Today’s Important Articles for Geography (04-04-2022)
Today’s Important Articles for Pub Ad (04-04-2022)
Today’s Important Articles for Sociology (04-04-2022)
WSDP Bulletin (04-04-2022)
(Newspapers, PIB and other important sources)
Prelim and Main
- NFC technology for instant payments READ MORE
- The key takeaways of a UNEP report on noise pollution READ MORE
- Government panel recommends inclusion of Covovax in national COVID-19 vaccination drive for 12-17 age group READ MORE
- India, Australia sign FTA, trade likely to ‘double in 5 yrs, generate 1 mn jobs’ READ MORE
- Technological advancements in India’s Aerospace and Defence sector READ MORE
- Prehistoric relics point to riverine settlement at Attappady READ MORE
- WHO records new recombinant SARS-CoV-2 variant READ MORE
Main Exam
GS Paper- 1
- Manual scavenging is a blot on society READ MORE
- Who Has an Authentic Conception of ‘Generation’? READ MORE
GS Paper- 2
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
- Explained: Reforming death penalty READ MORE
- Rethink the criminal identification bill READ MORE
- To fix India’s criminal justice system, weed out the corrupt first READ MORE
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
- Playing the strategic autonomy game: New Delhi should play its cards extremely well right now to invest in future geopolitical dividends READ MORE
- BIMSTEC can boost ties with the East READ MORE
- India puts itself first READ MORE
GS Paper- 3
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
- Renewable energy has a tariff problem. Here’s how to fix it READ MORE
- RBI’s shift in stance imminent READ MORE
- Ways to take Russia-India trade forward READ MORE
- Balance economic & environment policies READ MORE
- The need for evaluation of fiscal policies READ MORE
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
- Climate and Us | The Parvati Valley forest fire is a sign of the times to come READ MORE
- A Promising Conservation Policy for India: Climate Change and the Miyawaki Forests READ MORE
SECURITY
- For a full repeal: The relaxation of AFSPA is welcome, but the demand for full repeal should be considered READ MORE
GS Paper- 4
ETHICS EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDY
- Hellenic wisdom: Balm for frayed nerves READ MORE
- Clash and Creation READ MORE
- In Pursuit of Happiness: The efforts to officially prepare indexed happiness are nothing but an ideological production. READ MORE
Questions for the MAIN exam
- ‘Contemporary Indian diplomacy is a textbook example of a swing state that refuses to swing either way.’ Comment in the light of India’s stand on Ukraine-Russia war.
- “You must change your approach in order to change your results”. Explain the importance of given quotation in a Civil servant life?
- How far do you agree with this view that to achieve $5 Trillion economy, India needs a regional free trade agreement with neighbouring countries and BIMSTEC group is the ideal group for it? Analyse your view.
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
- New Delhi should play its cards extremely well right now to invest in future geopolitical dividends.
- You must change your approach in order to change your results.
- Shifting to a two-part tariff for solar and wind will incentivise private investments.
- Geopolitical choices are almost never black and white, nor are they always readily available. Sometimes, therefore, states must proactively try to shape the environment to generate new options. It is New Delhi’s turn to do so.
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict has only worsened the growth-inflation matrix and raised the spectre of tighter financial conditions.
- India cannot forsake defence ties with Russia. To sidestep Western sanctions, the two nations can revisit rupee-rouble system.
- India as well as other neighbouring countries on the east can gain mutually. This way, India’s act East policy may strengthened.
- Improved connectivity will usher in lower trade cost which could be the driving force for gains from BIMSTEC.
- Criminal identification bill places the privacy of individuals at the mercy of the State; allows for the retention of personal data of convicted individuals for lifetime; and goes against the best practices of data protection.
- The West’s real agenda is the reimposition of a unipolar world order to perpetuate its domination of the international economic and political order.
- The political leadership addressing BIMSTEC cooperation have to realise that pushing a free trade agreement is going to be a domestic exercise, where their own political opponents would create roadblocks.
