Today’s Important Articles for Geography (23-06-2022)
Today’s Important Articles for Sociology (23-06-2022)
Today’s Important Articles for Pub Ad (23-06-2022)
- Indian legislative processes need a framework for accountability READ MORE
- Delay in data law can prove costly READ MORE
- UNIFORM CIVIL CODE TO STRENGTHEN UNITY READ MORE
- SC’s Judgment on Compulsory Vaccination Addresses Executive Accountability READ MORE
- Why PILs Are Necessary for Securing a Welfare State READ MORE
WSDP Bulletin (23-06-2022)
(Newspapers, PIB and other important sources)
Prelim and Main
- Golden era of the Santhals in India, say community leaders READ MORE
- Understanding bird strikes and aviation safety READ MORE
- $1-trillion scope for digital economy: PM Modi READ MORE
- Indian Oil unveils indoor solar cooking system READ MORE
- CAD narrows on quarter to 1.5% in Q4, seen wider in Q1 READ MORE
- Globally 78.2 million children out of school: UN report READ MORE
- Sebi sets up panel on hybrid securities READ MORE
- Bharat Gaurav train connecting India and Nepal flagged off READ MORE
Main Exam
GS Paper- 1
- NE floods: Climate is not the only villain READ MORE
GS Paper- 2
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
- Indian legislative processes need a framework for accountability READ MORE
- Delay in data law can prove costly READ MORE
- UNIFORM CIVIL CODE TO STRENGTHEN UNITY READ MORE
- SC’s Judgment on Compulsory Vaccination Addresses Executive Accountability READ MORE
- Why PILs Are Necessary for Securing a Welfare State READ MORE
SOCIAL ISSUES AND JUSTICE
- Pride Matters | The fight for meaningful queer emancipation READ MORE
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
- BRICS summit needs to focus on breaking Western hegemony READ MORE
- Gulf nations must avow India’s step READ MORE
GS Paper- 3
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
- Towards a single low tax regime: The Finance Minister should do away with all the confusing tax slabs in one fell swoop READ MORE
- GST compensation to States can stop READ MORE
- View: WTO must emphasise that it is not just about free trade but also about fair trade READ MORE
- Fiscal weakness: State finances can impede growth READ MORE
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
- Rain-Triggered Floods in Assam and Bangladesh Conjure Climate Warnings READ MORE
- India’s rivers are heating up due to climate change, shows study READ MORE
GS Paper- 4
ETHICS EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDY
- Elusive ethics READ MORE
- MeitY To Hold Public Consultation For The Proposed IT Rules Changes READ MORE
- The dark side of corporate governance READ MORE
Questions for the MAIN exam
- Codes of conduct and business principles are necessary, but integrity and ethics are the essences of true professionalism. Comment.
- Why PILs are necessary for securing a welfare state? How Judicial review of State action assumes greater importance to protect the rights of the disadvantaged sections of society?
- Discuss, how the unsustainable level of debt in states would not only affect growth prospects, but could also pose risks to macroeconomic stability?
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
- Corporate governance in companies is suffering from nepotism, old networks, favouritism, we-use-each-other mentality.
- Corporate governance rules and regulations alone can’t change anything. It’s a deep human awakening that could positively impact a better corporate journey.
- Judicial review of State action (or inaction) assumes greater importance when the rights and aspirations of the disadvantaged sections of society are at stake.
- Democracy is often called a tyranny of the majority.
- An unsustainable level of debt in some of the large states would not only affect growth prospects but could also pose risks to macroeconomic stability.
- The Government has asserted its respect for all religions while the Gulf countries have often been suspect in establishing their secular credentials.
- The lack of law not only means that entities, private or public, are not required to take proactive steps to protect the sensitive personal information of the public, but also that when a person’s privacy is violated, the only recourse lies in the courts.
- The obstruction of the natural flow of water through dams, barrages, and embankments, deforestation and mining in the hills, the destruction of wetlands, development activities on river banks, and unplanned urbanisation have all contributed to rivers losing their navigability.
- Formalized impact assessments before and after any law is enacted or scheme rolled out may help deliver superior outcomes
50 WORD TALK
- This whole argument that the Indian Army soldiers are old and, therefore, the military needs a reform of the Agnipath type is a made-up argument. Individuals normally don’t do very well in their first exposure to fire. Operations need battle-hardened soldiers and not greenhorns. The word ‘veteran’ when used in the context of the Army, signifies exactly that. The combination of physical fitness, endurance and experience deliver in the battle.
