DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (MARCH 24, 2022)
THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
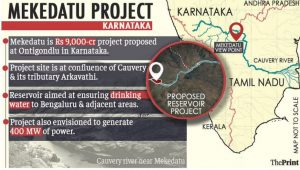
THE CONTROVERSY OVER THE PROPOSED MEKEDATU WATER PROJECT
THE CONTEXT: Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are at loggerheads over the Mekedatu drinking water project across river Cauvery. Tamil Nadu’s Assembly has passed a resolution against the project, while Karnataka’s legislative assembly is set to counter it with a resolution seeking the project’s early implementation and clearance.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Mekedatu is a drinking water cum power generation project proposed by Karnataka across the river Cauvery. The ₹9,000 crore balancing reservoir at Mekedatu on the Karnataka-Tamil Nadu border envisages impounding of 67.15 tmc (thousand million cubic feet) ft. of water.
- Karnataka has argued that since the project falls inside its own jurisdictional limit, Tamil Nadu’s permission is not needed.
What is the project?
- Originally mooted in 1948, Mekedatu (which translates as Goat’s crossing) is a drinking water cum power generation project across river Cauvery.
- Karnataka gave the project shape after the final award of the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal was notified in February 2013 allocating the riparian states their shares.
- After a pre-feasibility study report was submitted in 2018, the State submitted a detailed project report to the Central Water Commission in 2019.
- The project, which will involve submergence of nearly 5,100 hectares of forest in Cauvery wild life sanctuary hosting rich flora and fauna, will help the state in utilising the additional 4.75 tmc ft. of water allocated by Supreme Court in 2018 for consumptive use for drinking purpose for Bengaluru and neighbouring areas.
- Karnataka’s share in the award has been decided at 284.75 tmc ft. In July 2019, the Expert Appraisal Committee on River Valley and Hydroelectric Projects constituted by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has said the proposal could be reconsidered only after Tamil Nadu and Karnataka reach an “amicable solution.”
How will it benefit Karnataka?
- The water from Mekedatu is to be pumped to quench the thirst of the burgeoning population of Bengaluru which is estimated to be around 1.3 crore. Currently, more than 30% of Bengaluru is dependent on borewell water. Along with the 5th stage of the Cauvery Water Supply Scheme, which will be completed shortly, the water from Mekedatu is projected to meet the water requirement of the State capital for the next 30 years.
- Besides, there are also plans to generate 400 MW of power. The revenue earned from power generation is expected to compensate the Government its investment on the project within a few years.
- Karnataka argues that the reservoir will also help to ensure monthly flow stipulated in the award for Tamil Nadu rather than harm the neighbouring State’s interest in any way.
What is Karnataka’s stand?
- Karnataka says that there is no case for Tamil Nadu after its share of 177.75 tmc ft. of water is ensured at the inter-State border gauging centre at Biligundlu. Also, the project falls inside the jurisdictional limit of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu’s permission is not needed.
- The State also argues that since there is no stay in any court for the project, Karnataka can go ahead. On utilising the surplus water, Karnataka says that any allocation in this sphere should be done after hydrology studies to ascertain the quantum of excess water available in the basin.
Why is Tamil Nadu opposed to it?
- According to the TN Govt, through the project, Karnataka will impound and divert flows from “uncontrolled catchments” to it, a component which was taken into account by the Tribunal in the 2007 order while arriving at the water allocation plan for the State.
- As per an estimate, around 80 tmc ft of water flows annually to Tamil Nadu, thanks to the catchments including the area between Kabini dam in Karnataka and Billigundulu gauging site on the inter-State border, and the area between Krishnaraja Sagar dam in Karnataka and the gauging site.
- As the upper riparian State has adequate infrastructure even now to address the water needs of Bengaluru, there is no need for the Mekedatu project, according to Tamil Nadu.
- Mekedatu also does not find mention in the Tribunal’s final order or the Supreme Court judgement. Besides, given the unpleasant experiences that it has had with Karnataka in securing its share of the Cauvery water, as per the monthly schedule of water release, Tamil Nadu is wary of assurances from the other side.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
2. THE ARTEMIS PROGRAMME, NASA’S NEW MOON MISSION
THE CONTEXT: In early March 2022, the NASA rolled out its Artemis I moon mission to the launchpad for testing at the Kennedy Space Centre in Florida, United States. The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion capsule of the mission were hurled out to the launchpad by NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 vehicle.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is the Artemis mission?
- NASA’s Artemis mission is touted as the next generation of lunar exploration and is named after the twin sister of Apollo from Greek mythology. Artemis is also the goddess of the moon.

- Artemis I is the first of NASA’s deep space exploration systems. It is an uncrewed space mission where the spacecraft will launch on SLS — the most powerful rocket in the world — and travel 2,80,000 miles from the earth for over four to six weeks during the course of the mission. The Orion spacecraft is going to remain in space without docking to a space station, longer than any ship for astronauts has ever done before.