- In India, it is very difficult to stop a bad economic idea whose time has come, but there is a need for a rigorous assessment of the quality of expenditures by various state governments.
50-WORD TALK
- A longer-term option for countries that are adversely affected by the Western sanctions would be the development of financial messaging systems that can be alternatives to the SWIFT. Russia has developed its own financial messaging system, the SPFS (roughly translated as System for Transfer of Financial Messages) and China has its own Cross-Border Interbank Payment System, or CIPS.
- Air pollution is rising due to the failure of the State and the market forces to give importance to environment. Its genesis lies in policy failure and implementation of less stringent laws & regulations to attract more investment from the developed world. The free market considers only the private cost of production. It fails to consider the social cost of pollution.
Things to Remember:
- For prelims-related news try to understand the context of the news and relate with its concepts so that it will be easier for you to answer (or eliminate) from given options.
- Whenever any international place will be in news, you should do map work (marking those areas in maps and exploring other geographical locations nearby including mountains, rivers, etc. same applies to the national places.)
- For economy-related news (banking, agriculture, etc.) you should focus on terms and how these are related to various economic aspects, for example, if inflation has been mentioned, try to relate with prevailing price rises, shortage of essential supplies, banking rates, etc.
- For main exam-related topics, you should focus on the various dimensions of the given topic, the most important topics which occur frequently and are important from the mains point of view will be covered in ED.
- Try to use the given content in your answer. Regular use of this content will bring more enrichment to your writing.
DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (APRIL 03 & 04, 2022)
THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. NEW CRIMINAL PROCEDURE (IDENTIFICATION) BILL, 2022
THE CONTEXT: According to the new provisions of the Criminal Procedure (Identification) Bill, it will allow police and prison authorities to collect, store and analyze physical and biological samples including the retina and iris scans of convicted, arrested, and detained persons.
THE EXPLANATION
What is the legislation about?
- The Bill seeks to repeal the Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920. The over 100-year-old Act’s scope was limited to capturing finger impressions, footprint impressions, and photographs of convicted prisoners and a certain category of arrested and non-convicted persons on the order of a Magistrate.
- The Statement of Objects and Reasons of the 2022 Bill said that new ‘‘measurement’’ techniques being used in advanced countries are giving credible and reliable results and are recognized the world over. It said that the 1920 Act does not provide for taking these body measurements as many of the techniques and technologies had not been developed then.
What are the major changes proposed?
It proposes four major changes.
- First, it would define ‘‘measurements’’ to include “signature, handwriting, iris and retina scan, physical, biological samples, and their analysis, etc.” It does not specify what analysis means, implying that it may also include storing DNA samples. The “etc.” mentioned in the text of the Bill could give unfettered powers to law enforcement agencies to interpret the law at their convenience, sometimes to the disadvantage of the accused.
- Second, it empowers the National Crime Records Bureau of India (NCRB), under the Union Home Ministry, to collect, store and preserve the record of measurements for at least 75 years. The NCRB will be able to share the data with other law enforcement agencies as well. Police is a State subject and NCRB works under the Union government, and experts contend this provision may impinge on federalism.
- Third, it empowers a Magistrate to direct any person to give vital details, which till now was reserved for convicts and those involved in heinous crimes.
- Fourth, it empowers police or prison officers up to the rank of a Head Constable to take details of any person who resists or refuses to do so.
What are some other changes?
- The Bill also seeks to apply to persons detained under any preventive detention law. The Bill also authorizes taking vital details of “other persons” for identification and investigation in criminal matters. It doesn’t define the “other persons”, implying its ambit extends beyond convicts, arrested persons, or detainees.
- The Bill’s stated objective is it provides legal sanction for taking such details and will make the investigation of crime more efficient and expeditious, and help in increasing the conviction rate.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. INDIA-AUSTRALIA ECONOMIC COOPERATION AND TRADE AGREEMENT (ECTA)
THE CONTEXT: India and Australia signed an Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (IndAus ECTA) which is set to provide zero-duty access to 96 percent of India’s exports to Australia including shipments from key sectors such as engineering goods, gems, jewelry, textiles, apparel, and leather.
