DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (MARCH 09, 2022)
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
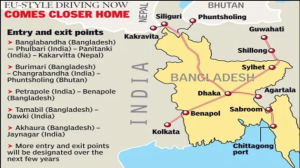
1. MOU FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF BBIN MOTOR VEHICLES AGREEMENT
THE CONTEXT: India, Bangladesh and Nepal finalized an enabling MoU to be signed by them for the implementation of the BBIN Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA), pending ratification of the MVA by Bhutan.
What is BBIN Motor Vehicle Agreement?
- India proposed a SAARC Motor Vehicle Agreement during the SAARC Summit in Kathmandu in November 2014. Due to objections from Pakistan, an agreement could not be reached. India instead pursued a similar motor vehicle agreement with the BBIN. The Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal Motor Vehicles Agreement was signed on 15 June 2015.
- It enables vehicles to enter any of the four nations without the need for trans-shipment of goods from one country’s truck to another’s at the border. Under the system, cargo vehicles are tracked electronically, permits are issued online and sent electronically to all land ports. Vehicles are fitted with an electronic seal that alerts regulators every time the container door is opened.
Significance:
- Signing of the BBIN agreement will promote safe, economical efficient and environmentally sound road transport in the sub-region and will further help each country in creating an institutional mechanism for regional integration. BBIN countries will be benefited by mutual cross border movement of passenger and goods for overall economic development of the region. The people of the four countries will benefit through seamless movement of goods and passenger across borders.
- The implementation of the agreement is expected to improve the value chain in sub-regional trade. BBIN sub-grouping was expected to be the gateway to southeast and east Asia. India is working for development of inter connectivity infrastructure for Myanmar and Thailand.
2. INDIAN WOMEN JOIN UN PEACEKEEPING MISSIONS
THE CONTEXT: In January 2022, at the United Nations Security Council, Indian officials called for more female participation in public life and the elimination of violence against them as a prerequisite for promoting lasting peace around the world.
THE EXPLANATION:
- For the first time in the history of UN peacekeeping, India sent an all-female Formed Police Unit (FPU) to be deployed in Liberia in 2007 after a civil war ravaged the African nation.
- According to the UN, of around 95,000 peacekeepers in 2020, women comprised 4.8% of military contingents and 10.9% of formed police units.
- Meanwhile, around 34% of personnel in peacekeeping missions were women.
About UN Peacekeeping Mission:
UN peacekeepers provide security and the political and peace building support to help countries make the difficult, early transition from conflict to peace.
UN Peacekeeping is guided by three basic principles:
- Consent of the parties.
- Non-use of force except in self-defence and defence of the mandate.
Peacekeeping is flexible and over the past two decades has been deployed in many configurations. There are currently 12 UN peacekeeping operations deployed on three continents.
Global partnership
- UN peacekeeping is a unique global partnership. It brings together the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Secretariat, troop and police contributors and the host governments in a combined effort to maintain international peace and security.
- Its strength lies in the legitimacy of the UN Charter and in the wide range of contributing countries that participate and provide precious resources.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
3. EXPLAINED: WHAT DOES RBI’S $5 BILLION DOLLAR-RUPEE SWAP MEAN?
THE CONTEXT: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) conducted a $ 5 billion dollar-rupee swap auction as part of its liquidity management initiative, leading to infusion of dollars and sucking out of the rupee from the financial system. The central bank’s move will reduce the pressure on inflation and strengthen the rupee.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The central bank said it received bids worth $13.56 billion for the sell/buy auction. It accepted 86 of these bids for $5.135 billion. The cut-off premium was set at 656 paise. The first leg of the settlement will be March 10, 2022, and the second leg will be March 11, 2024.
- The RBI sold $5.135 billion to banks on March 8,2022 and simultaneously agreed to buy back the dollars at the end of the swap settlement period. When the central bank sells dollars, it sucks out an equivalent amount in rupees, thus reducing the rupee liquidity in the system. Dollar inflow into the market will strengthen the rupee which has already hit the 77 level against the US dollar.
What’s the impact of the swap?
- The RBI would have removed close to Rs 39,000 crore ($5.135 billion) at rupee closing rate of 76.91 per dollar. The major impact will be that liquidity which currently averages around Rs 7.6 lakh crore will shrink.
- The RBI normally brings down liquidity in the system when inflation threatens to rise sharply. With crude oil prices rising sharply in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine war, inflation is set to rise in the coming days.
What is a Dollar–Rupee Swap auction?
- It’s a forex tool whereby the central bank uses its currency to buy another currency or vice versa.
- In a Dollar–Rupee buy/sell swap, the central bank buys dollars (US dollars or USD) from banks in exchange for Indian Rupees (INR) and immediately gets into an opposite deal with banks promising to sell dollars at a later date.
