example, by monitoring the long-term impact of climate change at regional, territorial, and national scales, governments would be able to devise more pragmatic and combative plans of action for farmers and dependent industries.
- Additionally, they can also serve as real-time monitoring and early-warning solutions against natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, wildfires, mining etc. Real-time tracking can also serve multiple purposes in defence.
- As for connectivity, satellite communication can reach more remote areas where conventional networks would require a heavy complimenting infrastructure.
- Additionally, as to reliability, the World Economic Forum had stated (in September 2020) that satellite communication can help connect 49% of the world’s unconnected population. In this light, it must be noted that satellite communications, which are used to facilitate telecommunication services, are among the major categories for investment in the space technology sector. Other prominent categories include spacecraft and equipment manufacturing.
Where does India stand in the global space market?
- As per SpaceTech Analytics, India is the sixth-largest player in the industry internationally having 6% of the world’s space-tech companies (as of 2021). U.S. holds the leader’s spot housing 56.4% of all companies in the space-tech ecosystem. Other major players include U.K. (6.5%), Canada (5.3%), China (4.7%) and Germany (4.1%).
- The Indian Space Industry was valued at $7 billion in 2019 and aspires to grow to $50 billion by 2024. The country’s standout feature is its cost-effectiveness. India holds the distinction of being the first country to have reached the Mars’ orbit in its first attempt and at $75 million — way cheaper than Western standards.
- India’s total budgetary allocation for FY 2022-23 towards the Department of Space was ₹13,700 crore. Further, as per Tracxn data, funding into the sector’s start-ups (in India) nearly tripled to $67.2 million on a year-over-year basis in 2021.
How is the private sector’s involvement regulated in India?
- In June 2020, the Union government announced reforms in the space sector enabling more private players to provide end-to-end services.
- An announcement for the establishment of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) was made. It was mandated the task of promoting, authorising and licensing private players to carry out space activities. As an oversight and regulatory body, it is responsible for devising mechanisms to offer sharing of technology, expertise, and facilities free of cost (if feasible) to promote non-government private entities (NGPEs).
- Additionally, constituted in March 2019, NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL), is mandated to transfer the matured technologies developed by the ISRO to Indian industries. All of them are under the purview of the Ministry of Defence.
- Private sector’s involvement in the long term, as with other commercial sectors, is believed to help spur investment and expertise in the realm which is capital-intensive and demands high technology.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
6.VOCAL FOR LOCAL IN FOOD PROCESSING SECTOR
THE CONTEXT: As part of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan – Vocal for Local Initiative in food processing sector, Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) is implementing a centrally sponsored “PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme” for providing financial, technical and business support for setting up / upgradation of micro food processing enterprises in the country.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The scheme is operational for a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25 with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 Crore. Scheme primarily adopts One District One Product (ODOP) approach to reap the benefit of scale in terms of procurement of inputs, availing common services and marketing of products. It provides the framework for value chain development and alignment of support infrastructure.
- As per the Annual Survey of Industries, 2015-16 and 73rd Round Survey of National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO), there are about 25 lakh unregistered/ unincorporated food processing enterprises in the country. The details of State-wise number of unregistered/unincorporated enterprises in the country are at Annexure-I.
ABOUT THE SCHEME:
The PMFME scheme is designed to address the challenges faced by the micro enterprises and to tap the potential of groups and cooperatives in supporting the upgradation and formalization of these enterprises. The scheme aims to enhance the competitiveness of new and existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry and promote formalization of the sector.
The details of assistance available to Micro Food Processing Enterprises under PMFME Scheme:
- Support to Individual / Group Category Micro Enterprises: Credit-linked capital subsidy @35% of the eligible project cost, maximum ceiling Rs.10 lakh per unit;
- Support to SHGs for seed capital: Seed capital @ Rs. 40,000/- per member of SHG engaged in food processing for working capital and purchase of small tools subject to maximum of Rs. 4 lakh per SHG Federation.
- Support for Common Infrastructure: Credit linked capital subsidy @35% subject to maximum of Rs. 3 crore to support FPOs, SHGs, Cooperatives and any Government agency for setting up of common infrastructure. The common infrastructure will also be available for other units and public to utilize on hiring basis for substantial part of the capacity.
- Branding and Marketing Support: Grant upto 50% for Branding and Marketing to groups of FPOs/ SHGs/ Cooperatives or an SPV of micro food processing enterprises.
- Capacity Building: The scheme envisages training for Entrepreneurship Development Skilling (EDP+): program modified to meet the requirement of food processing industry and product specific skilling.
- Capacity building and training is a critical component of the scheme in technical upgradation and formalization of micro food processing enterprises. The focus areas for capacity building are entrepreneurship development, compliance of Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) standards and general hygiene and other statutory compliances. District Resource Persons (DRPs) have been entrusted to provide handholding support to micro food processing enterprises for the compliance of FSSAI and other statutory requirements.
VALUE ADDITION:
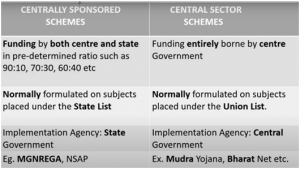
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CENTRALLY SPONSORED SCHEMES AND CENTRAL SECTOR SCHEMES