THE EXPLANATION:
- ECTA encompasses cooperation across the entire gamut of bilateral economic and commercial relations between the two friendly countries and covers areas like Trade in Goods, Rules of Origin, Trade in Services, Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, Dispute Settlement, Movement of Natural Persons, Telecom, Customs Procedures, Pharmaceutical products, and Cooperation in other Areas.
- Goods: The ECTA between India and Australia covers almost all the tariff lines dealt in by India and Australia respectively. India will benefit from preferential market access provided by Australia on 100% of its tariff lines.
- This includes all the labor-intensive sectors of export interest to India such as Gems and Jewellery, Textiles, leather, footwear, furniture, food, agricultural products, engineering products, medical devices, and Automobiles.
- On the other hand, India will be offering preferential access to Australia on over 70% of its tariff lines, including lines of export interest to Australia which are primarily raw materials and intermediaries such as coal, mineral ores and wines, etc.
- Services: As regards trade in services, Australia has offered wide-ranging commitments in around 135 sub-sectors and Most Favoured Nation (MFN) in 120 sub-sectors which cover key areas of India’s interest like IT, ITES, Business services, Health, Education, and Audiovisual.
- Some of the keys offered by Australia in the services space include a Quota for chefs and yoga teachers; a Post-study work visa of 2-4 years for Indian students on a reciprocal basis; mutual recognition of Professional Services and Other licensed/regulated Occupations; and Work & Holiday visa arrangement for young professionals.
- On the other hand, India has offered market access to Australia in around 103 sub-sectors and Most Favoured Nation in 31 sub-sectors from the 11 broad service sectors such as ‘business services’, ‘communication services’, ‘construction and related engineering services, and so on. Both sides have also agreed to a separate Annex on Pharmaceutical products under this agreement, which will enable fast-track approval for patented, generic, and biosimilar medicines.
- India and Australia are partners in the trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) arrangement along with Japan which seeks to enhance the resilience of supply chains in the Indo-Pacific Region. Further, India and Australia are also members of the recently formed Quad, also comprising the US, and Japan, to further enhance cooperation and develop partnerships across several issues of common concerns.
- The India-Australia ECTA will further cement the already deep, close, and strategic relations between the two countries and will significantly enhance bilateral trade in goods and services, create new employment opportunities, raise living standards, and improve the general welfare of the peoples of the two countries.
Background:
- India-Australia bilateral trade for both merchandise and services is valued at US$ 27.5 billion in 2021. India’s merchandise exports to Australia consist primarily of a broad-based basket largely of finished products like gold jewelry, polished diamonds, etc. India’s merchandise imports consist largely of raw materials, minerals, and intermediate goods.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3. NFC TECHNOLOGY FOR INSTANT PAYMENTS
THE CONTEXT: Google Pay has recently launched a new feature in India, ‘Tap to pay for UPI’, in collaboration with Pine Labs. The feature makes use of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is NFC and how does it work?
- NFC is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows NFC-enabled devices to communicate with each other and transfer information quickly and easily with a single touch — whether to pay bills, exchange business cards, download coupons, or share a document.
- NFC transmits data through electromagnetic radio fields, to enable communication between two devices. Both devices must contain NFC chips, as transactions take place within a very short distance. NFC-enabled devices must be either physically touching or within a few centimeters from each other for data transfer to occur.
How will this technology work with the recently launched feature, ‘Tap to pay for UPI’?
- Google Pay has been the first among UPI apps to bring the Tap to Pay feature working on POS terminals. It will allow users with UPI accounts configured on Google Pay to make payments just by tapping their NFC-enabled Android smartphones on any Pine Labs Android POS terminal.
- Once users tap their phones on the POS terminal, it will automatically open the Google pay app with the payment amount pre-filled. Users can then verify the amount and merchant name and authenticate the payment, using their UPI PIN. They will be notified once the payment is successful.
- The process is much faster compared to scanning a QR code or entering the UPI-linked mobile number which has been the conventional way till now.
