DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (MARCH 29, 2022)
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
1. MORADABAD 2ND IN WORLD IN NOISE POLLUTION: UN REPORT
THE CONTEXT: According to the latest report unveiled by the United Nations Environment Programme, Moradabad in Uttar Pradesh has emerged as the second noisiest city in the world, with Delhi, Kolkata, Asansol and Jaipur also exceeding permissible noise limits.
THE EXPLANATION: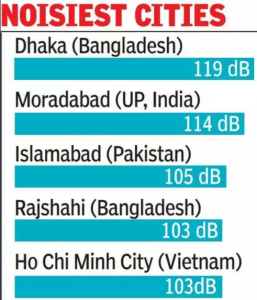
- The UN report titled ‘Frontiers 2022: Noise, Blazes and Mismatches’, released in February 2022, measured noise levels in 61 cities of the world.
- Notably, all the top three cities are from South Asia. Other Indian cities which recorded a higher decibel than the permissible levels were Delhi (83 dB), Kolkata and Asansol (both 89 dB) in West Bengal and Jaipur (84 dB).
- The UNEP report further found that Irbrid in Jordan at 60 decibels was the world’s quietest city, followed by Lyon in France (69 dB), Madrid in Spain (69 dB), Sweden’s capital Stockholm in (70 dB) and Belgrade in Serbia (70 dB).
What are permissible sound levels?
- According to 1999 WHO guidelines, the report said, the permissible noise level limits are 55 dB (decibels) LAeq (equivalent continuous sound level is the sound level in decibels) for outdoor residential areas and 70 dB LAeq for commercial areas and where there is traffic.
- According to experts that noise above 70 dB over a prolonged period of time can increase the risk of hearing loss. “High levels of noise impair human health and well-being – by disrupting sleep or drowning out the beneficial and positive acoustic communications of many animal species that live in these areas.
2. INDIAN OCEAN HIT BY SIX HEATWAVES IN 2021: DEPT OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: According to the Department of Science and Technology, the Indian Ocean witnessed six marine heatwaves in 2021 over a period of 52 days. The situation was grim in the Bay of Bengal, which suffered four of the six weather-related events.
THE EXPLANATION:
According to the Ministry, the weather-related incident is not a single event, and the tropical Indian Ocean has been facing the brunt of rising temperatures for decades. The minister informed that the western Indian Ocean region experienced a four-fold rise in marine heatwave events (increasing at a rate of 1.5 events per decade) and the North Bay of Bengal experienced a two-to-three-fold rise (at a rate of 0.5 events per decade).
What is Marine Heatwave?
A marine heatwave is defined as when seawater temperatures exceed a seasonally-varying threshold (usually the 90th percentile) for at least 5 consecutive days. Successive heatwaves with gaps of 2 days or less are considered part of the same event.
Value Addition:
- A report released by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) had dire warnings for India stating that 12 coastal cities in the country could be submerged by the end of the century.
- The cities could be nearly three feet underwater by the century’s end, the climate change report has warned. The cities include Mumbai, Chennai, Kochi, and Visakhapatnam, among others.
- Researchers have predicted that because of rising temperatures, extreme sea events along coastlines will become 100 times more frequent by the end of the century.
- Globally, areas likely to be affected most include the Southern Hemisphere, locations along the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Peninsula, the southern half of North America’s Pacific coast, and areas including Hawaii, the Caribbean, the Philippines, and Indonesia.
3. FIRST-EVER SIGHTING OF ROUGH-TOOTHED DOLPHINS IN WATERS
THE CONTEXT: A Marine Mammals Research (MMR) team of the Department of Environment and Forest in Lakshadweep has reported the first-ever live sighting of rough-toothed dolphins (Steno bredanensis) in Indian waters.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Rough-toothed Dolphin is a slender dolphin and has a forehead and the sides of the head sloping smoothly on to a long and slender beak, making the entire body in front of the flippers appear very long and nearly conical. There is no prominent melon and no crease between the beak and forehead, unlike many other dolphins. The flippers are moderately long. The dorsal fin is relatively tall and sickle shaped.
- Rough-toothed Dolphins are variable in coloration but are generally dark grey to purplish black above. The eyes are large and bulging.
Found In: Rough-toothed Dolphins are to be found mainly at and beyond the edges of the continental shelves in deep water. They feed on octopus, squid and fish.
