Day-17 | Daily MCQs | UPSC Prelims | History
[WpProQuiz 19]
[WpProQuiz 19]
INDIAN HISTORY
THE CONTEXT: Uttar Pradesh government has renamed the ‘Kakori Kand’ to ‘Kakori Train action’ as the word ‘Kand’ denotes a sense of insult to this incident under India’s Independence struggle.
ANALYSIS :
Source: NewsOnAIR
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister launched the second phase of the Ujjwala gas connection scheme for the poor.
ABOUT UJJWALA 2.0
BACKGROUND
SOURCE: TH
THE CONTEXT: The Supreme Court had directed political parties to publish the criminal history if any, of their election candidates on the homepage of their party websites under the caption ‘candidates with criminal antecedents’ within 48 hours of their selection.
ANALYSIS:
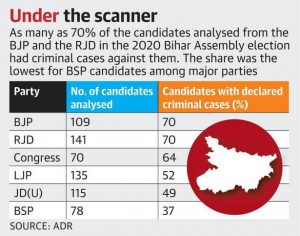
SOURCE: TH
THE CONTEXT: The Lok Sabha passed the 127th Constitution Amendment Bill, 2021, with unanimous support from the House.

ABOUT THE 127TH CAB 2011
BACKGROUND:
THE CONTEXT: India is ranked 122nd on a new Global Youth Development Index measuring the condition of young people across 181 countries, released by the Commonwealth Secretariat in London.
ANALYSIS:
SOURCE: THE PRINT
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: As per information provided in parliament, about 32 percent of the Indian coastline is under varying degrees of erosion (low, moderate or high), 27 percent is of accreting nature and the remaining 41 percent is in a stable state.
ANALYSIS:
FEW OTHER FACTS FOR PRELIMS
SOURCE: DTE
THE CONTEXT: The National Agricultural Research System (NARS) is involved in development of new high yielding and biotic/abiotic stress tolerant crop varieties of field and horticultural crops.
Analysis:
SOURCE: PIB
THE CONTEXT: About 96,000 farmed salmon are believed to have died when a leak in a nearby tank sent 15,000 liters (4,000 gallons) of chlorine into a fjord in Arctic Norway.
Analysis:
SOURCE: IE
THE CONTEXT: The Government has made a provision for the opening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) in each of the rural districts across the country. A total of 725 KVKs have been established across the country till date.
ABOUT KVKS
SOURCE: PIB
THE CONTEXT: Since inception and till 31.03.2021, National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) has disbursed Rs.1.77 lakh crore to cooperatives for their development. It includes assistance to agricultural and horticulture cooperative societies.
ABOUT NCDC
SOURCE: PIB
THE CONTEXT: Deep Ocean Mission to be implemented by Ministry of Earth Sciences at a total budget of Rs. 4077 Cr for 5 years during the period 2021-2026.
ANALYSIS:
ABOUT THE DEEP OCEAN MISSION
SOURCE: PIB
August 11, 2021 Prelim Practice Questions
Q 1. Consider the following statements about the Ujjwala scheme:
1. It was launched in 2015 with an aim to provide deposit-free LPG connections to BPL households.
2. The LPG connection under the scheme is given only in the name of the adult woman of the household.
3. Second phase of the scheme provides the first refill of the cylinder free of cost.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Q2. The Kakori Train Action was organized by?
a) Hindustan Republican Association
b) Hindustan Socialist Republican Association Army
c) Swadesh Bandhab Samiti
d) Bharat Naujawan Sabha
Answer for August 10, 2021 Prelims Practice Questions
ANSWER: C)
Explanation:
Prelims and Mains:
Main exam:
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
SOCIAL JUSTICE AND SOCIAL ISSUES
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
ETHICS EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDY
Questions for the MAIN exam
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
50-WORD TALK
Things to Remember:
[WpProQuiz 18]
Prelim and Main:
Main exam:
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
SOCIAL JUSTICE AND SOCIAL ISSUES
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
ESSAY TOPIC
50-WORD TALK
Things to Remember:
ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Government has decided to set up the ‘Indian Institute of Heritage’ at Noida.