What are the other applications of NFC technology?
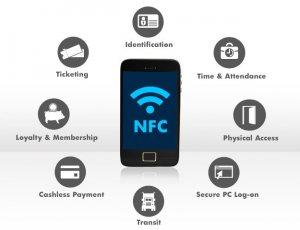
How safe is this technology?
- NFC technology is designed for an operation between devices within a few centimeters from each other. This makes it difficult for attackers to record the communication between the devices compared to other wireless technologies which have a working distance of several meters.
- The user of the NFC-enabled device determines by the touch gesture which entity the NFC communication should take place with, making it more difficult for the attacker to get connected. The security level of NFC communication is by default higher compared to other wireless communication protocols.
- The NFC Forum has also added Peer to Peer communication which is a mechanism to cipher all exchanged data to avoid external interpretation of recorded communication. Since the receiving device reads your data the instant you send it, NFCs also reduce the chance of human error.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN THE NEWS
4. IDEX INITIATIVE
THE CONTEXT: Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) framework was launched by the Government to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace Sector by engaging Industries including MSMEs, startups, individuals innovators, R&D institutes, and academia and promoting self-reliance.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Government has approved a central sector scheme for iDEX with budgetary support of Rs. 498.78 crore for the next 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Aim: to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace Sector by engaging Industries including MSMEs, startups, individual innovators, R&D institutes, and academia and promote self-reliance.
About Innovations for Defence Excellence (IDX):
- The Government has approved a central sector scheme for iDEX with budgetary support of Rs. 498.78 crore for the next 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective of the scheme: to provide financial support to nearly 300 Startups/ MSMEs/individual innovators and about 20 Partner incubators through the Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO).
- For the current financial year 2021-2022, Rs. 45 crore have been released by the Government to iDEX-DIO.
- The iDEX framework and establishment of the DIO by the Department of Defence Production (DDP) is aimed at promoting innovation and indigenization in the aerospace and defense sector at the start-up level.
- iDEX will be funded and managed by a “Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO)‟ formed as a “not for profit‟ company as per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 for this purpose.
- It aims at empowering a culture of technology co-creation and co-innovation in the sector and boosts innovation among the start-ups and encourages them to be a part of the ecosystem.
THE HEALTH AND COVID CORNER
5. WHO RECORDS THE NEW SARS-COV-2 VARIANT
THE CONTEXT: The World Health Organization (WHO) has flagged the emergence of a new variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the XE recombinant, in the United Kingdom, and with a possibly higher rate of transmission.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The WHO, in its recent epidemiological update, said the recombinant was detected in the United Kingdom on January 19, 2022, and over 600 sequences have been reported and confirmed since.
- It also added, “the early-day estimates indicate a community growth rate advantage of about 10% as compared to BA.2, however, this finding requires further confirmation.”
- The U.K. Health Security Agency (UKHSA), which tracks SARS-CoV-2 variants, analyzed three recombinants, known as XF, XE, and XD. Of these, XD and XF is recombinant of Delta and Omicron BA.1, while XE is a recombinant of Omicron BA.1 and BA.2.
- According to WHO, While XE only accounts for a small fraction of the cases, its extremely high transmissibility could mean that it becomes the most dominant strain shortly.
- A recombinant variant occurs when an individual becomes infected with two or more variants at the same time, leading to a mixing of genetic material in the human body. Several such recombinants have emerged in the past during the pandemic.
- The UKHSA has stated that in the United Kingdom, only 38 cases of XF recombinant have been identified, though none since mid-February 2022.
- The new variant is 10 percent more transmissible than the most contagious BA.2 subvariant.
THE DATASHEET
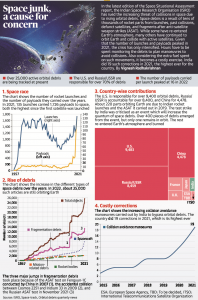
6. THE SPACE JUNK, A CAUSE OF CONCERN
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. UNEP hosts a secretariat of which of the following?