- Adopting new laws including a code of conduct themselves will not take us far without implementing the spirit and the word as well as political will. Integrity and ethics are the essences of true professionalism. Codes of conduct and business principles are necessary, but not sufficient. A moral standard is a set of values, norms or principles. This moral standard generates the general ethical demands on each functionary, which, in turn, creates an organisation’s ethos and culture.
Things to Remember:
- For prelims-related news try to understand the context of the news and relate with its concepts so that it will be easier for you to answer (or eliminate) from given options.
- Whenever any international place will be in news, you should do map work (marking those areas in maps and exploring other geographical locations nearby including mountains, rivers, etc. same applies to the national places.)
- For economy-related news (banking, agriculture, etc.) you should focus on terms and how these are related to various economic aspects, for example, if inflation has been mentioned, try to relate with prevailing price rises, shortage of essential supplies, banking rates, etc.
- For main exam-related topics, you should focus on the various dimensions of the given topic, the most important topics which occur frequently and are important from the mains point of view will be covered in ED.
- Try to use the given content in your answer. Regular use of this content will bring more enrichment to your writing.
DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (JUNE 23, 2022)
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
38TH INDIA – INDONESIA COORDINATED PATROL
THE CONTEXT: The 38th edition of India–Indonesia Coordinated Patrol (IND-INDO CORPAT) between the Indian Navy and the Indonesian Navy is being conducted from 13-24 Jun 22.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Maritime interaction between India and Indonesia has expanded substantially with frequent port visits, participation in bilateral/ multilateral exercises and training exchanges. Under the broad ambit of this strong maritime relationship, the two navies have been carrying out CORPATs along the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) every year since 2002, with the aim of keeping this vital part of the Indian Ocean Region safe and secure for commercial shipping and international trade.
- The CORPAT has also strengthened understanding and interoperability between the navies and facilitated the institution of measures to prevent unlawful activities at sea as well as conduct Search and Rescue (SAR) operations.
- The CORPAT has helped both navies to better understand each other’s operating procedures and enhance interoperability whilst facilitating institutional measures for preventing/ suppressing Illegal Unreported Unregulated (IUU) fishing, drug trafficking, maritime terrorism, armed robbery and piracy in the region. The sea phase for the 38thedition of CORPAT was undertaken from 20 – 21 Jun 22 along the IMBL in the Andaman Sea, whilst the closing ceremony is scheduled at Sabang, Indonesia on 23 June 22.
- The 38th Ind-Indo CORPAT will contribute to Indian Navy’s efforts to consolidate inter-operability and forge strong bonds of friendship with the Indonesian Navy.
VALUE ADDITION:
INDIA -INDONESIA TIES
- It is the World’s largest Island Country with more than 17,000 islands.
- It has the 4th largest population in the world.
- Indonesia was one of the founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement along with India.
- India is the largest buyer of crude palm oil from Indonesia and also imports coal, minerals, rubber, pulp and hydrocarbon in significant quantities. India exports refined petroleum products, maize, commercial vehicles, telecommunication equipment, oil seeds to Indonesia. There is a need to balance our bilateral trade as India’s import from Indonesia was US$ 15 billion against export of US$ 4 billion in 2014-15.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
INDIA REPORTS FY22 CAD OF 1.2% AS TRADE DEFICIT WIDENS
THE CONTEXT: According to data released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India recorded a current account deficit (CAD) of 1.2% of GDP in 2021-22 against a surplus of 0.9% in 2020-21 as the trade deficit widened to $189.5 billion from $102.2 billion a year earlier.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Net invisible receipts were higher in 2021-22 on account of an increase in net exports of services and net private transfer receipts though net income outgo was higher than a year ago.
- Net Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows at $38.6 billion in 2021-22 were lower than $44 billion in 2020-21. Net Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) recorded an outflow of $16.8 billion in 2021-22 as against an inflow of $36.1 billion a year earlier.
- For the January-March 2022 quarter, the CAD narrowed on a sequential basis to $13.4 billion, or 1.5% of GDP, against $22.2 billion, or 2.6% of GDP, in the December 2021 quarter.
- The merchandise trade deficit narrowed to $54.5 billion in the March quarter compared with a deficit of $60.4 billion in the previous quarter. The deficit in the same quarter a year earlier, however, had stood at $41.7 billion.
- As per the data, net External Commercial Borrowings to India recorded an inflow of $7.4 billion in 2021-22 compared with $0.2 billion in 2020-21. In 2021-22, there was an accretion of $47.5 billion to foreign exchange reserves on a Balance of Payment (BoP) basis, the RBI data showed.
- Net foreign portfolio investment recorded an outflow of $15.2 billion – mainly from the equity market. Net ECBs to India were lower at $3.3 billion in Q4 2021-22 as compared with $6.1 billion a year earlier.