ANALYSIS :
SOURCE: PIB
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE, AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister announced a National Edible Oil Mission-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to make India self-sufficient in cooking oils, including palm oil.
Analysis:
SOURCE: TH
THE CONTEXT: Parliament passed the Tribunals Reforms Bill, 2021. The Bill seeks to abolish many appellate tribunals set up under various Acts. The Bill replaces a similar Ordinance promulgated in April 2021.
THE KEY FEATURES OF THE TRIBUNALS REFORMS BILL, 2021
SOURCE: MONEY CONTROL
THE CONTEXT: According to NITI Aayog member Vinod Paul India is well on the path to achieving the World Health Organisation-recommended ratio of one doctor per thousand populations by 2024 and is increasing the number of hospital beds from 11 lakh to 22 lakh.
Analysis:
SOURCE: THE WEEK
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY, AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: IPCC released Sixth Assessment Report, “Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis”
Analysis:

SOURCE: TH
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: Chairing a high-level United Nations Security Council open debate on “Enhancing Maritime Security – A Case for International Cooperation”, Prime Minister put forward five principles: a global roadmap for maritime security cooperation can be prepared.
Analysis:
SOURCE: THE PRINT
August 10, 2021 Prelim Practice Questions
Q 1. Consider the following statements about IPCC:
Which of the above-given statements is/are incorrect?
a) 1 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 3 only.
Answer for August 08 & 09, 2021 Prelims Practice Questions
Q1: Answer: c)
Explanation:
Q2: Answer: a)
Explanation:
[WpProQuiz 17]
POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
SOCIAL JUSTICE AND SOCIAL ISSUES
INTERNATIONAL ISSUES
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
ETHICS EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDY
QUOTATIONS AND CAPTIONS
50-WORD TALK
Things to Remember:
ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: As part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav being celebrated to mark 75 years of Independence, National Archives of India is organizing an exhibition on the Quit India Movement on its 79th anniversary.

| CAUSES | SUCCESSES | FAILURE |
|---|---|---|
| Involvement of India in World War II without prior consultation with the leaders Failure of Cripps Mission Shortage of essential commodities Prevalence of anti-British sentiment Centralisation of many small movements. | Women empowerment Rise of future leaders Rise of nationalism. | The movement did not have the support of many organisations of the country itself. The Britishers were supported by the Princely States, British Indian Army, Indian Civil Services, Viceroy’s Council (which had Indians in the majority), All India Muslim League, and Indian Imperial Police. The Hindu Mahasabha, RSS & Muslim League also opposed the Quit India Movement. Many Congress members like C Rajagopalachari resigned from the provincial legislature as they did not favour Mahatma Gandhi's idea. |
SOURCE: NEWSONAIR
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Government launched PM-DAKSH Portal and PM-DAKSH Mobile App. Through these portal and app the youth of the target groups will now be able to avail the benefits of skill development training programmes more easily.
ABOUT PM-DAKSH
SOURCE: PIB
THE CONTEXT: The Government said that approximately five crore beneficiaries have been enrolled and more than four crores have been trained under the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan Scheme till the 2nd of August.
SOURCE: NEWSONAIR
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister will launch Ujjwala 2.0 (Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana – PMUY) by handing over LPG connections, at Mahoba Uttar Pradesh.
SOURCE: PIB
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Hundreds of Greek firefighters fought desperately on Sunday to control wildfires on the island of Evia that have charred vast areas of pine forest, destroyed homes and forced tourists and locals to flee.
Analysis:
SOURCE: TH
INDIAN ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: There has been a surge in China’s share in India’s trade basket by almost 3 percentage points for imports and 2 percentage points for exports.
ANALYSIS:
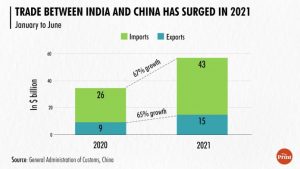
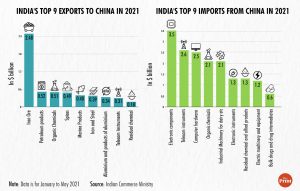
SOURCE: THE PRINT
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Johnson & Johnson’s single dose coronavirus vaccine was granted Emergency Use Authorization, making it the fourth vaccine to be approved by the Indian government.