- Convention on Migratory Species
- Minamata Convention
- Convention on Biodiversity
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of them
ANSWER FOR 2ND APRIL 2022
Answer: B
Explanation:
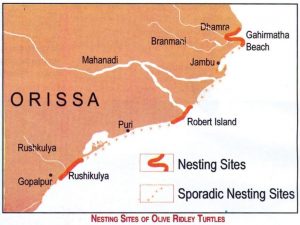
- Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea) are migratory species visiting Indian coasts for nesting.
- These turtles travel all the way from the South Pacific Ocean to breed on the coast of Gahirmatha.
- Their mass nesting phenomenon is called arribadas.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- They have the highest degree of protection as they are included in Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The turtle eggs normally take 45 days to hatch. After this, tiny hatchlings come out and make their way to the sea.
- Threats: Heavy predation of eggs by dogs and wild animals, indiscriminate fishing with trawlers and gill nets, and beach soil erosion.
Day-176 | Daily MCQs | UPSC Prelims | MODERN HISTORY OF INDIA
[WpProQuiz 192]
HOW DID THE LI-ION BATTERY SET OFF A TECHNOLOGY REVOLUTION?
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways said rapid strides in technology and green fuel will reduce the cost of electric automobiles, bringing them at par with petrol-run vehicles in two years. Also, the 2019 Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded to John B. Goodenough, M. Stanley Whittingham, and Akira Yoshino for working towards the development of practical lithium-ion batteries.
In this context, this article analyses the scope of the Lithium-Ion Battery Market: Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity, and the way forward.
THE EXPLANATION
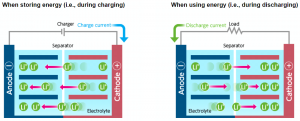
What is a lithium-ion battery and how does it work?
- A lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that is charged and discharged by lithium ions moving between the negative (anode) and positive (cathode) electrodes. (Generally, batteries that can be charged and discharged repeatedly are called secondary batteries, whereas disposable batteries are called primary batteries.)
- Because lithium-ion batteries are suitable for storing high-capacity power, they are used in a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics such as smartphones and PCs, industrial robots, production equipment, and automobiles.
Lithium-ion Battery – Applications
⦁ Electronic gadgets
⦁ Tele-communication
⦁ Aerospace
⦁ Industrial applications
⦁ Lithium-ion battery technology has made it the favorite power source for electric and hybrid electric vehicles
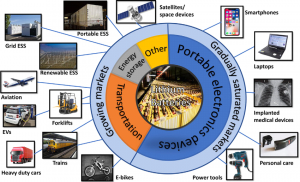
SIGNIFICANCE OF LI-ION BATTERIES IN THE CONTEXT OF THE ELECTRONIC MARKET
According to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, India imported lithium cells and batteries – including rechargeable li-ion type devices – worth INR 8,984 crore in the last fiscal year (2020-2021). This figure consisted of INR 173 crore of non-rechargeable lithium devices and INR 8,811 crore of lithium-ion products.
China and Hong Kong were the chief sources of imports with China shipping 72.73% of the lithium-ion products imported by India and 32.05% of the non-rechargeable lithium cell devices. Hong Kong products accounted for 23.48% and 37.32% of those respective markets.
Indian lithium battery demand is expected to surge with the products used in renewable energy storage facilities and electric vehicles as well as data centers and consumer electronics. According to other data, the Indian lithium-ion battery market reached a value of US$ 2.1 Billion in 2021.
THE DOMESTIC PUSH
Recently, the Geological Survey of India has taken up seven other lithium exploration projects in Karnataka, Arunachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Jammu and Kashmir, and Rajasthan.
The reason: The ancient igneous rock deposits in the region (a by-product of large-scale volcanic activity in the Deccan plateau millions of years ago) hold the first traces of Lithium ever to be discovered in India
MAJOR IMPACTS ON E-VEHICLES: A POTENTIAL ALTERNATIVE TO REDUCE THE COAL DEPENDENCY
One of the major factors driving the rising demand for Lithium-Ion batteries is the growing popularity of electric cars. Rising EV sales across the country, particularly in the 2- and 3-wheeler segments, have boosted the demand. Lithium batteries have transformed how they are utilized due to their advantages over lead-acid batteries.