- In a dollar–rupee sell/buy swap it sells USD in exchange for INR and promises to buy dollar from banks after some years.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
4. ASSAM’S MANAS NATIONAL PARK WITNESSES SHARP RISE IN TIGER, RHINO POPULATION
THE CONTEXT: Assam’s Manas National Park and Tiger Reserve has witnessed a sharp rise in the population of tigers and rhinos in recent times.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The authorities of the national park expect the tiger population will rise to more than 60 from 48 as per the 2021 census.
- In 2010, the tiger population of the park was recorded 10 while in 2020 it had increased to 30.
- In 2010, after the first tiger census in Manas National Park was conducted the Tiger Conservation Authority had said during their analysis that the national park’s tiger population will be increased by double in 2020 and it reached 30.
- In the 2021 census, 48 tigers were counted in the park which means the tiger population had increased by 18 within a year. The census for 2022 is ongoing and it will be finished by March and it is being expected that the population will increase to more than 60.
Rhino Population
The park’s Rhino population has also increased. Under the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020), the Assam government decided to reintroduce rhinos in Manas National Park in 2005, and the first rhino was translocated to the park in 2006, from the Centre for Wildlife Rehabilitation and Conservation (CWRC) near Kaziranga National Park.
About Manas National Park
- Manas National Park is situated on the bank of the river mans at the foothills of the Himalayas. The beautiful park earlier known as North Kamrup wildlife sanctuary is spread over an area of 519.77 sq km and was declared a sanctuary on December 01, 1928. It was established as the core of the Manas Tiger Reserve from April 1973 and elevated to the position of a National Park status on September 7, 1990.
- The wildlife spices found in national park are Hispid Hare, Pigmy Hog, Golden Langur, Indian Rhinoceros, Asiatic Buffalo etc. Other commonly seen animals are Elephant, Leopard, Clouded Leopard, Himalayan Bear, Wild Boar, Samber, Swamp Deer, Hog Deer etc.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5. FUSOBACTERIUM PLAYS IN ORAL CANCER PATIENTS IN INDIA
THE CONTEXT: Scientists at Tata Memorial Centre developed a highly sensitive and specific automated computational tool HPV Detector to quantify the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV).
THE EXPLANATION:
Since the beginning of the 20th Century, it is known that infections could play a role in cancer, with 18-20% of cancers associated with infectious agents. This could be relatively higher in developing countries like India.
- The analysis revealed significant occurrence of HPV 16, 18, and 31, among others, in cervical cancer. But a surprising finding was that Indian patients with oral tumours showing a distinct tobacco usage gene signature were devoid of HPV infection.

-
This was in sharp contrast to the oral tumours among Caucasian patients, wherein tobacco genetic signature is not common but is marked by a significant presence of HPV. Several groups have corroborated this finding, and it is well established that oral tumours among Indian patients are not driven by HPV infection.
- Interestingly, Fusobacterium nucleatum is known to play a vital role in colorectal cancer, wherein its presence affects the spread of the disease and the patient’s response to chemotherapy. However, a similar role of Fusobacterium in oral cancer was not known earlier. The presence of the bacteria was found in Indian and Caucasian oral cancer patients, with a much higher incidence among the Indian patients. Moreover, oral cancer patients positive for Fusobacterium were found to be negative for HPV infection, suggesting they are present in a mutually exclusive way.
Value Addition :
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a viral infection that’s passed between people through skin-to-skin contact. There are over 100 varieties of HPV, more than 40 Trusted Source of which are passed through sexual contact and can affect your genitals, mouth, or throat.
- Colon cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the large intestine (colon). The colon is the final part of the digestive tract.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
6. FIRST INDIAN TO GET BOLTZMANN MEDAL
THE CONTEXT: Professor Deepak Dhar, a physicist and emeritus faculty at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Pune, has been selected to receive the prestigious Boltzmann Medal for 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Dhar has been given the award for his seminal contributions to several areas of statistical physics, including exact solutions of self-organized criticality models, inter-facial growth, universal long-time relaxation in disordered magnetic systems, exact solutions in percolation and cluster counting problems and definition of the spectral dimension of fractals.
- He took on several areas of statistical physics to understand the behaviour of self-organised critical systems, explain the dynamics at phase interfaces, and define the spectral dimension of fractals”.
About Boltzmann Medal:
- The Boltzmann Medal (or Boltzmann Award) is a prize awarded to physicists that obtain new results concerning statistical mechanics; it is named after the celebrated physicist Ludwig Boltzmann.
- The Boltzmann Medal is awarded once every three years by the Commission on Statistical Physics of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics, during the STATPHYS conference.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY 9TH MARCH 2022
Q1. Consider the following statements about the office of Governor:
- The Sarkaria Commission recommended that the appointee should be someone from outside the respective State so that he would not have any personal interest to protect.
- The Punchhi commission recommended that Governor shall have fixed tenure.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER FOR 8th MARCH 2022
Q1. Answer: D
Explanation:
- The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) is a statutory body formed under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas, Act 2021.
- It will supersede bodies such as the central and state pollution control boards of Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, UP and Rajasthan.