Analysis:
SOURCE: IE
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) said that a combination of Covishield and Covaxin vaccines elicits better immunogenicity than two doses of the same vaccine.
ANALYSIS:

Source: TH
Q 1. Who is popularly known as the ‘Grand Old Lady’ of the Independence Movement?
a) Madam Bhikaiji Cama
b) Sarojini Naidu
c) Aruna Asaf Ali
d) Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay
Q2. The PM-DAKSH Yojana is being implemented by
a) The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
b) The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
c) The Ministry of Electronics and IT
d) The Ministry of Finance
Q1: Answer: d)
Explanation:
Q2: ANSWER a)
Explanation:
[WpProQuiz 16]
THE CONTEXT: Year-long celebrations marking 150 years of Abanindranath Tagore started with a host of online workshops and talks paying tributes to the leading light of the Bengal School of Art.
Analysis:
Source: The Hindu
THE CONTEXT: Poshan Tracker management application provides a 360-degree view of the activities of the Anganwadi Centre (AWC), service deliveries of Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) and complete beneficiary management for pregnant women, lactating mothers and children. Simultaneously, the mobile application also digitizes and automates physical registers used by AWWs that helps improving their quality of work.
Analysis:
POSHAN ABHIYAAN
The target for reducing the prevalence of stunting among children under 5 years is by 2% per annum and anemia among children under 5 years is by 3% per annum.
Source: PIB
THE CONTEXT: The Union Minister of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship has provided information on Sankalp Programme to parliament.
Analysis:
The institutions strengthened so far under SANKALP are as under:
ABOUT SANKALP PROGRAM
Source: PIB
THE CONTEXT: Drone flying has been completed in 52,970 villages and Property Cards distributed in 7440 villages to property owners.
ABOUT SVAMITVA SCHEME
ABOUT E-PANCHAYAT PROGRAMMES
Source: PIB
THE CONTEXT: India’s elderly population (aged 60 and above) is projected to touch 194 million in 2031 from 138 million in 2021, a 41 per cent increase over a decade, according to the National Statistical Office (NSO)’s Elderly in India 2021 report.
Analysis:
Source: The Print
THE CONTEXT: Studies using a 50-year (1970-2019) extreme weather events dataset of the India Meteorological Department (IMD) have shown that in recent decades, there has been increased occurrences of extreme weather events, including extremely severe cyclonic storms.
Analysis:
THE CONTEXT: In March, the annual white-bellied heron population survey by the Royal Society for Protection of Nature, Bhutan, a civil society organisation, recorded 22 herons. This was a decline by five compared to 27 birds in 2020.
Analysis:
Source: SCROLL
THE CONTEXT: Standing Committee report to the Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR) confirmed that there is no provision to declare any natural calamity as a ‘National Calamity’.
Analysis:
Source: Down to Earth
THE CONTEXT: Flooding has affected approximately 40 million hectares of India’s land area. From 1953-2018, 109,374 people died as a result of floods and heavy rains in the country, while 6,109,628 animals died. During these 65 years, the country is estimated to have lost Rs 400,097 crore. This information is contained in the report of the Standing Committee of Parliament (Water Resources).
Analysis:
Source: Down to Earth
THE CONTEXT: The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) kept the key policy rate unchanged at four per cent for the seventh time in a row, and reverse repo rate at 3.35 per cent. The panel has also raised the inflation target for fiscal 2001-22 but maintained the growth forecast at 9.5 per cent.
Analysis:
Source: The Indian Express
THE CONTEXT: India and China have completed troop disengagement from the Gogra area of eastern Ladakh, after 15 months of a “sensitive face-off”.
Analysis:
Source: The Print
THE CONTEXT: The Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna stands renamed as the “Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna”.
Analysis:
Source: The Hindu
Q 1. Consider the following statements:
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
Q2. Consider the following statements regarding targets under POSHAN Abhiyaan.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?