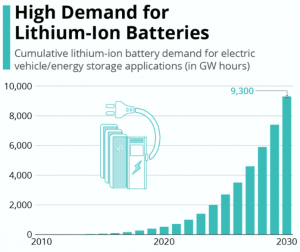
By 2030, the market for electric vehicle
power packs are expected to reach $300 billion, with a large secondary market of more than 2.5 million e-rickshaws and 4,00,000 lead-acid battery-powered two-wheelers now on the road.
The most expensive component of an electric car is the lithium-ion battery, which accounts for 40-50 percent of the total cost. With the growing use of electric vehicles in our transportation system, the demand for Li-ion batteries for EV applications is expected to soar. Other uses, such as renewable energy integration with the grid, will raise Li-Ion battery demand in addition to electric vehicles.
According to government projections, India would require a minimum of 10 GWh of Li-ion cells by 2022. By 2025, it will be around 60 GWh, and by 2030, it will be around 120 GWh.
Environmental Aspect:
- According to the World Air Quality Report 2021, published by Swiss Organization -IQ Air where it stated “India was home to 11 of the 15 most polluted cities in Central and South Asia in 2021. Delhi saw a 14.6% increase in PM2.5 concentrations in 2021, with levels rising to 96.4 µg/m3 from 84 µg/m3 in 2020.
- It also highlighted that sources of PM2.5 “include internal combustion engines, power generation, industrial processes, agricultural processes, construction, and residential wood and coal burning.
- According to a Government source, by 2030, nearly three-fourths of Indian two-wheelers and all new cars are expected to be EVs (electric vehicles). It will significantly reduce the dependency on coal and reduce pollution significantly.
MERITS OF LI-ION BATTERIES
Compared to their lead-acid counterparts, lithium-ion batteries are much lighter, more efficient, and have more power storage. These batteries are widely used commercially in mobiles, laptops, and other electronic equipment.
High energy density: High energy density is one of the chief advantages of lithium-ion battery technology. With electronic equipment such as mobile phones needing to operate longer between charges while still consuming more power, there is always a need for batteries with a much higher energy density.
For example, NiMH batteries would not be able to provide the charge capacity required for a modern smartphone. Using Nickel Metal Hydride battery technology, a smartphone would not last long enough, especially if the battery needed to keep within the same size constraints.
In addition to this, there are many power applications from power tools to electric vehicles. The much higher power density offered by lithium-ion batteries is a distinct advantage. Electric vehicles also need battery technology that has a high energy density.
Self-discharge: One issue with many rechargeable batteries is the self-discharge rate. The rate of self-discharge of Li-ion cells is much lower than that of other rechargeable cells such as Ni-Cad and NiMH forms. It is typically around 5% in the first 4 hours after being charged but then falls to a figure of around 1 or 2% per month.
Low maintenance: One major lithium-ion battery advantage is that they do not require maintenance to ensure their performance.
Ni-Cad cells required a periodic discharge to ensure that they did not exhibit the memory effect. As this does not affect lithium-ion batteries and cells, this process or other similar maintenance procedures are not required. Likewise, lead-acid cells require maintenance, some needing the battery acid to be topped up periodically.
Cell voltage: The voltage produced by each lithium-ion cell is about 3.6 volts. This has many advantages. Being higher than that of the standard nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal hydride, and even standard alkaline cells at around 1.5 volts and lead-acid at around 2 volts per cell, the voltage of each lithium-ion cell is higher, requiring fewer cells in many battery applications. For smartphones, a single cell is all that is needed and this simplifies the power management.
Variety of types available: There are several types of lithium-ion cells available. This advantage of lithium-ion batteries can mean that the right technology can be used for the application needed. Some forms of lithium-ion battery provide a high current density and are ideal for consumer mobile electronic equipment. Others can provide much higher current levels and are ideal for power tools and electric vehicles.