- The SLS rocket has been designed for space missions beyond the low-earth orbit and can carry crew or cargo to the moon and beyond. With the Artemis programme, NASA aims to land humans on the moon by 2024, and it also plans to land the first woman and first person of color on the moon.
- With this mission, NASA aims to contribute to scientific discovery and economic benefits and inspire a new generation of explorers.
- NASA will establish an Artemis Base Camp on the surface and a gateway in the lunar orbit to aid exploration by robots and astronauts. The gateway is a critical component of NASA’s sustainable lunar operations and will serve as a multi-purpose outpost orbiting the moon.
- The Canadian Space Agency has committed to providing advanced robotics for the gateway, and the European Space Agency will provide the International Habitat and the ESPRIT module, which will deliver additional communications capabilities among other things. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency plans to contribute habitation components and logistics resupply.
What is the mission trajectory?
- SLS and Orion under Artemis I will be launched from the Kennedy Space Centre in Florida, U.S. in the summer of 2022. The spacecraft will deploy the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), a liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen-based propulsion system that will give Orion the thrust needed to leave the earth’s orbit and travel towards the moon.
- The spacecraft will communicate with the control centre back on Earth through the deep-space network. The aim of the exercise is to collect data and to allow mission controllers to assess the performance of the spacecraft.
- To re-enter the earth’s atmosphere, Orion will do a close flyby within less than 100 km of the moon’s surface and use both the service module and the moon’s gravity to accelerate back towards the earth. The mission will end with the spacecraft’s ability to return safely to the earth.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES/ INITIATIVES IN NEWS
3. JAL SHAKTI MINISTRY LAUNCHES SUJLAM 2.0 CAMPAIGN TO BOOST GREYWATER MANAGEMENT
THE CONTEXT: On the occasion of World Water Day, the central government launched a nationwide campaign for greywater management. Called Sujlam 2.0, the campaign will focus on creation of community and institutional greywater management assets.
THE EXPLANATION:
The objective of this campaign
The Sujlam 2.0 campaign was launched with the objective of managing greywater through the participation of the people. Under this campaign, there are plans to mobilize communities such as schools, panchayats, and anganwadis to help in greywater management.
Funding of this campaign
Funds for greywater management will be provided from the Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin Phase II or through grants under the 15th Finance Commission as well as the MGNREGS or through the convergence between all of them.
What is Greywater?
Greywater refers to the domestic wastewater that is generated in households, office buildings, etc. and is without faecal contamination. Sources of greywater include showers, sinks, washing machines, baths, etc.’
Since greywater contains less pathogens compared to domestic wastewater, it is safer to treat, handle, and reuse for the purpose of landscape, toilet flushing, crop irrigation, etc.
How can Greywater be managed?
It can be best managed where greywater is generated. It can turn into a major infrastructure and management challenge if greywater is allowed to be accumulated and thus, can stagnate.
| Value Addition:
World Water Day · World Water Day is celebrated on March 22 every year to highlight the importance of fresh water. The tradition has continued since 1993. According to the United Nations website, more than 2.2 billion people live without the access to safe water. · This year the day is highlighting the global water crisis and aims to support achieving Sustainable Water and Sanitation for all by 2030. The concept and idea for this day goes back all the way to 1992 in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil when the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development took place. · The theme for this year: ‘Groundwater: making the invisible visible’. |
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
4. THE AHIR REGIMENT DEMAND
THE CONTEXT: An ongoing agitation by members of the Ahir community disrupted traffic on a 6-kilometre stretch of the Delhi-Gurgaon highway. The protesters demanding an Ahir Regiment in the Indian Army.
THE EXPLANATION:
WHAT IS THE REASON BEHIND THE DEMAND?
Members of the community have long argued that the Ahirs deserve a full-fledged Infantry Regiment named after them, not just two battalions in the Kumaon Regiment and a fixed percentage in other regiments.
The demand got a boost during the 50th anniversary of the 1962 War in 2012 when the saga of the Ahirs’ heroism was recounted repeatedly and has received renewed traction in the 60th anniversary year.
- The protesters contend that the Indian Army had several caste-based regiments (for Sikhs, Gorkhas, Jaats, Garhwals, Rajputs).
- In the battle of Rezang La in 1962, out of 120 casualties, 114 were Ahirs.
- It is unfortunate that Ahirs have not got the recognition like other communities.
- The recruitment to President’s Bodyguard (PBG) is open only for Rajputs, Jats and Sikh regiments.
- The Ahirs are variously described as a caste, a clan, a community, a race and a tribe.
- The traditional occupations of Ahirs are cattle-herding and agriculture.
What has been the Army’s response to the demand?