- As per preliminary data on India’s BoP for the fourth quarter (January to March), current account deficit (CAD) decreased to $13.4 billion (1.5% of GDP) in Q4 2021-22 from $22.2 billion (2.6 % of GDP) in Q3:2021-22. “The sequential decline in CAD in Q4 2021-22 was mainly on account of a moderation in trade deficit and lower net outgo of primary income”.
VALUE ADDITION:
Current Account Deficit:
- The current account deficit is a measurement of a country’s trade where the value of the goods and services it imports exceeds the value of the products it exports. The current account includes net income, such as interest and dividends, and transfers, such as foreign aid, although these components make up only a small percentage of the total current account.
- The current account represents a country’s foreign transactions and, like the capital account, is a component of a country’s balance of payments (BOP).
External Commercial Borrowing:
- External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) refers to the debt shouldered by an eligible entity in India for solely commercial purposes, that has been extended by external sources, i.e. from any recognized entity outside India. These borrowings are expected to conform to norms and conditions put forth by the RBI. The ECB’s fall under the umbrella of RBI regulations.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
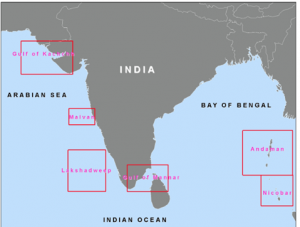
FOUR NEW CORALS WERE RECORDED FROM INDIAN WATERS
THE CONTEXT: Scientists have recorded four species of azooxanthellate corals for the first time from Indian waters. These new corals were found in the waters of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Azooxanthellate corals are a group of corals that do not contain zooxanthellae and derive nourishment not from the sun but from capturing different forms of plankton. These groups of corals are deep-sea representatives, with the majority of species reporting from between 200 m to 1000 m. Their occurrences are also reported from shallow coastal waters.
- Zooxanthellate corals, meanwhile, are restricted to shallow waters.
- “Most studies of hard corals in India have been concentrated on reef-building corals while much
 is not known about non-reef-building corals. These new records enhance our knowledge about non-reef-building, solitary corals”.
is not known about non-reef-building corals. These new records enhance our knowledge about non-reef-building, solitary corals”. - There are about 570 species of hard corals found in India and almost 90% of them are found in the waters surrounding Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The pristine and oldest ecosystem of corals shares less than 1% of the earth’s surface but they provide a home to nearly 25% of marine life.
- Four species of azooxanthellate corals were recorded for the first time from the waters of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) scientist behind these new records, said that all four groups of corals are from the same family Also, they noted that the coral reefs are one of the most productive, sustainable and pristine ecosystems of the world’s oceans, especially in shallow coastal waters.
VALUE ADDITION:
What are corals?
- Corals are invertebrate animals belonging to a large group of colourful and fascinating animals called Cnidaria.
- Each coral animal is called a polyp, and most live in groups of hundreds to thousands of genetically identical polyps that form a ‘colony’. The colony is formed by a process called budding, which is where the original polyp grows copies of itself.
What are coral reefs?
- Coral reefs are created by millions of tiny polyps forming large carbonate structures. Coral reefs are the largest living structure on the planet, and the only living structure to be visible from space.
- Corals are found across the world’s ocean, in both shallow and deep water, but reef-building corals are only found in shallow tropical and subtropical waters. This is because the algae found in their tissues need light for photosynthesis and they prefer water temperatures between 22-29°C.
DISTRIBUTION OF CORALS ALONG THE INDIAN COASTS
THE SECURITY AFFAIRS
DIGITAL WEARABLES CAN EXPOSE USERS TO CYBERATTACKS: IEEE
THE CONTEXT: The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), a global outfit for technical professionals warned that Digital wearables, smartwatches and fitness trackers pose unique threats to the security and privacy of customer data.
THE EXPLANATION:
- As per a document shared by the IEEE, most criminal intrusions of computer networks have a financial motive. That may lead people to conclude that wearables have a low cybersecurity risk. But wearables data, especially in healthcare settings, is often tied to financial information.
- It also noted that, “Depending on the organisation from which it was obtained, stolen health data can be extremely valuable because it often includes so much personally identifiable information – including birthdays, email addresses and other login information, that can be used for identity theft purposes.
- Hospitals, for example, should maintain extensive databases of personally identifiable information for billing purposes. Hence the rise of wearables, implants and other connected devices adds a new dimension to cybersecurity risk, the body suggested.
- India has been witnessing massive adoption of wearable technology in recent years. Wearables have become popular in the country as they allowed users to stay connected and also offered tracker services for health, medication, sleep, exercise/walk etc.