DEMERITS OF LI-ION BATTERIES
Fire Risk: Lithium-ion batteries, whether they are used in cars or electronic devices, can catch fire if they have been improperly manufactured or damaged, or if the software that operates the battery is not designed correctly.
The major weakness of lithium-ion batteries in electric cars is the use of organic liquid electrolytes, which are volatile and flammable when operating at high temperatures. An external force such as a crash can also lead to chemical leakage.
Protection/battery management system required: Lithium-ion cells and batteries are not as robust as some other rechargeable technologies. They require protection from being overcharged and discharged too far. In addition to this, they need to have the current maintained within safe limits. Accordingly, one lithium-ion battery disadvantage is that they require protection circuitry incorporated to ensure they are kept within their safe operating limits.
Aging: One of the major lithium-ion battery disadvantages for consumer electronics is that lithium-ion batteries suffer from aging. Not only is this time or calendar dependent, but it is also dependent upon the number of charge-discharge cycles that the battery has undergone.
Often batteries will only be able to withstand 500 – 1000 charge-discharge cycles before their capacity falls. With the development of Li-ion technology, this figure is increasing, but after a while, the battery may need replacing and this can be an issue if they are embedded in the equipment.
Cost: A major lithium-ion battery disadvantage is its cost. Typically, they are around 40% more costly to manufacture than Nickel-cadmium cells. This is a major factor when considering their use in mass-produced consumer items where any additional costs are a major issue.
Developing technology: Although lithium-ion batteries have been available for many years, they can still be considered an immature technology by some as it is very much a developing area. This can be a disadvantage in terms of the fact that the technology does not remain constant. However as new lithium-ion technologies are being developed all the time, it can also be an advantage as better solutions are coming available.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES TO PROMOTE ELECTRIC VEHICLES
- India is the fourth-largest auto market globally, and some estimates suggest there are close to 170 active investors in the country’s EV start-up ecosystem.
- To promote the adoption of EVs, the Department of Heavy Industry formulated a FAME India Scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid and) Electric Vehicles in India) in 2015.
The government has launched the following initiatives to Promote Electric Vehicles in India:
- Under the new GST system, GST on EVs is reduced from 12% to 5% against the 28% GST rate with up to 22% for conventional vehicles.
- The government has proposed the exemption of registration fees for battery-operated/electric vehicles to promote eco-friendly vehicles in the country.
- The Ministry of Power has also allowed the sale of electricity as a ‘service’ for electric vehicles’ charging. It will attract investors into the charging infrastructure.
- Also, The government has granted an exemption to battery-operated transport vehicles and vehicles that run on methanol and ethanol fuels from the requirements of the permit.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has allowed 16-18 years to obtain driving licenses to drive e-scooters.
- Lithium wars: Battery makers are also seeking to take advantage of the ₹18,100-crore production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme to manufacture lithium-ion cells within the country. In such a scenario, securing lithium supplies will play a critical role in the pivot towards a greener economy.
THE CONCLUSION: The use of Lithium-ion batteries is the future of a greener and eco-friendly environment. The use of lithium-ion batteries helps in cutting down the pollution level and improving the air quality. Energy storage and mobility are going to be the most popular concept in India as they won’t only save us costs but also have a huge positive impact on climate change. With the introduction of different government initiatives, the Indian Government is also trying to promote the use of batteries for a secure future. Having a manufacturing unit in India will help in cost reduction and increase employment.
Along with the batteries being manufactured, they can be recycled and reused too, decreasing the usage of gas and leading to an increase in pollution levels. For a better future, we need to start working today and have a clear vision toward the goal.
THE MAIN PRACTICE QUESTIONS:
- The Noble Prize in Chemistry of 2019 was jointly awarded to John B. Goodenough, M. Stanley Whittingham, and Akira Yoshino for working towards the development of practical lithium-ion batteries. How has this invention impacted the everyday life of human beings?
- What are the present challenges before the transition of shifting to e-vehicles? How do emerging technologies provide an opportunity for reducing coal dependency?