The Army has rejected the demand for any new class or caste-based regiment. It has said that while the older regiments based on castes and regions like the Dogra Regiment, Sikh Regiment, Rajput Regiment, and Punjab Regiment will continue, no new demands on the lines of an Ahir Regiment, Himachal Regiment, Kalinga Regiment, Gujarat Regiment, or any tribal regiment would be entertained.
| Value Addition:
· Rezang La is a mountain pass on the Line of Actual Control in Ladakh. · It is located between the village of Chushul and the Spanggur Lake that stretches across both Indian and Chinese territories. · Rezang La is one of the heights of the Kailash Range in the Chushul Sub-sector, occupied by India in August 2020, that provided leverage in the standoff negotiations. · The positions India occupied on the Kailash Ranges allowed the Indian troops to dominate not only China’s Moldo Garrison but also the strategically sensitive Spanggur Gap, which was used by China to launch an offensive during the 1962 War.
About the battle: · Troops from the 13 Kumaon Regiment defeated several waves of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in 1962. · Despite being heavily outnumbered, soldiers of the regiment fought to the last man standing, under freezing temperatures, and with limited ammunition. |
5. EXPLAINED: WHAT ARE BLACK BOXES, AND WHY ARE THEY IMPORTANT IN A CRASH INVESTIGATION?
THE CONTEXT: The Eastern Airlines of Boeing 737-800 with 132 people on board crashed in Guangxi province of southern China after a sudden plunge from cruising altitude at about the time when it would normally start to descend ahead of its landing.
THE EXPLANATION:
Black boxes
- These are two large metallic boxes containing recorders that are required to be kept on most aircraft, one in the front and the other in the rear. The recorders record the information about a flight, and help reconstruct the events leading to an aircraft accident.
- The cockpit voice recorder (CVR) records radio transmissions and other sounds in the cockpit, such as conversations between the pilots, and engine noises. The flight data recorder (FDR) records more than 80 different types of information such as altitude, airspeed, flight heading, vertical acceleration, pitch, roll, autopilot status, etc.
- Black boxes are mandatory on commercial flights. Their purpose on aircraft is not to establish legal liability, but to identify the causes of a mishap and, therefore, help to prevent adverse incidents in the future.
Orange, not black
Black boxes are a blazing, high-visibility orange in colour, so that crews looking for them at a crash site have the best chance of finding them. The use of black boxes dates back to the early 1950s, when, following plane crashes, investigators were unable to arrive at a conclusive cause for the accidents.
Surviving the crash
- In the initial days of the black box, a limited amount of data were recorded on wire or foil. Thereafter magnetic tape was used, and modern models contain solid state memory chips.
- The recording devices, each weighing about 4.5 kg, are stored inside a unit that is generally made out of strong substances such as steel or titanium, and are insulated from extreme heat, cold or wetness. The FDR is located towards the tail end of the aircraft because that is usually where the impact of a crash is the least.
- To make black boxes discoverable under water, they are equipped with a beacon that sends out ultrasound signals for 30 days.
Retrieving the data
- It usually takes 10-15 days to analyse the data recovered from the black boxes. Meanwhile investigators look for other clues such as taking accounts from air traffic control personnel and recordings of the conversation between ATC and the pilots’ moments before the crash.
- This helps investigators understand if pilots were aware that they were in a situation that was headed to such an eventuality and if so, whether they had reported any problems regarding controlling the aircraft.
6. ABEL PRIZE FOR 2022
THE CONTEXT: Dennis Parnell Sullivan, an American mathematician, has been announced as the winner of the Abel Prize 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The math genius received the award for his work in topology and its branches, specifically “for his groundbreaking contributions to topology in its broadest sense, and in particular its algebraic, geometric and dynamical aspects.”
- Topology is a branch of mathematics that considers two objects of different shapes equivalent if they can be deformed into one another through shrinking, stretching and similar forces, but gluing foreign parts or tearing them apart is not allowed in the study of topology. This stream of mathematics is comparatively new as it was born in the late 19th century. The study of topology has been remarkably important in maths and other fields such as economics, data science and physics.
Abel Prize
- Abel Prize is an annual prize given annually to a person by the King of Norway, who has done a remarkable job in the field of mathematics.
- The annual award for mathematics is named after the great Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel. The award is inspired by the famous Nobel Prize. It is pertinent to note that there is no Nobel Prize for mathematics, though some mathematicians have won the prestigious Nobel Prize in different fields other than Mathematics.
- The Fields Medal is another annual award that is sometimes considered the ‘Mathematics Nobel’ but is only awarded to those below 40 years of age.
| QUICK FACTS:
S. R. Srinivasa Varadhan, an Indian-American citizen, won the Abel Prize in the year 2007 for his valuable contribution in “probability theory and in particular for creating a unified theory of large deviation”. |
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY 24th MARCH 2022
Q1. Consider the following statements about Abel Prize:
- It recognizes contributions to the field of mathematics that are of extraordinary depth and influence.
- It is established by the Sweden government in 2002.
- The award has been awarded biennially since 2003.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
ANSWER FOR 23RD MARCH 2022
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: It was launched during 12th Five Year Plan. It was approved and notified on 29.09.2014.
- Statement 2 is correct: It is centrally sponsored scheme.
- Statement 3 is correct: Government of India has recently announced its continuation of its implementation up to 2026.