THE PARLIAMENTARY PROCEEDINGS: BUDGET SESSION 2022
1. PARLIAMENT PASSES CONSTITUTION (SCHEDULED TRIBES) ORDER (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2022
THE CONTEXT: Both the houses of the Parliament has passed the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Bill seeks to amend the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950, which specifies the tribes and tribal communities deemed to be Scheduled Tribes (STs) in various states and union territories.
- Inclusion of certain community in the list of STs in Tripura: The Bill seeks to amend Part XV of the Schedule to the 1950 Order, which specifies the STs in Tripura. It includes the Darlong community as a sub-tribe of the Kuki tribe in the list of STs in Tripura.
Value Addition:
- Darlongs is a small community of around 11,000 people in Tripura.
- Despite its small population, the community has a high prevalence of education, cultural activities and members of the community are serving in different high positions in the local administration.
- Tribal musicologist and Rosem (tribal instrument) maestro Thanga Darlong was conferred the prestigious Padma Shri award a few years back for his contribution to culture.
- Darlongs, despite being Scheduled Tribes, were never given ST certificates.
- Since they were considered a generic tribe under the Kuki community, they were handed their tribal certificates as members of ‘Kuki’ community.
- The subsequent identity crisis among them, especially Darlong youths, who were equipped with modern education, culminated in the demand for a separate statutory identity of their own in 1995.
Tribes of Tripura-
- Tripura, the tiny Northeast state of 37 lakh people houses 19 tribal communities.
- These include Tripuri or Debbarma, Reangs or Brus, Jamatia, Noatia, Uchoi, Chakma, Mog, Lushai, Kuki, Munda, Kour, Oram, Santhal, Bhil, Bhutia, Chaimar or Sermai, Garo, Khasi, Lepcha and Halam.
- Many of these communities are further divided into sub-tribes. For example, Kuki’s have nearly 17-18 sub-tribes within the community.
- It is an umbrella tribal community including many smaller clans like Khasi, Lushai, Hmars and other generic clans.
- In course of time, Lushai, Hmar, Garo etc. came out of Kuki as separate communities.
- Halam community also has several sub-tribes such as Rangkhawl, Ranglong, Dab, Chaimar or Sermai, Bong, Korbong, Harbong, Bongcher etc.
- Out of 37 lakh people of Tripura, nearly 30 per cent are tribals, who mostly live in areas under jurisdiction of the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council (TTAADC), spread in patches across all eight districts and covering 70 per cent of the state’s geographical area.
- The state, which was ruled by tribal kings for over 500 years till 1949, when it merged into the Indian Union, saw tribals become minority in their own state due to arrival of East Pakistani refugees who fled their country.
2. RESERVATION TO OBCS
THE CONTEXT: According to the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment,
(i) The following States have provided 27% to OBCs: –
Assam, NCT of Delhi, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana (27% in Class III & IV posts, 10% in Class I & II posts), Odisha, Uttar Pradesh, Chandigarh, Daman & Diu.
(ii) The following States have given more than 27% reservation to OBCs:-
Andhara Pradesh (29%), Bihar (33%), Karnataka (32%), Kerala (40%),Tamil Nadu (50%),Andaman & Nicobar (38%), Puducherry (34%).
(iii) The following States have given less than 27% reservation to OBCs:-
Chhattisgarh (14%), Himachal Pradesh (12% in Category-I posts & 18% in Category-II posts), Jharkhand (14%), Madhya Pradesh (14%), Manipur (17%), Punjab (12%), Rajasthan (21%), Sikkim (21%), Uttarakhand (14%), West Bengal (17%), Dadra & Nagar Haveli (5%).
(iv) The following States have not given any reservation to OBCs:-
Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Lakshadweep.
The reservation policy in State/UT Government services etc. is decided and implemented by the concerned Governments, while keeping in view the interests of the citizens of the State/UT. The Central Government has no role in deciding the reservation policy of State Government.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
3. INVESTMENT AND EXPORT IN STEEL SECTOR
THE CONTEXT: According to the Union Ministry of Steel, the investment and export in steel sector as follows:
THE EXPLANATION:
- Notification of the following policies having impact on investment and export in the steel sector:-
a. National Steel Policy 2017 which envisages inter-alia domestically meeting the entire demand of steel and high-grade automotive steel, electrical steel, special steel and alloys for strategic applications.
b. Domestically Manufactured Iron & Steel Products (DMI&SP) Policy for promoting procurement of Made in India steel.