IUCN REDLIST: LEAST CONCERN
Records from India: Found offshore along the southwest and east coasts of India and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Reported as by catch in gill nets in India.
4. DETECTING MICROPLASTICS IN HUMAN BLOOD
THE CONTEXT: A study by researchers from Netherlands published has examined blood samples of 22 persons, all anonymous donors and healthy adults, and found plastic particles in 17 of them.
THE EXPLANATION:
The report conveys that about half of these were PET (polyethylene tertraphthalate) plastics, which is used to make food grade bottles. The size of the particles that the group looked for was as small as about 700 nanometres (equal to 0.0007 millimetres). This is really small and it remains to be seen if there is a danger of such particles crossing the blood cell walls and affecting the organs. Also, a larger study needs to be conducted to firm up the present findings.
What are microplastics?
- Microplastics are tiny bits of various types of plastic found in the environment. The name is used to differentiate them from “macroplastics” such as bottles and bags made of plastic.

- There is no universal agreement on the size that fits this bill — the U.S. NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) and the European Chemical Agency define microplastic as less than 5mm in length. However, for the purposes of this study, since the authors were interested in measuring the quantities of plastic that can cross the membranes and diffuse into the body via the blood stream, the authors have an upper limit on the size of the particles as 0.0007 millimetre.
What were the plastics that the study looked for in the blood samples?
The study looked at the most commonly used plastic polymers. These were polyethylene tetraphthalate (PET), polyethylene (used in making plastic carry bags), polymers of styrene (used in food packaging), poly (methyl methylacrylate) and poly propylene. They found a presence of the first four types.
What are the key results of this study?
- The study found that 77% of tested people (17 of the 22 persons) carried various amounts of microplastics above the limit of quantification.
- In 50% of the samples, the researchers detected PET particles.
- In 36%, they found presence of polystyrene. 23% of polyethylene and 5% of poly(methyl methylacrylate) were also found. However, traces of poly propylene were not detected.
- They found in each donor, on average, 1.6 microgram of plastic particles per milli litre of blood sample.
What is the significance of the study?
- The authors of the paper also remark that validated methods to detect the tiny (trace) amounts of extremely small-sized (less than 10 micrometre) plastic particles are lacking. Hence this study, which builds up a method to check the same, is important.
- Owing to the small size of the participants, the study results cannot be taken as such to mould policy etc, but the power of this paper is in the method and in demonstrating that such a possibility of finding micro plastics in the blood exists.
5. THE PHENOMENON OF CORAL BLEACHING
THE CONTEXT: The management authority of the world’s largest coral reef system, Australia’s Great Barrier Reef, confirmed on March 25, 2022 that the reef is experiencing a mass coral bleaching event.
THE EXPLANATION:
- This is the sixth time that the coral reef system is being hit by a widespread and damaging bleaching event and the fourth time in six years that such an event has occurred. The bleaching event coincides with a 10-day UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) scientific mission currently underway in Australia.
What are coral reefs?
- Corals are marine invertebrates or animals not possessing a spine. Each coral is called a polyp and thousands of such polyps live together to form a colony, which grows when polyps multiply to make copies of themselves.
- Corals are of two types — hard coral and soft coral.
- Hard corals, also called hermatypic or ‘reef building’ corals extract calcium carbonate (also found in limestone) from the seawater to build hard, white coral exoskeletons. Soft coral polyps, however, borrow their appearance from plants, attach themselves to such skeletons and older skeletons built by their ancestors.
- Soft corals also add their own skeletons to the hard structure over the years and these growing multiplying structures gradually form coral reefs. They are the largest living structures on the planet.
- Corals share a symbiotic relationship with single-celled algae called zooxanthellae. The algae provides the coral with food and nutrients, which they make through photosynthesis, using the sun’s light. In turn, the corals give the algae a home and key nutrient. The zooxanthellae also give corals their bright colour.
- Australia’s Great Barrier Reef is the world’s largest reef system stretching across 2,300 km. It hosts 400 different types of coral, gives shelter to 1,500 species of fish and 4,000 types of mollusc.
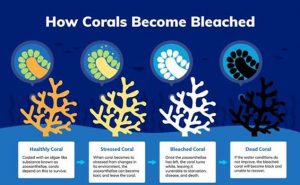
What is Coral Bleaching?