- The wearables market in India had record-breaking double-digit growth in the first quarter of 2022, with shipments surpassing 13.9 million devices, as per International Data Centre (IDC).

VALUE ADDITION:
What is wearable technology?
Wearable technology is any kind of electronic device designed to be worn on the user’s body. Such devices can take many different forms, including jewellery, accessories, medical devices, and clothing or elements of clothing. The term wearable computing implies processing or communications capabilities, but in reality, the sophistication among wearables can vary.
CHALLENGES OF WEARABLE TECHNOLOGIES
- Lack of authentication: Manufacturers often ship wearable devices without a built-in security mechanism such as user authentication or PIN system protection features.
- Lack of encryption: Data collected by wearables are very valuable but some third-party apps neglect to include basic security standards and send or store information that’s not encrypted.
- Insecure wireless connectivity: Wearable devices connect to smartphones wirelessly via protocols such as Bluetooth, NFC, and WiFi. But the security of these wireless channels can be insufficient against determined hackers.
- Insecure Cloud data: Data synchronized to cloud storage are also vulnerable to a number of threats such as distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, SQL injection or back door attacks.
If left unchecked, these vulnerabilities can be a point of entry for attackers that can exploit legitimate enterprise credentials or hospital records which would lead to loss of or the ransom of sensitive data.
THE HISTORICAL TIDBITS
THE TOTAL WAR
THE CONTEXT: Long-drawn wars such as the Russian-Ukraine war raise fears of another world war. But world wars are different from limited wars.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Total War?
- Total war is a military conflict in which the participants are willing to make any sacrifice in lives and other resources so that they obtain a total or complete victory. This feature makes it different from limited war.
- The modern concept of total war can be traced to the writings of the 19th-century Prussian military strategist Carl von Clausewitz. Clausewitz denied that wars could be fought by laws. In his major work Vom Kriege (On War) described wars as tending constantly to escalate in violence toward a theoretical absolute. Clausewitz also stressed the importance of crushing the adversary’s forces in battle.
What are some of the features of total war?
- Total war is categorised by the participation of most countries of the world. Most of the major powers of the world participate in a total war.
- Total war is fought at multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Total participation of warring nations is another important feature. It is not just military forces but the entire society that participates in the war to ensure favourable outcomes.
- It is also categorised by the latest weapons and technologies.
- Use of weapons for mass destruction is also an important feature of total war.
- A total war is always long-drawn.
- No difference is seen between the combats and non-combats in a total war.
- Development of new military infrastructure is witnessed during total war.
- Total war is also characterised by its decisive outcomes. One of the parties involved in the war has to lose to bring the war to an end.
- A total war is also a war of attrition.
- Total impact is another important feature of total war. As the entire nation participates, the impact of the war is felt by every dimension of human life.
THE MISCELLANEOUS
ISRAEL UNCOVERS A RARE EARLY MOSQUE IN NEGEV
THE CONTEXT: Israeli archaeologists unveiled a rare ancient mosque in the country’s south that the antiquities officials said sheds light on the region’s transition from Christianity to Islam.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the Archaeologists, the remains of the mosque, believed to be more than 1,200 years old, were discovered during works to build a new neighbourhood in the Bedouin city of Rahat.
- The mosque located in the Negev desert contains “a square room and a wall facing the direction of Mecca”, with a half-circle niche in that wall pointing to the south.
- “These unique architectural features show that the building was used as a mosque,” the authority said, noting it probably hosted a few dozen worshippers at a time.
- Three years ago, the authority unearthed another mosque nearby from the same era of the seventh to eighth century AD, calling the two Islamic places of worship “among the earliest known worldwide”.
- The mosques, estate and other homes found nearby illuminate “the historical process that took place in the northern Negev with the introduction of a new religion — the religion of Islam, and a new rulership and culture in the region”.
- “These were gradually established, inheriting the earlier Byzantine government and Christian religion that held sway over the land for hundreds of years.”

THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION FOR 23RD JUNE 2022
- Consider the following statements:
- Loktak lake is located in Nagaland.
- It is famous for the phumdis, floating organic matter.
- It is last natural refuge of the Sangai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2
b) 2 and 3
c) 1 and 3
d) 1, 2 and 3
ANSWER FOR 22ND JUNE 2022
ANSWER: C
EXPLANATION:
- Boyfriend loophole refers to a gap in American federal and some state gun laws that allow access to guns by dating abusers.
- It would prohibit dating partners- not just spouses- from owning guns if they had been convicted of domestic violence.
Day-230 | Daily MCQs | UPSC Prelims | INDIAN MODERN HISTORY
| [WpProQuiz 260] |