c. Steel Scrap Recycling Policy to enhance the availability of domestically generated scrap for making steel at competitive prices.
d. Steel Import Monitoring System (SIMS)in order to enhance production through disseminating advance information regarding grades of the imports for enhancing investment and import substitution.
e. Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Specialty Steel with an outlay of Rs 6,322 Crore to promote the manufacturing of specialty steel within the country for domestic use and export by attracting Capital investments.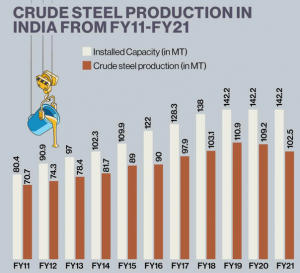
2. Establishment of Project Development Cell in the Ministry to attract and facilitate investment in the steel sector.
3. ‘Make in India’ initiative and the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, with further engagement with potential users, including from Railways, Defence, Petroleum and Natural Gas, Housing, Civil Aviation, Road Transport and Highways, Agriculture and Rural Development sectors to enhance the steel usage, overall demand for steel and investment in steel sector in the country.
4. Adjustments in basic custom duty on steel products and trade remedial measures like Anti-dumping duty (ADD), Countervailing duty (CVD) on certain raw materials and steel products to enhance competitiveness of India’s steel sector.
5. Other measures to improve Ease of Doing Business and Reducing Compliance burden, Market Access Initiatives (MAI), Startup India initiative etc. to help domestic industry in capacity creation, providing level playing field and creating a conducive business environment to attract investments and promote exports.
4. ADB PROJECTS INDIA’S ECONOMY TO GROW BY 7.5% IN FY23
THE CONTEXT: Asian Development Bank projected a 7 per cent collective growth for South Asian economies in 2022 with the subregion’s largest economy India growing by 7.5 per cent in the current fiscal year before picking up to eight per cent the next year.
THE EXPLANATION:
The Manila-based multilateral funding agency, Asian Development Bank (ADB) has projected the GDP growth rate of the Indian economy, in its flagship Asian Development Outlook (ADO) 2022, as follows:
- 2022-23 (FY23): 7.5 per cent
- 2023-24 (FY24): 8.0 per cent
ADB said developing Asia’s economies are forecast to grow 5.2% this year and 5.3% in 2023, thanks to a robust recovery in domestic demand and continued expansion in exports.
VALUE ADDITION:
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- ADB is a regional development bank established in 1966, Headquartered at Manila, Philippines
- It has 68 members. India is a founding member. Forty-nine are from within Asia and the Pacific and 19 outside.
- It aims to promote social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific.
Voting rights:
- It is modelled closely on the World Bank and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members’ capital subscriptions.
- As of 31 December 2020, ADB’s five largest shareholders are Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People’s Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
Roles and functions:
- Dedicated to reducing poverty in Asia and the Pacific through inclusive economic growth, environmentally sustainable growth, and regional integration.
- This is carried out through investments – in the form of loans, grants and information sharing – in infrastructure, health care services, financial and public administration systems, helping nations prepare for the impact of climate change or better manage their natural resources, as well as other areas.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5. GROSS EXPENDITURE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT (GERD)
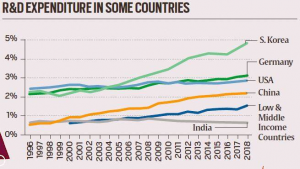
THE CONTEXT: According the Department of Science and Technology, that the Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD), in absolute terms, has been consistently increasing over the years and has increased 3 times during the last 10 years.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According the department, some of the key efforts made by Government include the successive increase in plan allocations for Scientific Departments, incentivizing investment by private sector to increase their share in GERD, improving the ease of doing business in the Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) activities; introducing flexible tools for public procurement; creating avenues for collaborative STI funding through portfolio-based funding mechanisms such as Public-Private-Partnerships and other innovative hybrid funding mechanisms.
- It also noted that, the Government has allowed corporate sector to make R&D investments under the provision of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). Corporates can invest in technology business incubators or contribute in research efforts carried out by institutions and national research laboratories as a part of their CSR.
- Also the Department noted that as part of the new draft Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) policy, several provisions have been included with the focus to increase GERD. Some of the key provisions include; greater participation of central, state, local governments and public sector enterprises; fiscal incentives to attract private sector; fiscal and non-fiscal incentives to attract Foreign Direct Investment; Micro-financing through crowdfunding and philanthropic sources; linking public procurement with domestic industries; Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) and industry led mission oriented joint initiatives; etc.