- Bleaching happens when corals experience stress in their environment due to changes in temperature, pollution or high levels of ocean acidity. Under stressed conditions, the zooxanthellae or food-producing algae living inside coral polyps start producing reactive oxygen species, which are not beneficial to the corals.
- So, the corals expel the colour-giving zooxanthellae from their polyps, which exposes their pale white exoskeleton, giving the corals a bleached appearance. This also ends the symbiotic relationship that helps the corals to survive and grow.
- Under all positive outlooks and projections in terms of cutting greenhouse gases, sea temperatures are predicted to increase by 1.5°C to 2°C by the time the century nears its end.
Why does it matter?
- Coral reefs support over 25% of marine biodiversity, including fish, turtles and lobsters; even as they only take up 1% of the seafloor. The marine life supported by reefs further fuels global fishing industries. Even giant clams and whales depend on the reefs to live.
- Besides, coral reef systems generate $2.7 trillion in annual economic value through goods and service trade and tourism. In Australia, the Barrier Reef, in pre-COVID times, generated $4.6 billion annually through tourism and employed over 60,000 people including divers and guides.
- Aside from adding economic value and being a support system for aquatic life, coral reefs also provide protection from storm waves.
About Great Barrier Reef:
|
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
6. INDIA CROSSES MILESTONE OF 50,000 ODF PLUS VILLAGES
THE CONTEXT: The country has crossed a milestone of 50 thousand open defecation-free (ODF) Plus villages. Among the top performing States are Telangana with 13 thousand 960 ODF Plus villages followed by Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the Ministry of Jal Shakthi, the mission towards becoming ODF Plus has several components including biodegradable waste management including the GOBAR dhan Scheme, Grey water management, Plastic waste management and Faecal sludge management.
- The Ministry has said, ODF Plus villages have been divided into three categories, Aspiring, Rising, and Model, to showcase their progress.
- This has created a healthy, competitive spirit, resulting in people participation for accelerated implementation of sustaining sampoorn swachhata. Also, it noted as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, more than one crore people across 22-thousand-gram panchayats participated in various sanitation activities.
| What is ODF?
‘Open defecation free’ (ODF) is a term used to describe communities that have shifted to using toilets instead of open defecation.
Necessary infrastructure and regulatory conditions to be achieved before declaring a city/ward as Open Defecation Free: · All households that have space to construct toilet, have constructed one. · All occupants of those households that do not have space to construct toilet have access to a functional community toilet within a distance of 500 meters. · All commercial areas have functional public toilets within a distance of 1 kilometer. |
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
7. WHAT IS ALOPECIA AREATA?
According to US Department of Health and Human Services, alopecia areata is condition that happens when the immune system attacks hair follicles and causes hair loss.
- The condition usually affects the head and face.
- Hair typically falls out in small, round patches about the size of a quarter, but in some cases, hair loss is more extensive. Most people with the disease are healthy and have no other symptoms, the US Department of Health said.
What causes the condition?
In alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing inflammation. Researchers do not fully understand what causes the immune attack on hair follicles, but they believe that both genetic and environmental (non-genetic) factors play a role.
Types of alopecia areata
Health experts have classified the hair loss condition in three types:
- Patchy: In the most common type, hair loss happens in one or more coin-sized patches on the scalp or other parts of the body.
- Totalis: People with this type lose all or nearly all of the hair on their scalp.
- Universalis: This is an extremely rare type, there is a complete or nearly complete loss of hair on the scalp, face, and rest of the body.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY 29th MARCH 2022
Q1. Consider the following statements:
- Zozila pass is located in the Pir Panjal range of Western Himalayas.
- It connects Jammu to Srinagar.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER FOR 28TH MARCH 2022
Answer: D
Explanation:
- The National Chambal Sanctuary (NCS), a protected riverine area, spans Rajasthan, MadhyaPradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- Chambal flows though the sanctuary, which is home to rare wildlife.
- The river harbours some of the most pristine sandbanks, which are the basking and egg-laying habitats for the critically endangered gharial, for the endangered Indian skimmer,the critically endangered, red-crowned roofed turtle, and a host of other threatened andendangered species. India’s national aquatic animal, the endangered Ganges river dolphin,is also spotted here.
- Illegal sand mining in the protected riverine area continues unabated, endangering several threatened species. According to reports, rampant sand mining within NCS is forcing gharialsto migrate to Kuno and Parbati rivers, tributaries of the Chambal, in search of safer egg-laying habitats.