Value Addition:
- According to UNESCO’s stats, the global expenditure on research and development (R&D) has crossed $1.7 trillion. The most used indicator to measure country-wise investments in R&D is the gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD) as the percentage of gross domestic product (GDP).
- A comparison of the R&D spending of some of the countries representing different regions of the world and India in terms of GERD as a percentage of GDP shows India to be a low spender (only 0.66 per cent of the GDP) in comparison to the developed countries and emerging economic powers of East Asia.
- Worst still, the percentage expenditure for the last couple of years is showing a downward trend. A quick analysis of the allocations to various R&D organisations in the recently presented 2022-23 budget shows continued stagnation.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
6. EXPLAINED: WHY CENTRE HAS OPPOSED ODISHA’S PLANS FOR LANDMARK LINGARAJ TEMPLE
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Home Affairs has said several sections of the proposed ordinance are in conflict with the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act.
THE EXPLANATION:
The Central government has told the Odisha government that its ordinance to bring the 11th-century Lingaraj temple in Bhubaneswar and its associated temples under a special law is outside the legislative competence of the state legislature. It also said the ordinance is in conflict with the rules laid down under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act).
What is the Lingaraj Temple Ordinance, 2020?
- Lingaraj temple, the largest in Bhubaneswar, was constructed by King Jajati Keshari in the 10th Century and completed by King Lalatendu Keshari in the 11th Century.
- In December 2019, the Odisha Government had announced a development plan for the temple and its peripheral area in Bhubaneshwar. The 66-acre “Ekamra Kshetra” development plan was launched to preserve the heritage and development of the nine sites and their nearby areas at a cost of around Rs 700 crore.
Why has the Centre opposed the ordinance?
The Ministry of Home Affairs has said several sections of the proposed ordinance conflicted with the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act. The AMASR Act provides for preservation of ancient and historical monuments and archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
Value Addition:
Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958
- The AMASR Act provides for the preservation of ancient and historical monuments and archaeological sites and remains of national importance. It also provides for the regulation of archaeological excavations and for the protection of sculptures, carvings and other like objects.
- The Archaeological Survey of India functions under the provisions of this act. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham- the first Director-General of ASI. Alexander Cunningham is also known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology”.
- The Act prohibits construction in a ‘prohibited area’, an area of 100 meters around a protected monument was amended in 2010 to declare the 100-metre radius of protected monuments as prohibited areas and the next 300-metre radius as regulated areas.
- It does not permit construction in such prohibited areas even if it is for public purposes, except under certain conditions. The iconic monuments in India, Taj Mahal, Ajanta Caves, The Great Stupa at Sanchi and the Sun Temple of Konark, among others are designated as “ancient monuments of national importance” and protected under the AMASR Act.
- The Archaeological Survey of India is the custodian of these monuments.
ABOUT LINGARAJ TEMPLE
· It was built by King Jajati Keshari in the 10th Century and completed by King Lalatendu Keshari in the 11th Century.
· This great temple represents the quintessence of the Kalinga type of architecture, the culminating result of the architectural activities at Bhubaneswar. (Only Hindus are allowed).It is built in red stone and is a classic example of Kalinga style of architecture (comes under Nagara architecture). |
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. Director of CBI is appointed by Central Government on the recommendation of a committee consisting of which of the following?
- The Prime Minister as Chairperson
- The Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha
- The Chief Justice of India or Judge of the Supreme Court nominated by him
- The union home minister
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 1, 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3 and 4 only
d) All of them
ANSWER FOR 6TH APRIL 2022
Answer: C
Explanation:
- Antarctic Treaty signed in 1959 — India joined the Treaty System in 1983.
- The Antarctic Treaty came into force on June 23, 1961, after ratification by the 12 countries that were then active in Antarctic science. (Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect).
- The Treaty covers the area south of 60°S latitude. (Statement 3 is correct).
- Its key objectives are to demilitarize Antarctica, to establish it as a zone free of nuclear tests and the disposal of radioactive waste, and to ensure that it is used for peaceful purposes only; to promote international scientific cooperation in Antarctica and to set aside disputes over territorial sovereignty. (Statement 4 is correct).
- Of the 54 signatory countries, 29 have ‘consultative’ status that give them voting rights. The Treaty parties meet each year at the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting.